Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
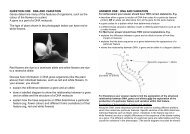
QUESTION ONE: DNA AND VARIATION<br />
Genes determine many of the features of organisms, such as the<br />
colour of the flowers on a plant.<br />
A gene is a part of a DNA molecule.<br />
The type of plant shown in the photograph below can have red or<br />
white flowers.<br />
QUESTION TWO: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION<br />
Meiosis is a particular form of cell division that produces male and<br />
female gametes.<br />
(a)<br />
Describe what gametes are and explain why they are needed<br />
for sexual reproduction.<br />
Meiosis contributes to genetic variation.<br />
Red flowers are due to a dominant allele and white flowers are due<br />
to a recessive allele.<br />
Discuss how information in DNA gives organisms (like the plant<br />
above) their individual features, such as red and white flowers. In<br />
your answer, you should:<br />
explain the difference between a gene and an allele<br />
draw a labelled diagram to show the relationship between a gene<br />
and an allele and the structure of a DNA molecule<br />
explain how the base sequence on DNA determines a particular<br />
feature (eg, flower colour) and different forms (variations) of that<br />
feature (eg, red and white flowers)<br />
(b)<br />
Discuss how meiosis contributes to genetic variation, and why<br />
genetic variation is important in a population. In your answer,<br />
you should:<br />
describe what is meant by genetic variation<br />
explain how the process of meiosis leads to genetic<br />
variation<br />
explain why genetic variation is of benefit to a population<br />
You could draw labelled diagrams to support your answer.
QUESTION THREE: MONOHYBRID CROSSES<br />
The allele for a cleft chin (D) is dominant over the allele for a<br />
smooth chin (d).<br />
The pedigree diagram below shows the chin types in a family.<br />
(c)<br />
Individuals A and B, as shown on the pedigree diagram,<br />
decide to have another child. They draw a Punnett square to<br />
find what type of chin their child might have.<br />
Explain why the result predicted by the Punnett square may<br />
not accurately tell them what type of chin their child will have.<br />
In your answer, you should:<br />
draw a Punnett square to show the cross between<br />
individual A and individual B<br />
determine the probabilities of the child having a cleft chin<br />
and having a smooth chin<br />
explain why the ratio of children born into the family with<br />
cleft and smooth chins may not match the probabilities.<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Explain how evidence in the pedigree diagram shows that the<br />
cleft chin allele (D) is dominant over the smooth chin allele (d).<br />
In your answer, you should:<br />
Describe what the term dominant allele means<br />
draw a Punnett square(s) to show your reasoning.<br />
Explain why the genotype of male A in generation 2 of the<br />
pedigree diagram must have the genotype Dd.
QUESTION FOUR: SURVIVAL<br />
Mutations can occur in DNA during cell division.<br />
Explain whether a mutation could be inherited if it occurred in a skin<br />
cell of an individual. In your answer, you should:<br />
describe what a mutation is<br />
explain what determines whether a mutation is able to be<br />
inherited or not.<br />
QUESTION SIX: VARIATION<br />
A population of plants, species A, living in a certain area shows a<br />
lot of variation in its leaf size, from very small to very large as<br />
shown in the graph below.<br />
Leaf size of plants of species A<br />
QUESTION FIVE: GENETICS<br />
Explain how two parents who don’t show a particular characteristic<br />
can have a child who does show that feature.<br />
In your answer include:<br />
The nature of the characteristic<br />
What causes a feature to be expressed (shown)<br />
What is different (genetically) between the parents and the child<br />
Leaf size affects the ability of a plant to absorb sunlight and make<br />
food. Plants with larger leaves can live in areas with lower light<br />
levels.<br />
A new plant, species B, starts growing in the same area as<br />
species A. Species B plants grow taller than species A plants,<br />
which reduces the light available to plants growing below species<br />
B.<br />
Discuss how variation in leaf size occurs in the starting population<br />
of species A and explain how this might help species A to survive<br />
when species B starts growing in the same area.<br />
In your answer, you should consider:<br />
what causes variation within a population<br />
the effect of reduced light on different individuals of plant<br />
species A
QUESTION SEVEN: GENETICS<br />
Cloning involves making an exact copy of an organism. Selective<br />
breeding involves the breeding together of organisms that possesses<br />
highly desirable characteristics.<br />
Compare and contrast selective breeding and cloning.<br />
Your answer should include<br />
How the offspring compare to their parents<br />
Their relative advantages and disadvantages<br />
QUESTION EIGHT: GENETICS<br />
There are many genes used by pedigree cat breeders to get a range of<br />
colours, fur length and body shapes. Several genes can control coat<br />
colour in cats.<br />
One of these produces the Agouti pattern, where each hair has a black tip<br />
but bands of light and dark towards the hair root. This causes a cat to<br />
have a striped appearance. This pattern is dominant, and denoted by the<br />
