Design & Manufacturing - Centurion University
Design & Manufacturing - Centurion University
Design & Manufacturing - Centurion University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
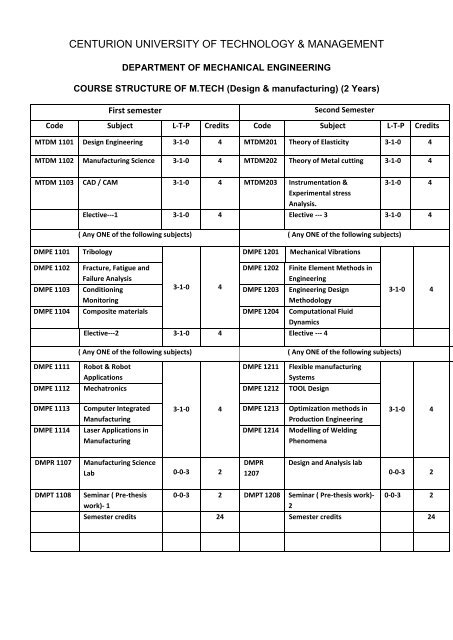
CENTURION UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT<br />
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING<br />
COURSE STRUCTURE OF M.TECH (<strong>Design</strong> & manufacturing) (2 Years)<br />
First semester<br />
Second Semester<br />
Code Subject L-T-P Credits Code Subject L-T-P Credits<br />
MTDM 1101 <strong>Design</strong> Engineering 3-1-0 4 MTDM201 Theory of Elasticity 3-1-0 4<br />
MTDM 1102 <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Science 3-1-0 4 MTDM202 Theory of Metal cutting 3-1-0 4<br />
MTDM 1103 CAD / CAM 3-1-0 4 MTDM203 Instrumentation &<br />
Experimental stress<br />
Analysis.<br />
3-1-0 4<br />
Elective---1 3-1-0 4 Elective --- 3 3-1-0 4<br />
( Any ONE of the following subjects) ( Any ONE of the following subjects)<br />
DMPE 1101<br />
Tribology<br />
DMPE 1201<br />
Mechanical Vibrations<br />
DMPE 1102<br />
DMPE 1103<br />
Fracture, Fatigue and<br />
Failure Analysis<br />
Conditioning<br />
Monitoring<br />
3-1-0 4<br />
DMPE 1202<br />
DMPE 1203<br />
Finite Element Methods in<br />
Engineering<br />
Engineering <strong>Design</strong><br />
Methodology<br />
DMPE 1104 Composite materials DMPE 1204 Computational Fluid<br />
Dynamics<br />
Elective---2 3-1-0 4 Elective --- 4<br />
3-1-0 4<br />
DMPE 1111<br />
( Any ONE of the following subjects) ( Any ONE of the following subjects)<br />
Robot & Robot<br />
Applications<br />
DMPE 1211<br />
Flexible manufacturing<br />
Systems<br />
DMPE 1112 Mechatronics DMPE 1212 TOOL <strong>Design</strong><br />
DMPE 1113<br />
Computer Integrated<br />
<strong>Manufacturing</strong><br />
3-1-0 4<br />
DMPE 1213<br />
Optimization methods in<br />
Production Engineering<br />
3-1-0 4<br />
DMPE 1114<br />
Laser Applications in<br />
<strong>Manufacturing</strong><br />
DMPE 1214<br />
Modelling of Welding<br />
Phenomena<br />
DMPR 1107<br />
<strong>Manufacturing</strong> Science<br />
Lab 0-0-3 2<br />
DMPR<br />
1207<br />
<strong>Design</strong> and Analysis lab<br />
0-0-3 2<br />
DMPT 1108<br />
Seminar ( Pre-thesis<br />
work)- 1<br />
0-0-3 2 DMPT 1208 Seminar ( Pre-thesis work)-<br />
2<br />
0-0-3 2<br />
Semester credits 24 Semester credits 24
THIRD SEMESTER<br />
FOURTH SEMESTER<br />
CODE SUBJECT L-T-P Credits CODE SUBJECT L-T-P Credits<br />
MTDM 2101<br />
Advanced Mechanics<br />
of Solids<br />
3-1-0 4 DMPT 2201 Thesis / Project<br />
(Part-2)<br />
20<br />
MTDM 2102<br />
Modern<br />
<strong>Manufacturing</strong><br />
Process<br />
3-1-0 4<br />
DMPT 2107<br />
Thesis / project<br />
(Part-1)<br />
10<br />
DMCV 2108 Comprehensive viva 2<br />
Semester credits 20 Semester<br />
credits<br />
20<br />
TOTAL CUMULATIVE CREDITS ( 4 SEMESTERS) ------------ 88
CENTURION UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT<br />
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING<br />
SYLLABUS of M.Tech (<strong>Design</strong> & <strong>Manufacturing</strong>)<br />
FIRST SEMESTER<br />
MTDM 1101 DESIGN ENGINEERING 3-1-0<br />
Module-I<br />
Fundamentals: principles of design, systematic approach, need analysis and design of specification;<br />
Conceptual design: developing function structure, developing concepts by systematic search with<br />
physical principles, classifying schemes; Concept selection: matrix methods, necessity methods,<br />
probability methods, fuzzy set based methods, case study on consumer product.<br />
Module-II<br />
Embodiment design: basic rules, system modeling, preliminary design calculations and material<br />
selection, design considerations like force alignment, vibration etc., failure modes and effects<br />
analysis, design for manufacturability and assembly, case studies on design of machines.<br />
Module-III<br />
Optimal and robust design: design problem formulation for analytical and numerical solution, design<br />
of experiments, Taguchi’s method; Reverse engineering; Physical prototyping; Lab: conceptual<br />
design, reverse engineering, design of simple sensors and actuators, hydraulic and pneumatic<br />
systems, motors and controller, product teardown and redesign, embodiment design, CAE analysis,<br />
prototyping, design project.<br />
Text Book<br />
1. Yousef Haik, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> Process, Vikas Publishing house, New Delhi, 2003.<br />
2. G. Pahl, and W. Beitz, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – A Systematic Approach, Springer – Verlag, 1996.<br />
References<br />
1. K. Otto and K. wood, Product <strong>Design</strong> – techniques in reverse engineering and new product<br />
development, Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2004.<br />
2. A. Ertas and J. C. Jones, The Engineering <strong>Design</strong> Process, 2nd ed., John Wiley and Sons, 1996.<br />
3. A. Kusiak, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – Products, Processes and Systems, Academic Press, 1999.<br />
4. C. L. Dym and P. Little, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – A Project based Introduction, John Wiley, 2000.<br />
5. G. E. Dieter, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – A Materials and Processing Approach, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill<br />
International, 2000.<br />
6. E. Kroll, S. S. Condoor and D. G. Jonsson, Innovative Conceptual <strong>Design</strong> – Theory and<br />
Application of Parameter Analysis, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2001.
