Genetics Biology Worksheet ANSWERS
Genetics Biology Worksheet ANSWERS
Genetics Biology Worksheet ANSWERS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
QUESTION ONE: DNA AND VARIATION<br />
Genes determine many of the features of organisms, such as the<br />
colour of the flowers on a plant.<br />
A gene is a part of a DNA molecule.<br />
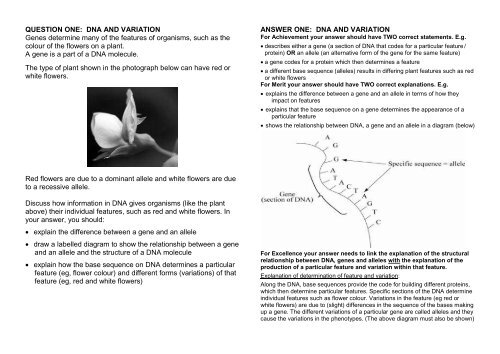
The type of plant shown in the photograph below can have red or<br />
white flowers.<br />
ANSWER ONE: DNA AND VARIATION<br />
For Achievement your answer should have TWO correct statements. E.g.<br />
describes either a gene (a section of DNA that codes for a particular feature /<br />
protein) OR an allele (an alternative form of the gene for the same feature)<br />
a gene codes for a protein which then determines a feature<br />
a different base sequence (alleles) results in differing plant features such as red<br />
or white flowers<br />
For Merit your answer should have TWO correct explanations. E.g.<br />
explains the difference between a gene and an allele in terms of how they<br />
impact on features<br />
explains that the base sequence on a gene determines the appearance of a<br />
particular feature<br />
shows the relationship between DNA, a gene and an allele in a diagram (below)<br />
Red flowers are due to a dominant allele and white flowers are due<br />
to a recessive allele.<br />
Discuss how information in DNA gives organisms (like the plant<br />
above) their individual features, such as red and white flowers. In<br />
your answer, you should:<br />
explain the difference between a gene and an allele<br />
draw a labelled diagram to show the relationship between a gene<br />
and an allele and the structure of a DNA molecule<br />
explain how the base sequence on DNA determines a particular<br />
feature (eg, flower colour) and different forms (variations) of that<br />
feature (eg, red and white flowers)<br />
For Excellence your answer needs to link the explanation of the structural<br />
relationship between DNA, genes and alleles with the explanation of the<br />
production of a particular feature and variation within that feature.<br />
Explanation of determination of feature and variation:<br />
Along the DNA, base sequences provide the code for building different proteins,<br />
which then determine particular features. Specific sections of the DNA determine<br />
individual features such as flower colour. Variations in the feature (eg red or<br />
white flowers) are due to (slight) differences in the sequence of the bases making<br />
up a gene. The different variations of a particular gene are called alleles and they<br />
cause the variations in the phenotypes. (The above diagram must also be shown)
QUESTION TWO: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION<br />
Meiosis is a particular form of cell division that produces male and<br />
female gametes.<br />
(a)<br />
Describe what gametes are and explain why they are needed<br />
for sexual reproduction.<br />
ANSWER TWO: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION<br />
(a) For Achievement you need TWO statements describing gametes. E.g.<br />
A gamete is a sex cell (e.g. an egg or sperm),<br />
A gamete has half the normal number of chromosomes as body cells.<br />
For Merit you need a correct explanation of the need for gametes:<br />
It is required in sexual reproduction to ensure that when a sperm fuses with an<br />
egg, the resulting first cell of the new organism has the correct number of<br />
chromosomes.<br />
Meiosis contributes to genetic variation.<br />
(b)<br />
Discuss how meiosis contributes to genetic variation, and why<br />
genetic variation is important in a population. In your answer,<br />
you should:<br />
describe what is meant by genetic variation<br />
explain how the process of meiosis leads to genetic<br />
variation<br />
explain why genetic variation is of benefit to a population<br />
You could draw labelled diagrams to support your answer.<br />
(b) For Achievement you need TWO statements describing genetic<br />
variation. E.g.<br />
Description of genetic variation:<br />
Genetic variation refers to a variety of different genotypes for a particular trait<br />
within a population.<br />
That the separation of alleles/ chromosomes during meiosis results in new<br />
combinations of alleles<br />
That variation aids survival when conditions change.<br />
For Merit you need a correct explanation of the need for gametes: E.g.<br />
meiosis produces genetic variation in a population by the separation of alleles<br />
which then allows new combinations of alleles to occur at fertilisation (this could<br />
include a labelled diagram of the meiosis process<br />
variations in a population might allow individuals to survive in changing<br />
conditions (and to pass on the ability to their offspring)<br />
For Excellence your answer needs to link the explanation of why genetic<br />
variation within a population is important for the survival of the species<br />
with the explanation of how inherited variation is constantly being<br />
generated by the process of meiosis, through the reshuffling of alleles. E.g.<br />
Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means<br />
that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis.<br />
At fertilisation, which sperm fertilise which egg is due to chance and this results<br />
in new combinations of alleles. These new combinations of alleles cause<br />
variation<br />
The advantage of variation to a species is that it may enable some individuals<br />
to survive if some threatening event occurs. For example, if a new disease<br />
arrives, not all individuals will be wiped out.