letter A. The recessive allele for this trait gives plain black hairs.<br />
(a)<br />
A breeder wishes to have a pure breeding group with the Agouti<br />
coat colour. He has a group of the Oriental breed pictured above,<br />
some of which are black and some of which are Agouti.<br />
Discuss how he would go about developing a pure breeding<br />
Agouti group. Include punnet square(s) in your answer.<br />
In the future it may be possible for breeders to simply sell copies of a<br />
cloned Agouti cat rather than rely on selective breeding. Cloning involves<br />
taking a cell from the parent and making an identical copy of the parent.<br />
The genetic characteristics of the animals obtained by these two breeding<br />
techniques will be different.<br />
(b) Discuss the reasons for the differences in the genetic characteristics<br />
of the cats produced by selective breeding and cloning. In your<br />
answer you should:<br />
Consider the type of cell division<br />
involved in each breeding technique.<br />
Variation (or lack of it) in the offspring
QUESTION NINE: BREEDING<br />
A chicken farmer discovers a chicken which has four legs.<br />
a) Explain what must have happened for the chicken to be born with<br />
four legs<br />
The farmer raises chickens to sell to a fried chicken restaurant. He gets<br />
paid for each leg he supplies.<br />
b) Discuss what he would have to do to get a pure breeding strain of<br />
four legged chickens. Assume the allele for four legs is dominant<br />
(L) and show punnett squares with your answer. A complete<br />
answer would mention any possible negative side effects as well)<br />
QUESTION TEN: GENETICS<br />
Read the following article and then answer the questions that<br />
follow it.<br />
The mistake that turned out to be worth a<br />
fortune!<br />
Back in 1930, nature made a “boo-boo”. This mistake led to<br />
a ram (male) lamb in an otherwise normal flock growing up<br />
with a fleece more like hair than wool. Dr F. W. Dry<br />
researched the new ram by introducing it into his breeding<br />
experiments. This success story has an intriguing twist to it.<br />
Dr Dry initially found that the hairiness was a dominant<br />
genetic factor. So instead of trying to breed it out, he later<br />
realised that it was a superior replacement for the resilient<br />
wool New Zealand always had to import. As a result, he was<br />
able to produce a flock of a new breed of sheep called the<br />
Drysdale.<br />
a) Explain how the first hairy ram could have come to be born.<br />
b) Discuss the steps Dr Dry would have taken to start with the<br />
one hairy ram and end up with a flock of pure breeding hairy<br />
male and female sheep
QUESTION ELEVEN: GENETICS<br />
The kiwifruit species need both female and male plants to be close<br />
to each other for it to reproduce. The kiwifruit has 58 chromosomes<br />
in a body cell.<br />
(a) Using the information above describe how meiosis in kiwifruit<br />
occurs.<br />
(b) Explain how meiosis causes a random assortment of genes<br />
from the parent plant.<br />
QUESTION TWELVE: GENETICS<br />
A mutation in an egg cell of a fish gave rise to a new DNA<br />
sequence.<br />
(a) Describe how the change in the DNA sequence could<br />
produce a new allele.<br />
(b)<br />
C A T G C T G A C T G C A<br />
G T A A G A C T G A C G T<br />
Above is a strand of fish DNA which contains a mutation.<br />
(i) Identify the mutation in the above sequence.<br />
(ii)<br />
(iii)<br />
Explain why this is a mutation.<br />
As a result of this mutation fish were able to resist<br />
pollution in a stream. Discuss whether this mutation<br />
may be passed along to future generations and what<br />
this may mean for this fish species.<br />
(c) An orchard is infected with the disease BSA which attacks<br />
kiwifruit vines. Discuss why some infected plants will survive.
QUESTION THIRTEEN: GENETICS<br />
A pure breeding homozygous dominant short haired Siamese cat<br />
is mated with a long haired recessive cat.<br />
QUESTION FOURTEEN: PEDIGREE TREES<br />
(a)<br />
Long-haired Siamese<br />
Define pure breeding.<br />
Short-haired Siamese<br />
(b) Complete the Punnett square for the cross described above<br />
and state the genotype and phenotype of the offspring (kittens).<br />
Use the letter L and l.<br />
(c) A breeder wishes to have an equal mixture of both long<br />
haired and short haired Siamese kittens to sell. Explain how she<br />
could best ensure that this occurs.<br />
The above diagram shows a pedigree tree for a family affected by cystic fibrosis.<br />
This is a recessive genetic disease which affects the entire body.<br />
(a) Explain how (in general terms) the genotypes of individuals can be<br />
determined from a pedigree tree.<br />
(b)<br />
(c)<br />
(i)<br />
Using the letters D and d state the genotypes of the following individuals:<br />
Generation I male (No. 1):<br />
Generation II female (No. 2):<br />
Generation III female (No. 2):<br />
Carry out a cross to determine the probability of the male (3) and female<br />
(4) in Generation II having another child affected with cystic fibrosis.<br />
(ii) Explain how you determined the genotypes of male (3) and female (4).
QUESTION FIFTEEN: SEX DETERMINATION<br />
A couple has four children, all girls. What are the chances that there<br />
next child will be a boy? Explain your answer.<br />
In your answer you should talk about:<br />
What chromosomes are needed for a boy to be born<br />
Which chromosomes are provided by each parent