MTDM 1102 MANUFACTURING SCIENCE 3-1-0<br />
UNIT – I<br />
<strong>Manufacturing</strong> concepts : Product cycle; Job, batch and mass production; Primary and secondary<br />
manufacturing processes.<br />
CASTING : Steps involved in making a casting . Advantage of casting and its applications.<br />
Patterns and Pattern making Types of patterns. Materials used for patterns, pattern allowances and<br />
their construction, Principles of Gating, Gating ratio and design of Gating systems.<br />
Solidification of casting . Concept , Solidification of pure metal and alloys, short & long freezing range<br />
alloys.<br />
Risers : Types, function and design, casting design considerations, special casting processes 1)<br />
Centrifugal 2)Die, 3) Investment.<br />
Methods of Melting : Crucible melting and cupola operation, steel making processes.<br />
UNIT – II<br />
Welding : Classification of welding process, types of welds and welded joints and their characteristics,<br />
design of welded joints, Gas welding, ARC welding, Forge welding, resistance welding, Thermit<br />
welding and Plasma (Air and water ) welding.<br />
Inert Gas welding, TIG & MIG welding, Friction welding, Induction welding, Explosive<br />
welding, Laser welding, Soldering & Brazing. Heat affected zones in welding & its effects. Welding<br />
defects, causes and remedies. Destructive & nondestructive testing of welds.<br />
Cutting of Metals: Oxy Acetylene Gas cutting, water plasma. Cutting of ferrous, nonferrous metals.<br />
UNIT – III<br />
Hot working, cold working, strain hardening, recovery, recrystallisation and grain growth, Comparison<br />
of properties of Cold and Hot worked parts.<br />
Rolling fundamentals : theory of rolling, types of Rolling mills and products. Forces in rolling and<br />
power requirements.<br />
Stamping, forming and other cold working processes : Blanking and piercing. Bending and forming.<br />
Drawing and its types: wire drawing and Tube drawing. Coining. Hot and cold spinning. Types of<br />
presses and press tools. Forces and power requirement in the above operations.<br />
UNIT – IV<br />
EXTRUSION OF METALS : Basic extrusion process and its characteristics. Hot extrusion and cold<br />
extrusion - Forward extrusion and backward extrusion. Impact extrusion. Hydrostatic extrusion.<br />
Forging processes: Principles of forging. Tools and dies . Types Forging : Smith forging, Drop Forging<br />
, Roll forging , Forging hammers : Rotary forging , forging defects.<br />
Brief introduction to powder metallurgy : Advantages and limitations of powder metallurgy,<br />
Manufacture of metal powders, mixing & blending, compacting, sintering and secondary operations<br />
TEXT BOOKS :<br />
1. Process and materials of manufacturing :Lindberg/PE<br />
2. Principles of Metal Castings / Roenthal.<br />
3. Welding Process / Paramar /<br />
4. Production Technology /Sarma P C /<br />
5. <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Technology / P.N. Rao/TMH
MTDM 1103 CAD / CAM 3-1-0<br />
Module – 1: Basic concepts (10hrs.)<br />
Introduction: contents & tools, definition of CAD/CAM tools, industrial look at CAD/CAM<br />
Hardware: types of systems, system evaluation criteria, I/O devise<br />
Software: graphic standards, basic definitions, user interface, software modules, modelling & viewing<br />
Module – 2: Geometric Modelling (14hrs.)<br />
Representation of curves: wire frame models, wire frame entities, representation of analytic &<br />
synthetic curves.<br />
Representation of surfaces: models and entities, parametric representation of analytic & synthetic<br />
surfaces.<br />
Representation of solids: set theory, half – spaces, boundary representations, CSG, sweep<br />
representation, analytic solid modelling.<br />
Module – 3: (14hrs.)<br />
CAD/CAM data exchange: IGES, PDES<br />
Numerical control: NC, NC models, NC elements, NC machine tools, structure of CNC machine tools,<br />
features of machining centre, turning centre.<br />
CNC part programming: fundamentals, manual part programming methods, computer aided part<br />
programming, ATP programming.<br />
TEXT BOOKS:<br />
1. CAD/CAM – A Zimmers & P. Groover/PE/PHI<br />
2. CAD/CAM Theory & Practice/Ibrahim Zeid/TMH<br />
REFERENCES:<br />
1. Automation, production systems & Computer integrated manufacturing/Groover/ P.E<br />
2. CAD/CAM/CIM/ Radhakrishnan and Subramanian/ New age<br />
3. Principles of Computer Aided <strong>Design</strong> and manufacturing/Farid Amirouche/Pearson<br />
TRIBOLOGY 3-1-0<br />
Module I<br />
Introduction-Historical background, Bearing concepts and typical applications. Lubricant and<br />
lubrication, Types of bearings, properties and testing of lubricants, Basic equations: Generalized<br />
Reynolds equation, Flow and Shear Stress, Energy equation, Equation of state. Viscous flow<br />
concepts-Conservation of laws and its derivations: continuity, momentum (N-S equations) and<br />
energy, Solutions of Navier-Strokes equations. Order of magnitude analysis, General Reynolds<br />
equation-2D and 3D (Cartesian and Cylindrical)<br />
Module II<br />
Hydro dynamic lubrication : Mechanism of pressure development and load carrying capacity, Planeslider<br />
bearing, Idealized slider bearing with a pivoted shoe, Step bearing, Idealized journal bearing. –
infinitely long journal bearing, Petroffs equation for a lightly loaded bearing, narrow bearing, Oil flow<br />
and thermal equilibrium - Heat balance of lubricants<br />
Hydrostatic Bearing : Principles, Component of hydrostatic lubrication , Hydrostatic circular thrust<br />
bearing , calculation of pressure, load carrying capacity, flow rate , power loss in bearing due to<br />
friction.<br />
Concept of gas lubricated bearing Concept of Elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication, <strong>Design</strong> and selection<br />
of antifriction bearing<br />
Module III<br />
Friction and wear of metals : Theories of friction, surface contaminants, Effect of sliding speed on<br />
friction, classification and mechanism of wear, Wear resistant materials.<br />
Wear and wear types. ; Mechanisms of wear - Adhesive, abrasive, corrosive, erosion, fatigue,<br />
fretting, etc., Wear of metals and non-metals. Wear models - asperity contact, constant and variable<br />
wear rate, geometrical influence in wear models, wear damage. Wear in various mechanical<br />
components, wear controlling techniques.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Introduction to Tribology of Bearings B.C.Majumdar, S.Chand<br />
2. Fundamentals of fluid film lubricant Bernard J.Hamrock, , Mc Graw-Hill Co.,1994<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. Basic Lubrication theory, A. Cameron, John Wiley & sons<br />
2. Lubrication Fundamentals, D.M.Pirro and A.A.Wessol, CRC Press<br />
3. Theory and Practice of Lubrication for Engineers, Fuller, D., New York company 1998<br />
4. Principles and Applications of Tribiology, Moore, Pergamaon press 1998<br />
5. G Bayer, Mechanical wear prediction and prevention,-Marcel Dekkar. Inc. New York<br />
6. P.Sahoo, Industrial Tribology Tata Mc Graw Hill<br />
7. Dr S.P.Srivastava, Lubricants Additives & Tribology, 2008, Tech book international,New Delhi<br />
Module – I<br />
FRACTURE, FATIGUE AND FAILURE ANALYSIS<br />
Fatigue: Types of fatigue loading and failure, endurance limit and S-N diagram; Fatigue under<br />
combine stresses; Notch sensitivity, Fatigue test methods; Various failure relations; Factors<br />
influencing fatigue strength; Influence of stress concentration; Fatigue crack growth initiation and<br />
propagation. Fatigue failures: characteristics of fatigue, unidirectional bending fatigue, torsion fatigue<br />
facture, contact fatigue fracture, thermal fatigue failure.<br />
Module – II<br />
Creep: The evolution of creep damage, primary, secondary and tertiary creep. Micro-mechanisms of<br />
creep in materials and the role of diffusion. Ashby creep deformation maps. Stress dependence of<br />
creep,power law dependence. Comparison of creep performance under different conditions,<br />
extrapolation and the use of Larson-Miller parameters. Creep-fatigue interactions.Creep-stress-time<br />
temperature relations, Mechanics of creep in tension, bending, torsion, creep buckling. Members<br />
subjected to creep and combined stresses<br />
Module – III<br />
Fracture: Basic modes of fracture, Griffith of brittle fracture, Irwin’s theory of fracture in elastic-plastic<br />
materials. Theories of linear elastic fracture mechanics, stress intensity factors, fracture toughness<br />
testing. Mechanisms of crack growth and fracture; Basic modes of fracture; Stress Concentration<br />
factor.