QUESTION THREE: MONOHYBRID CROSSES<br />
The allele for a cleft chin (D) is dominant over the allele for a<br />
smooth chin (d).<br />
ANSWER THREE: MONOHYBRID CROSSES<br />
For Achievement you need THREE statements (from of a), b), and c) E.g.<br />
In (a) describes what a dominant allele OR relevant punnet square linked to<br />
pedigree diagram<br />
in (b), gives a reason for the presence of one of the alleles of the genotype<br />
in (c), completes the Punnett Square correctly<br />
D<br />
d<br />
D DD Dd<br />
The pedigree diagram below shows the chin types in a family.<br />
d Dd dd<br />
in (c), gives the correct probabilities for cleft chin and smooth chin.<br />
Probability of cleft chin = ¾ or 75% or 3 out of 4<br />
Probability of smooth chin = ¼ or 25% or 1 out of four<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
Explain how evidence in the pedigree diagram shows that the<br />
cleft chin allele (D) is dominant over the smooth chin allele (d).<br />
In your answer, you should:<br />
Describe what the term dominant allele means<br />
draw a Punnett square(s) to show your reasoning.<br />
Explain why the genotype of male A in generation 2 of the<br />
pedigree diagram must have the genotype Dd.<br />
For Merit you need TWO explanations<br />
in (a), explains the evidence that shows that cleft chin allele is dominant. E.g.<br />
A and B who both have a cleft chin produce a smooth chin child. If the cleft chin<br />
allele was recessive (d) they would not be able to produce a child with a<br />
smooth allele (as they would both have to be dd and would have no D allele to<br />
pass on), so the cleft chin allele must be dominant OR other correct evidence<br />
from chart.<br />
In (b), explains why individual A must have a dominant and a recessive allele<br />
using evidence from the pedigree diagram. E.g. As male A has a cleft chin this<br />
must mean that he carries at least one cleft chin allele (D). Male A and female<br />
B have a smooth chin boy, which means that A must have passed on a smooth<br />
chin allele (d) to the boy as to be smooth chinned the boy must have two<br />
recessive alleles, one from each parent.<br />
In (c), gives the correct probabilities based on the completed Punnet square<br />
parent alleles AND indicates that these can’t be used to predict what an<br />
individual will be. E.g.<br />
Probability of cleft chin = ¾ or 75% or 3 out of 4<br />
<br />
<br />
Probability of smooth chin = ¼ or 25% or 1 out of four<br />
However these are only probabilities and cannot be used to<br />
predict the genotype of individuals
(c)<br />
Individuals A and B, as shown on the pedigree diagram,<br />
decide to have another child. They draw a Punnett square to<br />
find what type of chin their child might have.<br />
Explain why the result predicted by the Punnett square may<br />
not accurately tell them what type of chin their child will have.<br />
In your answer, you should:<br />
draw a Punnett square to show the cross between<br />
individual A and individual B<br />
determine the probabilities of the child having a cleft chin<br />
and having a smooth chin<br />
explain why the ratio of children born into the family with<br />
cleft and smooth chins may not match the probabilities.<br />
For Excellence you need to have at least ONE Merit explanation from a) and<br />
b) and for c) your answer needs to link the theoretical probabilities derived<br />
from the correctly completed Punnett Square for with the explanation of<br />
why the actual outcomes for families will not necessarily match the<br />
predicted outcomes, especially when dealing with small population<br />
samples.<br />
Explanation of discrepancy:<br />
Random fertilisation of eggs by sperm means that number of offspring showing<br />
a particular variation will not always match the probability predicted by a<br />
Punnett square, unless the number of offspring is quite large. Each child is a<br />
unique and random genetic event.
