ExamView Pro - CP Bio Chapter 14.tst
ExamView Pro - CP Bio Chapter 14.tst
ExamView Pro - CP Bio Chapter 14.tst
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________<br />
ID: A<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 14 - The Human Genome - Practice Test<br />
Multiple Choice<br />
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
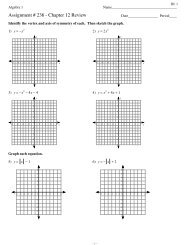
1. Which of the following are shown in a karyotype?<br />
a. homologous chromosomes c. autosomes<br />
b. sex chromosomes d. all of the above<br />
2. What is the approximate probability that a human offspring will be female?<br />
a. 10 percent c. 50 percent<br />
b. 25 percent d. 75 percent<br />
3. What is the probability that a human sperm cell will carry an X chromosome?<br />
a. 0 percent c. 50 percent<br />
b. 25 percent d. 100 percent<br />
4. A pedigree CANNOT be used to<br />
a. determine whether a trait is inherited.<br />
b. show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next.<br />
c. determine whether an allele is dominant or recessive.<br />
d. none of the above<br />
5. A person who has PKU<br />
a. inherited the allele for the trait from one parent.<br />
b. inherited the allele for the trait from both parents.<br />
c. is heterozygous for the trait.<br />
d. will not pass the allele for the trait to his or her offspring.<br />
6. Which of the following genotypes result in the same phenotype?<br />
a. IAIA and IAIB c. IBIB and IAIB<br />
b. IBIB and IBi d. IBi and ii<br />
7. A change in a single gene causes the protein called CFTR to<br />
a. become less soluble.<br />
b. fold improperly.<br />
c. destroy the cell membrane.<br />
d. transport sodium ions instead of chloride ions.<br />
8. Chromosomes 21 and 22 contain long stretches of repetitive DNA, which<br />
a. contain genes for colorblindness.<br />
b. are able to code for proteins.<br />
c. are unstable sites where rearrangements can occur.<br />
d. contain genes for Lou Gehrig’s disease.<br />
9. Colorblindness is more common in males than in females because<br />
a. fathers pass the allele for colorblindness to their sons only.<br />
b. the allele for colorblindness is located on the Y chromosome.<br />
c. the allele for colorblindness is recessive and located on the X chromosome.<br />
d. males who are colorblind have two copies of the allele for colorblindness.<br />
1
Name: ________________________<br />
ID: A<br />
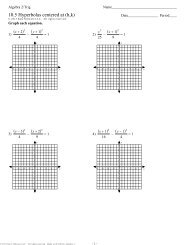
____ 10. A Barr body is<br />
a. a condensed X chromosome that is inactive.<br />
b. a condensed Y chromosome that is inactive.<br />
c. an activated X chromosome.<br />
d. an activated Y chromosome.<br />
____ 11. Because the X chromosome contains genes that are vital for normal development, no baby has been born<br />
a. with one X chromosome. c. without an X chromosome.<br />
b. with three X chromosomes. d. with four X chromosomes.<br />
____ 12. Which of the following combinations of sex chromosomes represents a female?<br />
a. XY c. XXXY<br />
b. XXY d. XX<br />
____ 13. The process of DNA fingerprinting is based on the fact that<br />
a. the most important genes are different among most people.<br />
b. no two people, except identical twins, have exactly the same DNA.<br />
c. most genes are dominant.<br />
d. most people have DNA that contains repeats.<br />
____ 14. The human genome was sequenced<br />
a. by sequencing each gene on each chromosome, one at a time.<br />
b. using DNA fingerprinting.<br />
c. by looking for overlapping regions between sequenced DNA fragments.<br />
d. using open reading frames.<br />
____ 15. Which of the following is the first step in gene therapy?<br />
a. splicing the normal gene to viral DNA<br />
b. allowing recombinant viruses to infect human cells<br />
c. using restriction enzymes to cut out the normal gene from DNA<br />
d. identifying the faulty gene that causes the disease<br />