Text Books<br />
1. Strength and Resistance of Metals - J. M. Lessels, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1954.<br />
2. Mechanical Behaviour of Engineering Materials - Joseph Marin, PHI, 1966.<br />
3. Fatigue Testing and Analysis - Y. Lee, J.Pam, R.B. Hathaway & M.E. Barkey Elsevier Press<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Mechanical Metallurgy - G. E. Dieter, Mc-Graw Hill Book Co., 1961<br />
2. Engineering Fracture Mechanics - S. A. Meguid, Elsevier Press, 1989.<br />
3. Introduction to Fracture Mechanics, - K. Hellan, McGraw-Hill.<br />
CONDITION MONITORING 3-1-0<br />
UNIT – I<br />
Introduction : Principles, Economics and Application; Condition Monitoring Methods. Economics of<br />
Condition Monitoring, Setting up a CM Activity, Implementation of Condition Based Maintenance,<br />
Consequences of implementation of CBM. Information System, Selection of Monitoring Methods,<br />
Assessment of monitoring techniques. Case studies.<br />
UNIT – II<br />
Vibration Monitoring and analysis: Introduction, Machinery signatures, Selection of Transducers.<br />
Analysis of techniques, Machine failure modes, Measurement location, Vibration severity criteria,<br />
Vibration frequency analysis. Permanent Monitoring, Case studies.<br />
Vibration Monitoring of ball and roller bearings: Introduction, Shock pulse method, SPM for<br />
testing Antifriction bearings, Manual Monitoring, Continuous monitoring, The Kurtosis method, Fiber<br />
optics system, Vibration signature analysis, Contact resistance method, Case studies. SPM and its<br />
Applications.<br />
UNIT – III<br />
Specialized techniques of condition monitoring:<br />
Acoustic imaging: Ultra sonic triangulation fault location Acoustic emission technique (AET)-<br />
Instrumentation, Transducers, Preamplifier and filter, Main amplifier and Signal processing/ Display<br />
unit, Signals and processing, Magnetic testing Methods, Current flow Magnetisation, Induction<br />
Magnetic Flow Method, Induction Threading bar method, Induction Magnetising Coil method, Induced<br />
Current flow method, Magnetic particle Inspection Inks, Strippable Magnetic film, Eddy Current<br />
apparatus,<br />
Thermography- Thermographic Equipment, Application of Thermography,<br />
Corrosion monitoring: Need for corrosion monitoring, Fields of application, Monitoring Techniques,<br />
Resistance techniques. Other probe techniques-Analytical technique and others.<br />
Performance Trend monitoring: Introduction, Thermodynamic and Fluid dynamic analysis, Primary<br />
and Secondary, performance parameter, Steam turbine performance parameters, Case examples.<br />
UNIT – IV<br />
Mechanical Fault Diagnosis By Wears Monitoring & Lubricant Analysis:<br />
Introduction, Source of Contamination, Significant oil contaminants, Used oil Contamination-time<br />
trends, Changes in the carrier fluid, Ferratic wear debris. Wear process monitoring techniques- Direct<br />
debris detection methods, Debris collection methods. Lubricant sampling & analysis-Sampling,<br />
Lubricant sampling methods, Lubricant analysis methods, Interpretation of results, Indications from
the amount of debris present, Indication from the size distribution of debris, Application of chemical<br />
analysis of debris, Wear detection using proximity monitors, Case examples.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. R.A., Caollacatt Chapman “Mechanical Fault Diagnosis and Condition<br />
Monitoring”, Chapman and hall 1977.<br />
References:<br />
2. L.F.Pau Marcel Deker “Failure Diagnosis and Performance Monitoring”.<br />
3. Update CEP ISTE New Delhi “Condition Monitoring and condition based<br />
maintenance”.<br />
COMPOSITE MATERIAL 3-1-0<br />
Module-I.<br />
Introduction to Composite Materials – Classification and characteristics of composite materials, Metal<br />
Matrix Composites, Ceramic Matrix Composites, Carbon–Carbon Composites, Fiber-Reinforced<br />
Composites and nature-made composites, and applications. Reinforcements: Fibres- Glass, Silica,<br />
Kevlar, carbon, boron, silicon carbide, and born carbide fibres. Particulate composites, Polymer<br />
composites, Thermoplastics, Thermosetting, Metal matrix and ceramic composites.<br />
Module- II<br />
Micromechanical Analysis of a Lamina: Introduction, Definitions: Stress, Strain, Elastic moduli, Strain<br />
Energy. Hooke’s Law for Different Types of Materials, Hooke’s Law for a Two-dimensional<br />
unidirectional lamina, Plane Stress Assumption, Reduction of Hooke’s Law in Three Dimensions to<br />
Two Dimensions, Relationship of Compliance and Stiffness Matrix to Engineering, Elastic Constants<br />
of a Lamina.<br />
Module III<br />
Micromechanical Analysis of Laminates: Introduction, Laminate Code, Stress–Strain Relations for a<br />
Laminate, In-Plane and Flexural Modulus of a Laminate, Hygrothermal Effects in a Laminate,<br />
Warpage of Laminates.<br />
Failure, Analysis, and <strong>Design</strong> of Laminates: Introduction, Special Cases of Laminates, Failure<br />
Criterion for a Laminate, <strong>Design</strong> of a Laminated Composite, Other Mechanical <strong>Design</strong> Issues.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. R. M. Jones, Mechanics of Composite Materials. Taylor & Francis.<br />
2. K.K. Chawla, Composite Materials – Science & Engineering, Springer-Verlag, New York,<br />
1987.<br />
3. B. D. Agarwal and L. J. Broutman, Analysis and performance of fibre Composites,<br />
Wiley- Interscience, New York, 1980.<br />
References:<br />
1. L. R. Calcote, Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures, Van Nostrand Rainfold,<br />
New York, 1969.<br />
2. F.L. Matthews and R.D. Rawlings, Composite Materials: Engineering and Science, Chapman<br />
& Hall, London, 1994.<br />
3. M.W.Hyer, Stress analysis of fibre reinforced composite materials, Tata McGraw Hill.<br />
4. J. N. Reddy, Mechanics of laminated composite plates ,Theory and analysis, CRC Press.
ROBOT & ROBOT APPLICATIONS 3-1-0<br />
UNIT – I<br />
Introduction: Automation and Robotics, CAD/CAM and Robotics – An over view of Robotics –<br />
present and future applications – classification by coordinate system and control system.<br />
Components of the Industrial Robotics: Function line diagram representation of robot arms,<br />
common types of arms. Components, Architecture, number of degrees of freedom. Requirements and<br />
challenges of end effectors, determination of the end effectors, comparison of Electric, Hydraulic and<br />
Pneumatic types of locomotion devices.<br />
UNIT – II<br />
Motion Analysis: Homogeneous transformations as applicable to rotation and translation –<br />
problems.<br />
Manipulator Kinematics: Specifications of matrices, D-H notation joint coordinates and world<br />
coordinates Forward and inverse kinematics – problems. Differential transformation and<br />
manipulators, Jacobians – problems. Dynamics: Lagrange – Euler and Newton – Euler formations –<br />
Problems.<br />
Trajectory planning and avoidance of obstacles, path planning, Skew motion, joint integrated motion –<br />
straight line motion.<br />
UNIT – III<br />
Robot Programming: Robot languages: AL, AML, RAIL, RPL, VAL, Demonstration of points in<br />
space: Continuous path (CP), Via points (VP), Programmed points (PP).<br />
Robot actuators and Feed back components: Actuators: Pneumatic, Hydraulic actuators, electric &<br />
stepper motors. Feedback components: position sensors – potentiometers, revolvers, encoders –<br />
Velocity sensors.<br />
UNIT – IV<br />
Robot Application in <strong>Manufacturing</strong>: Material Transfer - Material handling, loading and unloading-<br />
Processing - spot and continuous arc welding & spray painting - Assembly and Inspection.<br />
TEXT BOOKS :<br />
1. Industrial Robotics / Groover M P /Pearson Edu.<br />
2. Robotics and Control / Mittal R K & Nagrath I J / TMH.<br />
REFERENCES :<br />
1. Robotics / Fu K S/ McGraw Hill.<br />
2. An Introduction to Robot Technology, / P. Coiffet and M. Chaironze / Kogam Page Ltd. 1983<br />
London.