QUESTION FOUR: SURVIVAL<br />
Mutations can occur in DNA during cell division.<br />
Explain whether a mutation could be inherited if it occurred in a skin<br />
cell of an individual. In your answer, you should:<br />
describe what a mutation is<br />
explain what determines whether a mutation is able to be<br />
inherited or not.<br />
ANSWER FOUR: SURVIVAL<br />
For Achievement you need ONE statement E.g.<br />
Correctly defines or describes a mutation: A mutation is a change to the base<br />
sequence of a gene along the DNA of an organism or a change in the genetic<br />
code.<br />
States that a skin cell mutation is not inheritable (or similar)<br />
For Merit you need ONE explanation E.g.<br />
If the mutation occurs in a gamete (or a cell that undergoes meiosis), then it<br />
would be inherited. As a skin cell is not a gamete, a mutation in a skin cell<br />
cannot be inherited.<br />
QUESTION FIVE: GENETICS<br />
Explain how two parents who don’t show a particular characteristic<br />
can have a child who does show that feature.<br />
In your answer include:<br />
The nature of the characteristic<br />
What causes a feature to be expressed (shown)<br />
What is different (genetically) between the parents and the child<br />
ANSWER FIVE: GENETICS<br />
For Achievement your answer should talk about 2 – 3 points from:<br />
The characteristic must be recessive<br />
For a recessive feature to show a person must have two alleles for that feature<br />
For a dominant feature to be shown (or a recessive feature to be hidden) the<br />
person must have at least one allele for that feature<br />
The parents must be heterozygous<br />
The child is homozygous recessive for that feature<br />
The parents must have at least one allele each for the (recessive) characteristic<br />
in order to pass it on to the child<br />
The child must have both alleles for the (recessive) feature for it to be shown<br />
For Merit a reasonable explanation covering all the bullet points must be<br />
given<br />
The feature is linked to a recessive allele. Recessive alleles are only expressed if<br />
a dominant allele is not present. Both parents would have to be heterozygous for<br />
that characteristic. This means that they would have the dominant allele and the<br />
recessive one and only show the characteristic represented by the dominant<br />
allele. The child inherits one allele from each parent and if they inherit the two<br />
recessive alleles then they will exhibit the recessive characteristic.
QUESTION SIX: VARIATION<br />
A population of plants, species A, living in a certain area shows a<br />
lot of variation in its leaf size, from very small to very large as<br />
shown in the graph below.<br />
Leaf size of plants of species A<br />
ANSWER SIX: VARIATION<br />
For Achievement you need ONE statement E.g.<br />
For Merit you need ONE explanation E.g.<br />
explains what causes variation (e.g. The variation in plants of species A may be<br />
due to differences (mutations) in the sequence of bases in a particular gene)<br />
Explains how variation aids the survival of the species. E.g.<br />
Plants of species A have different sized leaves, and when the environment<br />
becomes more shaded some plants will be better adapted to the new<br />
conditions and therefore will survive).<br />
Explanation of effect of reduced light:<br />
Those individuals of plant species A whose leaves are large will be better<br />
adapted to live under lower light levels. They will survive better and produce<br />
more offspring, increasing the number of larger leaves plants in the<br />
population.<br />
Explanation of fate of poorly adapted plants:<br />
Plants with average or small leaves will not be able to absorb enough<br />
sunlight and make sufficient food. In time these plants might die off.<br />
Leaf size affects the ability of a plant to absorb sunlight and make<br />
food. Plants with larger leaves can live in areas with lower light<br />
levels.<br />
A new plant, species B, starts growing in the same area as<br />
species A. Species B plants grow taller than species A plants,<br />
which reduces the light available to plants growing below species<br />
B.<br />
Discuss how variation in leaf size occurs in the starting population<br />
of species A and explain how this might help species A to survive<br />
when species B starts growing in the same area.<br />
In your answer, you should consider:<br />
what causes variation within a population<br />
the effect of reduced light on different individuals of plant<br />
species A<br />
For Excellence your answer needs to link the explanation of how genetic<br />
variation arises within a plant species with the explanation of how that<br />
genetic variation aids survival of the species in a changing environment<br />
(eg, when environmental conditions are changed to lower light levels, the<br />
larger leaves of some plants of species A, means that they are better<br />
adapted to survive and reproduce, thus ensuring the survival of some<br />
individuals, and hence the species).<br />
Explanation of causes of variation: The variation in plants of species A may be<br />
due to differences (mutations) in the sequence of bases in a particular gene.<br />
AND<br />
Explanation of effect of reduced light:<br />
Those individuals of plant species A whose leaves are large will be better<br />
adapted to live under lower light levels. They will survive better and produce<br />
more offspring, increasing the number of larger leaves plants in the population.<br />
OR<br />
Explanation of fate of poorly adapted plants:<br />
Plants with average or small leaves will not be able to absorb enough sunlight<br />
and make sufficient food. In time these plants might die off.
