CS 598: Spectral Graph Theory: Lecture 3 - Corelab
CS 598: Spectral Graph Theory: Lecture 3 - Corelab
CS 598: Spectral Graph Theory: Lecture 3 - Corelab
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
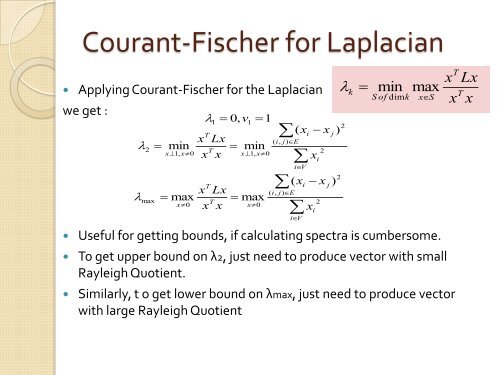
Courant-Fischer for Laplacian<br />
• Applying Courant-Fischer for the Laplacian<br />
we get :<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
max<br />
min<br />
x1,<br />
x0<br />
<br />
1<br />
0,<br />
v 1<br />
1<br />
T<br />
x Lx<br />
<br />
T<br />
x x<br />
min<br />
x1,<br />
x0<br />
T<br />
x Lx<br />
max max<br />
x0<br />
T<br />
x x x0<br />
S of dim k<br />
• Useful for getting bounds, if calculating spectra is cumbersome.<br />
• To get upper bound on λ2, just need to produce vector with small<br />
Rayleigh Quotient.<br />
• Similarly, t o get lower bound on λmax, just need to produce vector<br />
with large Rayleigh Quotient<br />
<br />
( i,<br />
j)<br />
E<br />
<br />
( i,<br />
j)<br />
E<br />
( x<br />
<br />
iV<br />
( x<br />
<br />
iV<br />
i<br />
i<br />
x<br />
x<br />
2<br />
i<br />
x<br />
x<br />
2<br />
i<br />
j<br />
j<br />
)<br />
)<br />
<br />
2<br />
2<br />
k<br />
<br />
min<br />
max<br />
xS<br />
T<br />
x Lx<br />
T<br />
x x