3. Robotic Engineering / Richard D. Klafter, Prentice Hall<br />
4. Robot Analysis and Intelligence / Asada and Slow time / Wiley Inter-Science.<br />
5. Introduction to Robotics / John J Craig / Pearson Edu.<br />
6. Robot Dynamics & Control – Mark W. Spong and M. Vidyasagar / John Wiley & Sons (ASIA) Pte<br />
Ltd.<br />
MECHATRONICS 3-1-0<br />
Module – I (10 hours)<br />
INTRODUCTION : Definition – Trends - Control Methods: Standalone , PC Based<br />
(Real Time Operating Systems, Graphical User Interface , Simulation ) Applications:<br />
SPM,Robot,CNC,FMS,CIM.<br />
SIGNAL CONDITIONING : Introduction – Hardware - Digital I/O , Analog input – ADC , resolution ,<br />
sped channels. Filtering Noise using passive components – Resistors, capacitors - Amplifying signals<br />
using OP amps –<br />
Software - Digital Signal Processing – Low pass , high pass , notch filtering<br />
PRECISION MECHANICAL SYSTEMS : Pneumatic Actuation Systems - Electro-pneumatic Actuation<br />
Systems - Hydraulic Actuation Systems - Electro-hydraulic Actuation Systems - Timing Belts – Ball<br />
Screw and Nut - Linear Motion Guides - Linear Bearings - Harmonic Transmission - Bearings- Motor /<br />
Drive<br />
Selection.<br />
Module – II (10 hours)<br />
ELECTRONIC INTERFACE SUBSYSTEMS : TTL, CMOS interfacing - Sensor interfacing-Actuator<br />
interfacing – solenoids , motors Isoation schemes- opto coupling, buffer IC’s - Protection schemes –<br />
circuit breakers , over current sensing , resetable fuses , thermal dissipation - Power Supply - Bipolar<br />
transistors/ mosfets<br />
ELECTROMECHANICAL DRIVES : Relays and Solenoids - Stepper Motors - DC brushed motors –<br />
DC brushless motors - DC servo motors - 4-quadrant servo drives PWM’s - Pulse Width Modulation –<br />
Variable Frequency Drives, Vector Drives –Drive System load calculation<br />
Module – III (10 hours)<br />
MICROCONTROLLERS OVERVIEW : 8051 Microcontroller , micro processor structure – Digital<br />
Interfacing - Analog Interfacing - Digital to Analog Convertors - Analog to Digital Convertors -<br />
Applications. Programming –Assembly , C ( LED Blinking , Voltage measurement using ADC).<br />
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS : Basic Structure - Programming : Ladder diagram -<br />
Timers, Internal Relays and Counters - Shift Registers - Master and Jump Controls - Data Handling -<br />
Analog input / output - PLC Selection - Application.<br />
Module – IV (10 hours)<br />
PROGRAMMABLE MOTION CONTROLLERS : Introduction - System Transfer Function -<br />
Laplacetransform and its application in analysing differential equation of a control system - Feedback<br />
Devices : Position , Velocity Sensors - Optical Incremental encoders - Proximity Sensors : Inductive ,<br />
Capacitive , Infrared - Continuous and discrete processes - Control System Performance & tuning -<br />
Digital Controllers- P , PI , PID Control - Control modes – Position , Velocity and Torque - Velocity<br />
Profiles – Trapezoidal- S. Curve - Electronic Gearing - Controlled Velocity Profile - Multi axis<br />
Interpolation , PTP , Linear ,Circular - Core functionalities – Home, Record position , Go to Position -
Applications : SPM, Robotics.<br />
TEXT BOOKS :<br />
1. Mechatronics Electronics Control Systems in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering by W Bolton,<br />
Pearson Education Press, 3rd edition, 2005.<br />
2. Mechatronics/M.D.Singh/J.G.Joshi/PHI.<br />
REFERENCES :<br />
1. Mechatronics Source Book by Newton C Braga, Thomson Publications, Chennai.<br />
2. Mechatronics – N. Shanmugam / Anuradha Agencies Publisers.<br />
3. Mechatronics System <strong>Design</strong> / Devdas shetty/Richard/Thomson.<br />
COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING 3-1-0<br />
Module I (12 hours)<br />
Fundamentals of <strong>Manufacturing</strong> and Automation: Production systems, automation principles and its<br />
strategies; <strong>Manufacturing</strong> industries; Types of production function in manufacturing; Automation<br />
principles and strategies, elements of automated system, automation functions and level of<br />
automation; product/production relationship, Production concept and mathematical models for<br />
production rate, capacity, utilization and availability; Cost-benefit analysis.<br />
Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong>: Basics of product design, CAD/CAM, Concurrent<br />
engineering, CAPP and CIM.<br />
Module II (12 hours)<br />
Industrial Robotics: Robot anatomy, control systems, end effectors, sensors and actuators;<br />
fundamentals of NC technology, CNC, DNC, NC part programming; Robotic programming, Robotic<br />
languages, work cell control, Robot cleft design, types of robot application, Processing operations,<br />
Programmable Logic controllers: Parts of PLC, Operation and application of PLC, Fundamentals of<br />
Net workings; Material Handling and automated storage and retrieval systems, automatic data<br />
capture, identification methods, bar code and other technologies.<br />
Module III (12 hours)<br />
Introduction to manufacturing systems: Group Technology and cellular manufacturing,Part families,<br />
Part classification and coding, Production flow analysis, Machine cell design, Applications and<br />
Benefits of Group Technology.Flexible <strong>Manufacturing</strong> system: Basics of FMS, components of FMS,<br />
FMS planning andimplementation, flexibility, quantitative analysis of flexibility, application and benefits<br />
of FMS. Computer Aided Quality Control: objectives of CAQC, QC and CIM, CMM and Flexible<br />
Inspection systems.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Automation, Production Systems and Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong>: M.P. Groover, Pearson<br />
Publication.<br />
2. Automation, Production systems & Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong>, M.P Groover, PHI.<br />
3. CAD/CAM/CIM, P.Radhakrishnan, S.Subramanyam and V.Raju, New Age International<br />
4. Flexible <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Systems in Practice, J Talavage and R.G. Hannam, Marcell Decker<br />
Reference Books:
1. CAD/CAM Theory and Practice, Zeid and Subramanian, TMH Publication<br />
2. CAD/CAM Theory and Concepts, K. Sareen and C. Grewal, S Chand publication<br />
3. Computer Aided <strong>Design</strong> and <strong>Manufacturing</strong>, L. Narayan, M. Rao and S. Sarkar, PHI.<br />
4. Principles of Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong>, S.K.Vajpayee, PHI<br />
5. Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong>, J.A.Rehg and H.W.Kraebber, Prentice Hall<br />
LASER APPLICATIONS IN MANUFACTURING 3-1-0<br />
Module – I (10 hours)<br />
Laser Fundamentals: spontaneous & stimulated emission/absorbtion, population inversion &<br />
pumping, cavity design , coherence and interference. Common industrial lasers and their output<br />
characteristics: CO2, Ruby, Nd-YAG, Nd-glass, excimer & He-Ne.<br />
Overview of laser Applications: Laser application in various fields, advantages & disadvantages,<br />
economics.<br />
Module – II (10 hours)<br />
Laser processing fundamentals: beam characteristics, optical components and design of beam<br />
delivery systems, absorption characteristics of materials, heat flow theory and metallurgical<br />
considerations. Cutting and drilling: Process characteristics, material removal modes, development of<br />
theoretical models and practical performance.<br />
Module – III (12 hours)<br />
Welding: Process mechanisms like keyhole & plasma, development of theoretical models, operating<br />
characteristics and process variation. Surface modification: heat treatment, rapid solidification,<br />
alloying and cladding, surface texturing, development of theoretical models, LCVD, LPVD.<br />
Module – IV (8 hours)<br />
Introduction to interferometry: working principles of Michelson interferometer and Fabry-Perot<br />
interferometer and elementary holography. Special topics: detection and measurement of radiation,<br />
laser safety.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Steen W.M. ; Watkins. K. Laser Material Processing 3 rd Edition, Springer London, 2003<br />
2. Cartisan. C. L. Laser cutting Guide for <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Society of <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Engineers,<br />
USA.