QUESTION SEVEN: GENETICS<br />
Cloning involves making an exact copy of an organism. Selective<br />
breeding involves the breeding together of organisms that possesses<br />
highly desirable characteristics.<br />
Compare and contrast selective breeding and cloning.<br />
Your answer should include<br />
How the offspring compare to their parents<br />
Their relative advantages and disadvantages<br />
ANSWER SEVEN: GENETICS<br />
For Achievement your answer should talk about 3 – 4 points from:<br />
Cloned offspring have the same DNA as the parent (No variation)<br />
Selective breeding means that the offspring have differences to their parents<br />
(variation)<br />
Advantages of selective breeding: All offspring are slightly different so there is an<br />
increased chance that some will survive changes in the environment / diseases<br />
It more likely that wanted characteristics will be passed on<br />
Selective breeding can enhance a particular characteristic (I.e. make cows<br />
bigger)<br />
Disadvantages of selective breeding: There is no guarantee that the desired<br />
features will be passed on (random process);<br />
If the breeding group is too small inbreeding may occur with undesirable<br />
characteristics being passed on<br />
Advantages of cloning: Unlike selective breeding, which is a random process,<br />
with cloning you know exactly what you will get<br />
There is a 100% chance that any desired feature will be passed on<br />
Disadvantages of cloning:<br />
As there is no variation (change) you cannot improve on the original<br />
As there is no variation a disease that will affect one will affect all<br />
The cloned organism may develop “old age conditions” earlier than they should<br />
For Merit you need to give a definition of what cloning and selective<br />
breeding are and at least 2 advantages or disadvantages explained in detail<br />
Selective breeding involves the breeding together of organisms that possess<br />
highly desirable characteristics. This increases the chances of the desired<br />
characteristics being passed onto the offspring. It is a random process and the<br />
outcome / offspring are not guaranteed to possess the desired characteristic.<br />
Therefore a number of the offspring will not have the desired characteristic.<br />
Offspring will have a range of characteristics, inherited from both parents (I.e.<br />
there is genetic variation) and will be different in multiple ways (Possibly superior<br />
or inferior).<br />
Cloning is also about getting desired characteristics in offspring. However,<br />
cloning produces offspring that carry the DNA of only one parent, making<br />
offspring genetically identical to that parent. This means there is a 100% chance<br />
that the offspring will have the desired features. (No variation) This means that<br />
there is no chance the offspring will be superior or inferior to the parent in some<br />
way.<br />
In summary while both methods are about increasing the chances of offspring<br />
having desired characteristics; selective breeding gives variation but no certainty,<br />
while cloning gives certainty but no variation.<br />
For Excellence as for Merit but 3 advantages / disadvantages explained
QUESTION EIGHT: GENETICS<br />
There are many genes used by pedigree cat breeders to get a range of<br />
colours, fur length and body shapes. Several genes can control coat<br />
colour in cats.<br />
One of these produces the Agouti pattern, where each hair has a black tip<br />
but bands of light and dark towards the hair root. This causes a cat to<br />
have a striped appearance. This pattern is dominant, and denoted by the<br />
letter A. The recessive allele for this trait gives plain black hairs.<br />
(a)<br />
A breeder wishes to have a pure breeding group with the Agouti<br />
coat colour. He has a group of the Oriental breed pictured above,<br />
some of which are black and some of which are Agouti.<br />
Discuss how he would go about developing a pure breeding<br />
Agouti group. Include punnet square(s) in your answer.<br />