____ 16. How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype?<br />
a. 2 c. 44<br />
b. 23 d. 46<br />
____ 17. In humans, a male has<br />
a. one X chromosome only.<br />
b. two X chromosomes.<br />
c. one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.<br />
d. two Y chromosomes.<br />
____ 18. Human females produce egg cells that have<br />
a. one X chromosome. c. one X or one Y chromosome.<br />
b. two X chromosomes. d. one X and one Y chromosome.<br />
____ 19. In a pedigree, a circle represents a(an)<br />
a. male. c. child.<br />
b. female. d. adult.<br />
2
Name: ________________________<br />
ID: A<br />
____ 20. Which of the following is caused by a dominant allele?<br />
a. Huntington’s disease c. Tay-Sachs disease<br />
b. PKU d. none of the above<br />
____ 21. Which of the following is determined by multiple alleles?<br />
a. Rh blood group c. PKU<br />
b. ABO blood group d. Huntington’s disease<br />
____ 22. Sickle cell disease is caused by a<br />
a. small change in the DNA of a single gene.<br />
b. change in the size of a chromosome.<br />
c. change in two genes.<br />
d. change in the number of chromosomes in a cell.<br />
____ 23. Compared with normal hemoglobin, the hemoglobin of a person with sickle cell disease<br />
a. is longer.<br />
b. is shorter.<br />
c. has a different sequence of amino acids.<br />
d. is sickle-shaped.<br />
____ 24. The sequencing of human chromosomes 21 and 22 showed that<br />
a. some regions of chromosomes do not code for proteins.<br />
b. all of the DNA of chromosomes codes for proteins.<br />
c. different chromosomes have the same number of genes.<br />
d. different chromosomes contain the same number of DNA bases.<br />
____ 25. Sex-linked genes are located on<br />
a. the autosomes.<br />
b. the X chromosome only.<br />
c. the Y chromosome only.<br />
d. both the X chromosome and Y chromosome.<br />
____ 26. Which of the following form(s) a Barr body?<br />
a. the Y chromosome in a male cell<br />
b. the X chromosome in a male cell<br />
c. one of the X chromosomes in a female cell<br />
d. both of the X chromosomes in a female cell<br />
____ 27. The failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis is called<br />
a. nondisjunction. c. Turner’s syndrome.<br />
b. X-chromosome inactivation. d. Down syndrome.<br />
____ 28. Scientists test for alleles that cause human genetic disorders by<br />
a. making karyotypes. c. using DNA probes.<br />
b. making DNA fingerprints. d. making pedigrees.<br />
3
Name: ________________________<br />
ID: A<br />
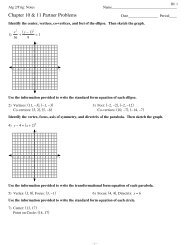
____ 29. The Human Genome <strong>Pro</strong>ject is an attempt to<br />
a. make a DNA fingerprint of every person’s DNA.<br />
b. analyze the human DNA sequence.<br />
c. cure human diseases.<br />
d. identify alleles in human DNA that are recessive.<br />
____ 30. The purpose of gene therapy is to<br />
a. cure genetic disorders.<br />
b. determine the sequences of genes.<br />
c. search for genes on chromosomes.<br />
d. identify an individual using DNA.<br />
Completion<br />
Complete each sentence or statement.<br />
31. People who have sickle cell disease inherited ____________________ copy(ies) of the sickle cell allele.<br />
32. A boy who has hemophilia inherited the disorder from his ____________________.<br />
33. A person with the alleles ii has blood type ____________________.<br />
34. A person who has ____________________ is unable to break down the amino acid phenylalanine.<br />
35. The human genes associated with color vision are located on the ____________________ chromosome.<br />
Short Answer<br />
36. How are human chromosomes 21 and 22 similar?<br />
37. A man who does not have hemophilia and a woman who is a carrier of the disorder have a son. What is the<br />
probability that their son has hemophilia?<br />
38. Why are all X-linked alleles expressed in males, even if they are recessive?<br />