MANUFACTURING SCIENCE LAB-1<br />
1. Exercise in computer aided drafting and design, mesh generation, modeling, use of packages<br />
2. Assembly drawings using drafting package.<br />
3. Surface flatness measurement using slip gauges.<br />
4. Experiments on CAM using CNC Miller.<br />
5. Experiments on CAM using CNC Lathe.<br />
6. Study of various machine tools their operational details and attachments.<br />
7. Study of Moulds with single pattern and split pattern.<br />
8. Experiment on surface grinding with measurement of surface roughness.
SECOND SEMESTER<br />
MTDM 1201 Theory of Elasticity 3-1-0<br />
Module I<br />
Revision of two-dimensional elasticity – introduction to three dimensional elasticity-equations of<br />
equilibrium and Generalized Hooke’s law, constitutive relations. Kinematic relations, compatibility<br />
equations – equations of equilibrium in terms of strains and displacements, compatibility equations in<br />
terms of stresses – in Cartesian and cylindrical co-ordinates. Airy’s stress function.<br />
Module II<br />
Variational techniques, principle of minimum potential energy-Euler equations-derivation of governing<br />
equation and natural boundary conditions for a beam. Solution of axisymmetric problems, Bending of<br />
beams and axi-symmetric plates, Kirkhhof and Mindlin concept. Solid circular plates with different load<br />
and support conditions.<br />
Module III<br />
Theoretical concepts of plasticity of structural metals under tension, compression and combined<br />
stress, Yield criteria - Tresca and Von Mises criterion of yielding, Plastic stress strain relationship,<br />
Elastic plastic problems in bending and torsion. Theory of plastic constitutive equations; Axisymmetric<br />
and spherically symmetric problems;<br />
Text Books<br />
1. Timoshenko, S. and Goodier J.N. Theory of Elasticity, McGraw Hill Book Co., Newyork, 1988.<br />
2. J. Chakrabarty, Theory of Plasticity, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York 1990<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Hoffman and Sachs, Theory of Plasticity - McGraw Hill., 2nd ed. 1985<br />
2. Kachanov L.M. – Foundations of Theory of plasticity<br />
3. E.P. Popov, Engineering Mechanics of Solids, 2nd Ed., Prentice Hall India, 1998.<br />
4. Irving H.Shames and James,M.Pitarresi, Introduction to Solid Mechanics,Prentice Hall of<br />
India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi -2002.<br />
5. Johnson and Mellor, Engineering Plasticity- Van-Nostrand., 1st edition, 1983<br />
Unit I (12 hours)<br />
MTDM 1202 THEORY OF METAL CUTTING 3-1-0<br />
Machining Process: Introduction, Different type of machining processes,Machining with single edge<br />
cutting tools, Tool nomenclature: tool axis reference system, machine reference system. Geometry of<br />
cutting tools in ASA,ORS& Normal working system. Conversion of tool angles, selection of tool<br />
angles. Effect of Geometrical parameters on cutting force and surface finish. Introduction to multi<br />
point cutting tools.<br />
Unit II (12 hours)<br />
Review of deformation mechanism, an overview of chip formation, classification of chips: irregular<br />
shaped chips, continuous chips with no built up edge, continuous chips with built up edge, element<br />
chips & partially continues chips.<br />
Measurement of cutting forces: Measurement of forces, Electrical transducers for force measurement.<br />
Dynamometers for measuring forces during turning process, drilling process and milling process.<br />
Theoretical determination of cutting forces: Analytical approach, Merchant’s circle method.
Unit III (12 hours)<br />
Cutting temperature – causes, effects, assessment and control of cutting temperature and cutting fluid<br />
application.<br />
Tool wear and tool life: Introduction, tool wear, types of tool wear: flank wear, crater wear. Progressive<br />
tool wear. Tool life, variables affecting tool life, determination of tool life equations.<br />
Economics of machining: Introduction, machining cost, optimum cutting speed. Restriction on cutting<br />
conditions, comparison of the three criteria.<br />
Unit IV (4 hours)<br />
Grinding of metals: Introduction, the grinding wheel, mechanics of grinding process, grinding forces<br />
and specific energy, wheel wear and grinding performances, grinding temperature, surface<br />
roughness.<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Fundamentals of Machining and Machine Tools, G.Boothroyd and W.A.Knight,<br />
CRC Press<br />
2. Metal Cutting Principles, M.C.Shaw, Oxford <strong>University</strong> Press<br />
3. Metal Cutting Theory and Practice, A.Bhattacharya, Central Book Publishers<br />
4. Principles of Metal Cutting, G.Kuppuswamy, Universities Press<br />
5. Metal Cutting and Machne Tools, G.T.Reddy, Scitech<br />
MTDM 1203<br />
INSTRUMENTATION & EXPERMENTAL STRESS ANALYSIS<br />
Module-I<br />
Basic elasticity theory, Stress analysis by strain measurement: Principal stresses and strains. Basic<br />
Characteristics of a Strain Gauge, Types of Shell Gauge; Mohr’s circle-measurement of strains-Strain<br />
gauges- Electric Resistance strain gauges, semiconductor strain gauges, Grid Method of Strain<br />
Analysis, Factors Influencing Strain sensitivity in Metallic Alloys, Gauge Construction Temperature<br />
Compensation, Factors-Influencing Gauge Section Gauge Sensitivity and Gauge Factor, Correction<br />
for transverse Strain Effects, strain gauge circuits, transducer applications, recording instruments for<br />
static and dynamic applications<br />
Module-II<br />
Photo elasticity: Photo elasticity – Polariscope – Plane and circularly polarized light, Bright and dark<br />
field setups, Photo elastic materials – Isochromatic fringes – Isoclinics. Three dimensional Photo<br />
elasticity: Introduction, locking in model deformation, materials for three-dimensional photo elasticity,<br />
machining cementing and slicing three-dimensional models, slicing the model and interpretation of the<br />
resulting fringe patterns, effective stresses, the shear difference method in three dimensions,<br />
applications of the Frozen-stress method, the scattered light method.<br />
Module-III<br />
Gauges. Rosette Analysis - three element rectangular Rosette, the three and Four Element Delta<br />
Rosette, The Stress Gauge, Strain Circuits, Potentiometer Circuits, The Wheatstone Bridge. Brittle<br />
Coating Method: Coating Stresses, Failure Theories. Brittle Coating Crack Patterns Produced by
Direct Loading, refrigeration Techniques and Releasing the Load. Double Crack Pattern, Crack<br />
Detection, Load-Time Relation and Its influence on the threshold Strain Effects of a Biaxial stress<br />
Field.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. J.W. Dally and W.F. Riley, Experimental Stress Analysis, 2nd Ed. MGH.<br />
2. Mubin Khanna, Experimental Stress Analysis, 2003.<br />
Reference Books:<br />
1. R. C. Dove and P. H. Adams Experimental Stress Analysis and Motion Measurement PHI, 1965.<br />
2. A. J. Durelli Applied Stress Analysis PHI, 1970.<br />
3. Srinath et.al. An Introduction to Experimental Stress Analysis - MGH<br />
Mechanical Vibration 3-1-0<br />
Module I<br />
Review of vibration fundamentals for SDOF systems. Model study through single degree of freedom<br />
analysis:Un-damped free Vibration : Equilibrium method, Energy method, Raylegh’s method, Stiffness<br />
of spring elements. Damped Vibrations : Viscous damping, Laws of damping, Logarithmic decrement.<br />
Forced vibrations ;coulomb damping; Response to harmonic excitation; Steady state solution with<br />