In the future it may be possible for breeders to simply sell copies of a<br />
cloned Agouti cat rather than rely on selective breeding. Cloning involves<br />
taking a cell from the parent and making an identical copy of the parent.<br />
The genetic characteristics of the animals obtained by these two breeding<br />
techniques will be different.<br />
(b) Discuss the reasons for the differences in the genetic characteristics<br />
of the cats produced by selective breeding and cloning. In your<br />
answer you should:<br />
Consider the type of cell division<br />
involved in each breeding technique.<br />
Variation (or lack of it) in the offspring<br />
<strong>ANSWERS</strong> EIGHT: GENETICS<br />
(a) For Achievement your answer should have ONE correct statement.<br />
Eg:<br />
He needs to do a test/back cross to find AA cats to breed together / AA are pure<br />
breeding for agouti (a)<br />
Breed agouti with black to find out which are AA<br />
AND punnet/s (a)<br />
For Merit your answer should explain process of test / back cross (m)Eg:<br />
He needs to do a test/back cross to find AA cats to breed together/AA are pure<br />
breeding for agouti. This means breeding the agouti with the black, if any black<br />
kittens result, the agouti parent must be Aa and not pure breeding (m)<br />
OR<br />
appropriately annotated punnets ie<br />
Punnet 1 – all agouti<br />
A A<br />
a Aa Aa<br />
a Aa Aa<br />
Punnet 2 – ½ agouti. ½ black<br />
A a<br />
a Aa aa<br />
a Aa aa<br />
For Excellence your answer should discuss the process of test cross to<br />
establish pure breeding group (e) Eg:<br />
The breeder first needs to find the AA agouti cats to breed from. By breeding the<br />
agouti cats he has with the black ones, he can see this as AA x aa will only<br />
produce Aa agouti kittens as in punnet 1. Quite a large number are needed to<br />
ensure no black kittens will result. If a single black kitten is born, the agouti<br />
parent must be Aa as in punnet 2, it must have given an a allele. When the<br />
breeder is certain he has AA individuals he can breed only these, as all offspring<br />
will be AA true breeding agouti, as no recessive alleles are present.<br />
AND<br />
Correct Punnett squares.<br />
(b) For Achievement you need to describe a difference between cloning<br />
and selective breeding or describe the processes of cloning and<br />
selective breeding. (a) Eg<br />
Cloning is a mitotic division but selective breeding is meiosis. OR<br />
Cloning means there is no variation in the offspring whereas in selective breeding<br />
there is variation in offspring. OR<br />
Only one parent contributes all the genes/ genetic material / chromosomes in<br />
cloning but two parents do in selective breeding.
For Merit you should give a reason for the difference in the genetic<br />
characteristics based on the type of cell division in EITHER selective<br />
breeding OR cloning. (m) Eg<br />
Cloning means there is no variation in the offspring because they are produced<br />
by mitosis<br />
Or<br />
In selective breeding there is variation in offspring. This is due to meiosis.<br />
For Excellence you should give a reason for the difference in the genetic<br />
characteristics based on the type of cell division in BOTH selective<br />
breeding AND cloning. Eg<br />
Cloning means there is no variation in the offspring whereas in breeding there is<br />
variation in offspring. This is due to meiosis being used in normal breeding. In<br />
meiosis, the homologous pairs line up and genetic material is exchanged<br />
(causing variation) They are pulled apart, ie the alleles are separated. Each<br />
gamete receives one allele for each gene, ie 1/2 the genetic material of the<br />
parent. This combines randomly at fertilization with another gamete to give the<br />
various different outcomes.<br />
Cloning would lack variation as it uses mitosis. In mitosis the chromosomes line<br />
up along the equator of the cell and an exact copy of each chromosome is made.<br />
The chromosomes are then pulled apart and the cell splits in two leaving two<br />
identical chromosomes (no variation)