12. Case Study: Using EES in Electronics Cooling
12. Case Study: Using EES in Electronics Cooling
12. Case Study: Using EES in Electronics Cooling
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
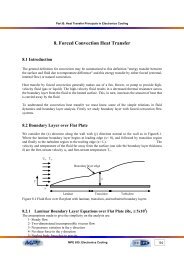
Part B: Heat Transfer Pr<strong>in</strong>cipals <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>12.</strong> <strong>Case</strong> <strong>Study</strong>: <strong>Us<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>EES</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
What is <strong>EES</strong>?<br />
<strong>EES</strong> (pronounced 'ease') stands for Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Equation Solver. The basic function provided by <strong>EES</strong><br />
is the solution of a set of algebraic equations. <strong>EES</strong> can solve differential equations, equations with<br />
complex variables, do optimization, provide l<strong>in</strong>ear and non-l<strong>in</strong>ear regression and generate plots.<br />
There are two major differences between <strong>EES</strong> and exist<strong>in</strong>g numerical equation-solv<strong>in</strong>g programs.<br />
First, <strong>EES</strong> automatically identifies and groups equations that must be solved simultaneously. This<br />
feature simplifies the process the user and ensures that the solver will always operate at optimum<br />
efficiency.<br />
Second. <strong>EES</strong> provides many built-<strong>in</strong> mathematical and thermophysical property functions useful for<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g calculations. So that we can use <strong>EES</strong> for solv<strong>in</strong>g many electronics cool<strong>in</strong>g problems<br />
<strong>EES</strong> Features List<br />
• Flexible for any eng<strong>in</strong>eer to use it<br />
• Solves up to 6000 simultaneous non-l<strong>in</strong>ear equations<br />
• Extremely fast computational speed<br />
• SI and English units<br />
• Parametric studies with spreadsheet-like table<br />
• S<strong>in</strong>gle and multi-variable optimization capability<br />
• Multi-dimensional optimization<br />
• Uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty analysis<br />
• L<strong>in</strong>ear and non-l<strong>in</strong>ear regression<br />
• Professional plott<strong>in</strong>g (2-D, contour, and 3-D) with automatic updat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Graphical user <strong>in</strong>put/output capabilities with Diagram w<strong>in</strong>dow<br />
MPE 635: <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
124
Part B: Heat Transfer Pr<strong>in</strong>cipals <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
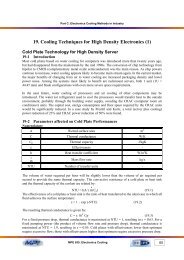
<strong>EES</strong> Applications <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g Problems<br />
Problem 1:<br />
A cable 10 mm diameter at 80 o C surface temperature is to be <strong>in</strong>sulated to maximize its current carry<strong>in</strong>g<br />
capacity. The heat transfer coefficient for the outer surface is estimated to be 10 W /m 2 .K. and<br />
25 o C outside air temperature.<br />
What should be the radius of the chosen <strong>in</strong>sulation at 0.15 W /m .K. <strong>in</strong>sulation thermal conductivity?<br />
By what percentage would the <strong>in</strong>sulation <strong>in</strong>crease the energy carry<strong>in</strong>g capacity of the bare cable?<br />
Objective: (1) model<strong>in</strong>g any problems (2) Optimization (3) Plot results<br />
Solution:<br />
1- Govern<strong>in</strong>g equations or the equation w<strong>in</strong>dow.<br />
2- Press the follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
MPE 635: <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
125
Part B: Heat Transfer Pr<strong>in</strong>cipals <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
3- Change the dialog box to appear as the follow<strong>in</strong>g one<br />
4- Press OK, the follow<strong>in</strong>g w<strong>in</strong>dow appears with the solution<br />
MPE 635: <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
126
Part B: Heat Transfer Pr<strong>in</strong>cipals <strong>in</strong> <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
5- Press cont<strong>in</strong>ue, the follow<strong>in</strong>g w<strong>in</strong>dow appears (out put w<strong>in</strong>dow)<br />
6- Out put graphical representations<br />
MPE 635: <strong>Electronics</strong> Cool<strong>in</strong>g<br />
127