viscous damping, method of complex algebra rotating unbalance and support excitation ;Vibration<br />
isolation and transmissibility. Energy dissipated by damping. Equivalent viscous damping, structural<br />
damping, sharpness of resonance.<br />
Module II<br />
Two degrees and Multidegree of freedom systems with applications: Two degree of freedom systems<br />
: Generalized Derivation of Equation of motion, Normal mode vibration, coordinate coupling,<br />
Langrange’s equations, Dynamic Vibration absorber. Multi-degree of freedom system : Derivation of<br />
Equations, influence co-efficients, modal analysis, orthogonality of normal modes. Torsional Vibration<br />
multi-rotor systems and branched system.<br />
Module III<br />
Vibration of continuous system. Vibration of strings, membranes, rods and beams with different end<br />
conditions Euler-Bernoulli equation for beams.<br />
Vibration Measuring Instruments: Vibrometers, velocity meters & accelerometers, Vibration testing<br />
equipments. Critical speeds without and with damping.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Theory of Vibration with Applications, W. T. Thomson, CBS Publ., 1990.<br />
2. Mechanical Vibration analysis, P. Srinivasan, TMH.1995<br />
Reference Books<br />
1. Elements of Vibration Analysis, L. Meirovitch, TMH, Second edition, 2007<br />
2. Mechanical Vibration, S.S.Rao, Pearson, 2004<br />
3. Theory and Problems of Mechanical Vibrations, Willam W.Seto, TMH<br />
4. Introductory course on Theory and Practice of Mechanical Vibrations, J.S. Rao & K.Gupta, New<br />
Age Pub
FINITE ELEMENT METHODS IN ENGINEERING 3-1-0<br />
Module – I (10 hours)<br />
Fundamental Concepts: Introduction, Historical background, Outline of presentation, Stresses and<br />
Equilibrium, Boundary conditions, Strain-Displacement relations, Stress-Strain relations, Plane stress,<br />
Plane strain problems, Temperature effects, Potential energy and equilibrium. The Rayleigh-Ritz<br />
method, Hamilton's principle. Galerkin's method, Saint Venant's principle.<br />
Module – II (10 hours)<br />
One-dimensional Problems: Introduction, Finite element modeling, Coordinates and Shape<br />
functions. The potential energy approach. The Galerkin approach, Assembly of the global stiffness<br />
matrix- mass matrix and load vector, Treatment of boundary conditions, Quadratic shape functions,<br />
Temperature effects. Trusses: Introduction, Plane trusses, Three-dimensional trusses, Assembly of<br />
global stiffness matrix for the Banded and Skyline solutions.<br />
Module – III (10 hours)<br />
Two-dimensional Problems Using Constant Strain Triangles: Introduction, Finite element modeling,<br />
Constant strain triangle, In plane and Bending, problem modeling and boundary conditions.<br />
Axisymmetric Solids Subjected to Axisymmetric Loading: Introduction, Axisymmetric formulation,<br />
Finite element modeling, Triangular element, Problem modeling and boundary conditions.<br />
Module – IV (10 hours)<br />
Two-dimensional Isoparametric Elements and Numerical Integration: Introduction, The four-node<br />
quadrilateral, Numerical integration, Higher-order elements. Beams and Frames: Introduction, Finite<br />
element formulation, Load vector, Boundary considerations, Shear force and bending moment,<br />
Beams on elastic supports, Plane frames.<br />
Text Book:<br />
1. Introduction to Finite Elements in Engineering, by Tirupathi R. Chandrupatla, Ashok D.Belegundu<br />
(chapters 1 to 8 only).<br />
References:<br />
1. Introduction to Finite Element Method, by S.S.Rao<br />
2. Finite Element Method, by O.C. Zienkiewicz.<br />
3. Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis, by Robert D. Cook.<br />
4. Introduction to Finite Element Method, by J.N.Reddy.<br />
ENGINEERING DESIGN METHODOLOGY 3-1-0<br />
Module-I<br />
Fundamentals: principles of design, systematic approach, need analysis and design of specification;<br />
Conceptual design: developing function structure, developing concepts by systematic search with<br />
physical principles, classifying schemes; experimental and design criteria. <strong>Design</strong> methodologies:<br />
axiomatic design methodology, design for manufacturing, design for assembly.<br />
Module-II<br />
Concept selection: matrix methods, necessity methods, probability methods, fuzzy set based<br />
methods, case study on consumer product; Embodiment design: basic rules, system modeling,<br />
preliminary design calculations and material selection, design considerations like force alignment,
vibration etc., failure modes and effects analysis, design for manufacturability and assembly, case<br />
studies on design of machines;<br />
Module-III<br />
Optimal and robust design: Algorithms for constructing optimal design, design problem formulation<br />
for analytical and numerical solution, design of experiments, Taguchi’s method; Physical prototyping,<br />
reverse engineering, product teardown and redesign, embodiment design, CAE analysis, prototyping,<br />
design project.<br />
Text Book<br />
3. Yousef Haik, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> Process, Vikas Publishing house, New Delhi, 2003.<br />
4. G. Pahl, and W. Beitz, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – A Systematic Approach, Springer – Verlag, 1996.<br />
References<br />
7. K. Otto and K. wood, Product <strong>Design</strong> – techniques in reverse engineering and new product<br />
development, Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2004.<br />
8. A. Ertas and J. C. Jones, The Engineering <strong>Design</strong> Process, 2nd ed., John Wiley and Sons, 1996.<br />
9. A. Kusiak, Engineering <strong>Design</strong> – Products, Processes and Systems, Academic Press, 1999.<br />
10. Beno Benhabib, <strong>Manufacturing</strong>: <strong>Design</strong>, Production, Automation and Integration, Marcel Dekker,<br />
INC.<br />
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS 3-1-0<br />
MODULE-I Introduction: Basic tools of CFD, Numerical Vs experimental tools. ; Mathematical<br />
Behavior of PDEs: Parabolic, Hyperbolic and Elliptic PDEs.Methodology of CFDHT: Discrete<br />
representation of flow and heat transfer domain: Grid generation,Solution of 1-D/2-D steady/unsteady:<br />
Diffusion problems, Solution of Navier-Stokes Equations for Incompressible Flows; Special Topics in<br />
CFDHT: Numerical Methodology for Complex Geometry, Multi-block structured grid system, Solution<br />
of phase change Problems.<br />
MODULE-II Finite difference schemes: backward,central and forward schemes.stability analysis,<br />
Finite volume method for incompressible flows , Vertex centered and cell centered FVM , Treatment<br />
of convection term – Upwind, hybrid, upwind least square reconstruction and QUICK schemes<br />
,staggered and collocated grids, solution algorithms for both types ,<br />
MODULE-III Evaluation of velocity field – SIMPLE, SIMPLER, and projection methods – Time<br />
dependent problems – Implicit, Crank-Nicolson and Explicit schemes –Finite volume method for<br />
compressible flows-Treatment of convection terms – Flux vector splitting method – Artificial diffusion –<br />
Structured and unstructured grids – Solution of system of equations – Tridiagonal matrix algorithm –<br />
Line by line solver.<br />
TEXT BOOKS<br />
1. S.V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Taylor and Francis, ISBN-10:<br />
0891165223.<br />
2. H. K. Versteeg and W. Malalasekra, Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite<br />
Volume Method, Prentice Hall (2nd Edition), ISBN-10: 0131274988.<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS<br />
