Gr 10 Data Handling 3 - Maths Excellence
Gr 10 Data Handling 3 - Maths Excellence
Gr 10 Data Handling 3 - Maths Excellence
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
INDIVIDUAL<br />
FORMATIVE<br />
ASSESSMENT<br />
Activity 1<br />
1. For each set of data, determine the quartiles:<br />
A 2 3 5 7 9 <strong>10</strong> 11 13 15 16 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 25 32<br />
B 2 3 5 7 9 <strong>10</strong> 11 13 15 16 16 17 18 19 21 22 23<br />
C 2 3 5 7 9 <strong>10</strong> 11 13 15 16 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 25 32 34<br />
D 2 3 5 7 9 <strong>10</strong> 11 13 15 16 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 25<br />
DVD<br />
Lesson<br />
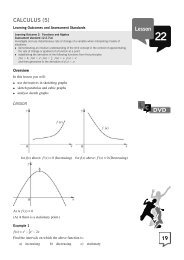
Range<br />
The range is the difference between the largest and the smallest value in the<br />
data. The bigger the range, the more spread out the data is. The range cannot<br />
be used with grouped data and it doesn’t deal with values between these<br />
extremes. Also, a single very small or very large value would give a misleading<br />
impression of the spread of the data.<br />
Consider for example, the following set of marks for Class A:<br />
Class A 1 1 2 2 3 4 4 5 5 6 7 8 8 9 <strong>10</strong><br />
Range = largest score – smallest score = <strong>10</strong> – 1 = 9<br />
Deciles and percentiles<br />
Deciles subdivide the data into tenths. Percentiles divide the data into<br />
hundredths.<br />
The interquartile range (IQR)<br />
The difference between the lower and upper quartile is called the interquartile<br />
range. It is a better measure of dispersion than the range because it is not<br />
affected by extreme values. It is based on the middle half of the data. It<br />
indicates how densely the data in the middle is spread around the median.<br />
Example<br />
Calculate the interquartile range for the following data set.<br />
2 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 7 8 9<br />
Lower<br />
Quartile<br />
Q 1<br />
IQR = Q 3<br />
– Q 1<br />
= 7 – 3 = 4<br />
The semi-interquartile range<br />
Median<br />
Q 2<br />
Upper<br />
Quartile<br />
Q 3<br />
The semi-interquartile range is half of the interquartile range.<br />
The semi-IQR for the previous example is _<br />
Q – Q 3 1<br />
2<br />
= _ 7 – 3 = 2.<br />
2<br />
18<br />
<strong>10</strong> LC G<strong>10</strong> MATHS LWB.indb 18 2008/09/09 12:22:45 PM