39. Why do scientists use sections of DNA that have little or no known function to do DNA fingerprinting?<br />
40. Why did scientists expect that humans would have more genes than they actually do?<br />
4
Name: ________________________<br />
ID: A<br />
Other<br />
USING SCIENCE SKILLS<br />
The pedigree shows the inheritance of free earlobes and attached earlobes in five generations of a family.<br />
Attached earlobes is caused by a recessive allele (f).<br />
Figure 14–1<br />
41. Inferring Is individual 2 in Figure 14-1 homozygous or heterozygous for free earlobes? Explain.<br />
42. Inferring Can you be certain of the genotype of individual 5 in Figure 14-1? Explain.<br />
USING SCIENCE SKILLS<br />
Figure 14–2<br />
43. Applying Concepts In the human karyotype in Figure 14-2, what are the chromosomes in each numbered<br />
group called?<br />
44. Interpreting Graphics In the human karyotype in Figure 14-2, how many chromosomes are shown?<br />
5
Name: ________________________<br />
ID: A<br />
45. Inferring Is the individual represented by the karyotype in Figure 14-2 male or female? Explain.<br />
6
ID: A<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 14 - The Human Genome - Practice Test<br />
Answer Section<br />
MULTIPLE CHOICE<br />
1. ANS: D REF: p. 341<br />
2. ANS: C REF: p. 342<br />
3. ANS: C REF: p. 342<br />
4. ANS: D REF: p. 342<br />
5. ANS: B REF: p. 345<br />
6. ANS: B REF: p. 344<br />
7. ANS: B REF: p. 346<br />
8. ANS: C REF: p. 349<br />
9. ANS: C REF: p. 350<br />
10. ANS: A REF: p. 352<br />
11. ANS: C REF: p. 353<br />
12. ANS: D REF: p. 342<br />
13. ANS: B REF: p. 357<br />
14. ANS: C REF: p. 358<br />
15. ANS: D REF: p. 359<br />
16. ANS: D REF: p. 341<br />
17. ANS: C REF: p. 342<br />
18. ANS: A REF: p. 342<br />
19. ANS: B REF: p. 342<br />
20. ANS: A REF: p. 346<br />
21. ANS: B REF: p. 344<br />
22. ANS: A REF: p. 347<br />
23. ANS: C REF: p. 347<br />
24. ANS: A REF: p. 349<br />
25. ANS: D REF: p. 350<br />
26. ANS: C REF: p. 352<br />
27. ANS: A REF: p. 352<br />
28. ANS: C REF: p. 355<br />
29. ANS: B REF: p. 357<br />
30. ANS: A REF: p. 359<br />
COMPLETION<br />
31. ANS: two<br />
REF: p. 347<br />
32. ANS: mother<br />
REF: p. 351<br />
1
ID: A<br />
33. ANS: O<br />
REF: p. 344<br />
34. ANS: PKU<br />
REF: p. 345<br />
35. ANS: X<br />
REF: p. 350<br />
SHORT ANSWER<br />
36. ANS:<br />
Chromosomes 21 and 22 are the smallest human autosomes, they contain hundreds of genes, and they contain<br />
long stretches of repetitive DNA that do not code for proteins.<br />
REF: p. 349<br />
37. ANS:<br />
The probability that their son has hemophilia is 50%.<br />
REF: p. 351<br />
38. ANS:<br />
Males have just one X chromosome.<br />
REF: p. 350<br />
39. ANS:<br />
These sections of DNA vary widely from person to person.<br />
REF: p. 357<br />
40. ANS:<br />
Scientists expected humans to have more genes because a human is a very complex organism.<br />
REF: p. 358<br />
OTHER<br />
41. ANS:<br />
The individual is heterozygous (Ff), since her daughter has attached earlobes. The daughter inherited one<br />
allele for attached earlobes from individual 2 and another from individual 1.<br />
REF: p. 342<br />
42. ANS:<br />
No, the genotype of individual 5 is uncertain because his children have free earlobes. Thus, individual 5<br />
could be homozygous (FF) or heterozygous (Ff) for free earlobes. If, however, one of his children had<br />
attached earlobes, it would be certain that individual 5 is heterozygous.<br />
REF: p. 342<br />
2
ID: A<br />
43. ANS:<br />
The chromosomes in each group are called homologous chromosomes.<br />
REF: p. 341<br />
44. ANS:<br />
Forty-seven chromosomes are shown.<br />
REF: p. 341<br />
45. ANS:<br />
The individual is male. In the presence of the Y chromosome, the human embryo will also develop as a male,<br />
no matter how many X chromosomes are present.<br />
REF: p. 341<br />
3