1. Jr. D. A. Anderson, Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer by McGraw-Hill<br />
Education<br />
2. M. N. Ozisik, Finite Difference Method, CRC (1st Edition).<br />
3. Computational fluid dynamics, T. J.Chung, Cambridge<br />
<strong>University</strong> press,2002.<br />
4. C A J Fletcher : Computational Techniques for Fluid Dynamics – Vol 1 & 2, Springer Verlag,<br />
1988
FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS 3-1-0<br />
Module I (12 hours)<br />
Introduction: Types of production, characteristics, applications, Flexibility in Machining systems, need<br />
for FMS, Flexible Automation, where to apply FMS technology.<br />
Flexible <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Cell: Characterstics, Flexible Machining systems, achieving flexibility in<br />
machining systems, Machine cell design, quantitative techniques.<br />
Group Technology(GT) –Part classification and coding systems: Part families, Parts classification and<br />
coding, Optiz system, structure, MULTICODE, differences between Optiz and MULTICODE systems,<br />
relative benefits.GT- production flow analysis: Composite part concept, numerical problems for parts<br />
clustering, advantages of GT in manufacturing and design.<br />
Module II (12 hours)<br />
Components of FMS: FMS layout configurations, Planning the FMS, FMS’s Work- stations, Material<br />
Handling systems, Automatic Guided vehicle systems, Automated storage and retrieval systems, and<br />
Computer control systems.<br />
Implementing FMS: FMS Layout configurations, Quantitative Analysis methods for FMS , Applications<br />
and benefits of FMS, problems in implementing FMS.<br />
Computer Aided Process planning: Importance, generative and retrieval systems, advantages and<br />
disadvantages, Generation of route sheets, selection of optimal machining parameters, methods.<br />
Module III (12 hours)<br />
Computer aided quality control and testing: Coordinate measuring machines, over view, contact and<br />
non contact inspection principles, Part programming coordinate measuring machines, In-cycle<br />
gauging.<br />
NETWORKING FOR MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS: Hierarchy of computers in manufacturing,<br />
benefits of hierarchical structure, types of networks, characteristics, methods of communication, local<br />
area networks, network topologies, access methods and <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Automation Protocol (MAP).<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. Automation, Production systems and Computer Integrated <strong>Manufacturing</strong> System – Mikell P.<br />
Groover<br />
2. The design and operation of FMS –Dr. Paul Ranky Nort –Holland Publishers<br />
References:<br />
1. Flexible <strong>Manufacturing</strong> systems in practice by Joseph Talvage and Roger G. Hannam, Marcel<br />
Dekker Inc., NewYork<br />
2. Hand book of FMS – Nand Jha .K.<br />
3. FMS and Control of Machine Tools - V. Ratmirov, MIR publications<br />
4. Flexible <strong>Manufacturing</strong> – David J. Parrish
TOOL DESIGN 3-1-0<br />
Module I (10 hours)<br />
Basic Features and Kinematics of Machine Tools: Features of basic machine tools construction<br />
and operation, types of machine tools, machine tools motions, transmission-rotation in to rotation,<br />
rotation in to translation, kinematic-structures of machine tools: elementary, complex and compound<br />
structure, kinematic-features of gear shapers and gear hobbing machine.<br />
Module II (10 hours)<br />
Regulation of Speed: <strong>Design</strong> of gear boxes- need for variation of speed, selection of speed range,<br />
laws of stepped regulation, standardization of speeds, speed diagram, analysis of productivity loss,<br />
kinematic advantage of GP, structural diagrams, ray diagram and speed chart. Gear Drives: Belt and<br />
cone pulley, slip gear type, north gear drive, draw key gear drive, clutch type, mechanical step less<br />
drives, electrical drives; hydraulic drive.<br />
Module III (10 hours)<br />
<strong>Design</strong> of Metal working Tools: <strong>Design</strong> of press working tools, shearing, piercing, blanking, dies,<br />
compound die design principles for forging dies, bending, forming drawing dies, tooling for forgingdesign<br />
principles for forging dies, drop forging, upset forging, design principles and practice for rolling,<br />
roll press design.<br />
Module IV (10 hours)<br />
<strong>Design</strong> of Jigs and Fixtures: Principles of location, locating method and devices, principles of<br />
clamping, clamping devices, drilling jigs, types, drill bushes, fixture and economics, types of fixture,<br />
milling, grinding, broaching, assembly fixtures indexing jig and fixtures, indexing devices.<br />
<strong>Design</strong> of Gauges and Inspection Features: <strong>Design</strong> of gauges for tolerance for dimensions and<br />
form inspection; dies and mould design for Ppastics & rubber parts: compression molding, transfer<br />
molding, blow molding.<br />
Tool Engineering and Machine Tools References:<br />
1. Mehta N.K.; Machine Tool <strong>Design</strong> and Numerical Control; TMH<br />
2. Sen G.C, Bhattacharya A; Principles of Machine Tools; New Central Book Agency.<br />
3. Donaldson; Tool <strong>Design</strong> T.M.H.<br />
4. Jain KC and Chitale AK; Text Book Of Production Engineering; PHI Learning<br />
5. Juneja, Sekhon and Seth; Fundamentals of Metal Cutting and Machine Tools; New Age.<br />
6. Krar SF, Gill AR, Smid P; Technology of Machine Tools;TMH<br />
7. Sharma P.C; Production Engineering; Chand S<br />
8. Wilson; Fundamentals of Tool <strong>Design</strong>; ASTME<br />
9. Paqwin J.R; Die <strong>Design</strong> Handbook; The Industrial Press-NY<br />
10. ASTME; Die <strong>Design</strong> Hand Book; McGraw Hill<br />
11. Archinov; Metal Cutting & Cutting Tool <strong>Design</strong>; MIR
OPTIMIZATION METHODS FOR ENGINEERING SYSTEMS<br />
Module I (12 hours)<br />
Introduction: Engineering Applications; Statement of the Optimal Problem: Classification;<br />
Optimization Techniques. Classical Methods: Single Variable Optimization; Multivariable Optimization<br />
without any Constraints with Equality and Inequality Constraints.<br />
Module II (12 hours)<br />
One-Dimensional Minimization Methods: Uni-model Function; Elimination Methods – Dichotomous<br />
Search, Fibonacce and Golden Section Methods; Interpolation Methods – Quadratic and Cubic<br />
Interpolation Methods. Unconstrained Minimization Methods: Univariate, Conjugate Directions,<br />
Gradient and Variable Metric Methods.<br />
Module III (12 hours)<br />
Constrained Minimization Methods: Characteristics of a constrained problem; Direct Methods of<br />
feasible directions; Indirect Methods of interior and exterior penalty functions.<br />
Geometric Programming : Formulation and Solutions of Unconstrained and Constrained geometric<br />
programming problems.<br />
Module IV (12 hours)<br />
Dynamic Programming: Concept of Sub-optimization and the principle of optimality; Calculus, Tabular<br />
and Computational Methods in Dynamic Programming; An Introduction to Continuous Dynamic<br />
Programming.Integer Programming : Gomory’s Cutting Plane Method for Integer Linear<br />
Programming; Formulation & Solution of Integer Polynomial and Non-linear problems.<br />
Text Books :<br />
1. Optimization ( Theory & Applications ) – S.S. Rao, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
2. Optimization Concepts and Applications in Engineering – Ashok D.Belegundu and Tirupathi R<br />
Chandrupatla — Pearson Education.<br />
Reference Books :<br />
1. Optimization: Theory and Practice, C.S.G. Beveridge and R.S. Schechter, MGH, New York.<br />
MODELING OF WELDING PHENOMENA 3-1-0<br />
Module I (12 hours)<br />
Introduction, computer simulation of welding processes, models for welding heat sources, Gaussian<br />
surface flux distribution, hemi-spherical power density distribution, ellipsoidal power density<br />
distribution, double ellipsoidal power density distribution, , kinematic models for welding heat transfer,<br />
evaluation of double ellipsoidal model,<br />
Module II (12 hours)<br />
Modeling thermal stresses and distortions in welds, thermal analysis of welds, heat transfer theory,<br />
weld heat source, data to characterize a weld heat source, power input, prescribed temperature<br />
model, starting transient, and boundary conditions, FEM solutions with prescribed temperature
Module III (12 hours)<br />
Evolution of microstructure depending on temperature, evolution of microstructure depending on<br />
deformations, carburized and hydrogen diffusion analysis, welded structures and applications of<br />
welding in industrial fields, analysis of welded structure, real time for CWM, current performance for<br />
CWM, implications of real time CWM, fracture mechanics, input data for computational welding<br />
mechanics, computer simulation of welding technique,<br />
Module IV (12 hours)<br />
Process modeling, simulation and optimization techniques. Application of artificial inteligence<br />
techniques for welding process modeling, simulation and optimisation: Neural networks, genetic<br />
algorithm & fuzzy logic.<br />
Text Books:<br />
1. S. V. Nadkarni, Text Book: Analysis of welded structure, 1988, Oxford & IBH Publishing<br />
company Pvt. Ltd.<br />
2. K.Masubhchi, Analysis of welded structure, 1980, Pergamon Press Oxford<br />
<strong>Design</strong> and Analysis lab<br />
1. Study of the chip formation in turning process<br />
2. Study of operation of tool and cutter grinder, twist drill grinder, centreless grinder<br />
3. Determination of cutting forces in turning;<br />
4. Determination of cutting forces in Milling<br />
5. Inspection of parts using CMM<br />
6. Experiments and demonstration of EDM<br />
7. Experiments on surface technology.<br />
8. Operation of FMS
THIRD SEMESTER<br />
MTDM 2101 ADVANCED MECHANICS OF SOLIDS 3-1-0<br />
MODULE I<br />
Analysis of Stresses and Strains in rectangular and polar coordinates. 3D Equilibrium equations:<br />
Cauchy’s formula, Principal stresses and principal strains, 3D Mohr’s Circle of stresses and strains.<br />
Ellipse of stress and strain, Octahedral Stresses State of pure shear, Plane stress and plane strain,<br />
compatibility conditions. Introduction to curvilinear coordinates. Generalized Hooke’s law and theories<br />
of failure.<br />
MODULE II<br />
Energy methods: Work done by forces and elastic strain energy stored. Reciprocal relations, Theorem<br />
of virtual work, Castigliano’s theorems. Bending of symmetric and un-symmetric straight beams.<br />
Curved effect of shear stresses, Shear center and shear flow, Shear centre in thin walled section with<br />
symmetric and un-symmetric thin walled beams, shear in closed thin walled sections. Bending of<br />
curved beams, curved beam theory, Winkler Bach formula for circumferential stress, radial stress in<br />
curved beams. Stress distribution in beam with rectangular, circular and trapezoidal cross section,<br />
stresses in crane hooks, ring and chain links.<br />
MODULE III<br />
Torsion of prismatic bars- Saint Venant’s semi inverse and Prandtl’s stress function approach, Torsion<br />
of Straight bars: Circular, Elliptic and Equilateral triangular cross section – Torsion of narrow<br />
rectangular section. Thick walled cylinder subjected to internal and external pressures, Compound<br />
cylinders, Shrink fit, Lame’s theory, Rotating disks and cylinders, Thick spherical shells.<br />
Text book:<br />
1. L. S. Srinath, Advanced Mechanics of Solids, 2 nd Edition, TMH Publishing Co. Ltd., New<br />
Delhi, 2003.<br />
2. Theory of elasticity by Timoschenko S.P. and Goodier J.N. McGraw-Hill Publishers 3 rd Edition<br />
3. Strength of Materials by S.S.Rattan, Tata Mc Graw Hill<br />
Reference book:<br />
1. Advanced Mechanics of Materials : Siley and Smith<br />
2. Strength of Materials Vol.II, by S.Timoshenko<br />
3. Strength of Materials by G. H. Ryder, Macmillan Press<br />
4. Mechanics of Materials by Beer and Johnston, Tata McGraw Hill<br />
5. Mechanics of Materials by R.C.Hibbeler, Pearson Education<br />
6. Mechanics of Materials by James M. Gere, Thomson Learning<br />
7. Advanced Mechanics of Materials, Boresi.A.P., Schimidt. R.J. John Wiley<br />
8. Strength of materials & Theory of structures (Vol I & II) by B.C Punmia<br />
9. Strength of materials by Sadhu singh
MTDM 2102 Modern <strong>Manufacturing</strong> Processes 3-1-0<br />
UNIT – I<br />
INTRODUCTION – Need for non-traditional machining methods-Classification of modern machining<br />
processes – considerations in process selection. Materials. Applications.<br />
Abrasive jet machining: Process, Basic principles, equipments, process variables, mechanics of metal<br />
removal, MRR, application and limitations.<br />
Water jet Machining: Process, operating principle, mechanism of jet cutting, process parameters,<br />
Machining characteristics, effects of exit pressure, effect of feed rate.<br />
UNIT II<br />
THERMAL METAL REMOVAL PROCESSES : General Principle and applications of Electric<br />
Discharge Machining: The process, operating principles: Theories of material removal concepts.<br />
Dielectric fluid: break down mechanism. Electrode material: metallic electrodes, non-metallic<br />
electrodes, combined metallic and non-metallic electrode, electroformed electrode. Equipment: Power<br />
generator, waveforms in EDM process, Hybrid generator, control system. Requirements of modern<br />
EDM.<br />
Wire cut electro discharge machine (WEDM):<br />
Process parameters and their effects: operating parameters, evaluation. Gap Flushing: practical<br />
flushing techniques, pressure or injection flushing, vacuum or suction flushing, side flushing,<br />
reciprocating electrode flushing.<br />
Unit III<br />
Electron Beam Machining: Introduction, process technology, gun construction, current control, control<br />
of spot diameter, control of focal distance of magnetic lens. Current pulsing. Applications<br />
Laser Beam Machining: Process, lasing process, lasing materials, processing with lasers, machining<br />
applications of laser.<br />
Plasma Arc Cutting: Process, principles of plasma arc, plasma arc torches, parameters affecting<br />
cutting, advantages of plasma arc cutting.<br />
Unit IV<br />
Ultrasonic Machining: process, working principle, selection of process, material removal rate, horn<br />
design, acoustic head clamping, applications & limitations.<br />
Chemical Machining: process, principle of operation, equipment & applications.<br />
Electro Chemical Machining: process, principles of operation, the equipment, power supply and<br />
control, analysis of material removal, dynamics of ECM process. Hydrodynamics of ECM process, tool<br />
design and applications.<br />
TEXT BOOK :<br />
1. Advanced machining processes/ VK Jain/ Allied publishers.<br />
2. Non-conventional machining/P.K.Mishra/Narosa Publishing house<br />
3. Modern Machining Process / Pandey P.C. and Shah H.S./ TMH.<br />
4. New Technology / Bhattacharya A/ The Institution of Engineers, India 1984.