PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGIES (ET4377): INSTRUCTION 2 ...
PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGIES (ET4377): INSTRUCTION 2 ...
PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGIES (ET4377): INSTRUCTION 2 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>PHOTOVOLTAIC</strong> <strong>TECHNOLOGIES</strong> (<strong>ET4377</strong>): <strong>INSTRUCTION</strong> 2<br />
LIGHT MANAGEMENT<br />
Question 1:<br />
Solar simulator spectra and External Quantum Efficiency<br />
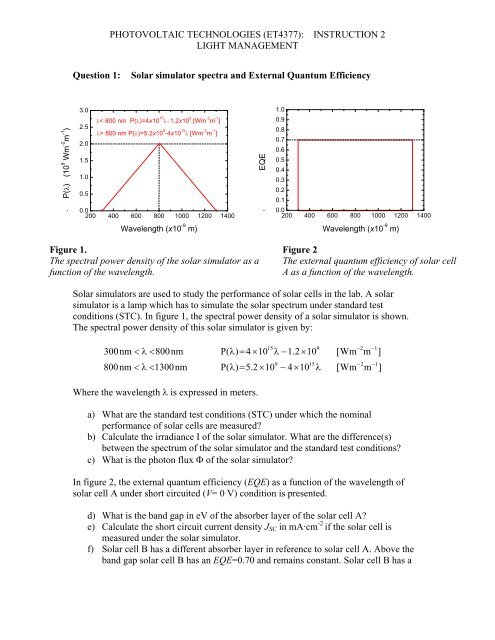
P() (10 9 Wm -2 m -1 )<br />
3.0<br />
2.5<br />
2.0<br />
1.5<br />
1.0<br />
0.5<br />
< 800 nm P()=4x10 15 1.2x10 9 [Wm -2 m -1 ]<br />
> 800 nm P()=5.2x10 9 -4x10 15 [Wm -2 m -1 ]<br />
0.0<br />
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400<br />
EQE<br />
1.0<br />
0.9<br />
0.8<br />
0.7<br />
0.6<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
0.1<br />
0.0<br />
200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400<br />
Wavelength (x10 -9 m)<br />
Wavelength (x10 -9 m)<br />
Figure 1. Figure 2<br />
The spectral power density of the solar simulator as a The external quantum efficiency of solar cell<br />
function of the wavelength.<br />
A as a function of the wavelength.<br />
Solar simulators are used to study the performance of solar cells in the lab. A solar<br />
simulator is a lamp which has to simulate the solar spectrum under standard test<br />
conditions (STC). In figure 1, the spectral power density of a solar simulator is shown.<br />
The spectral power density of this solar simulator is given by:<br />
300nm 800nm<br />
800nm 1300nm<br />
P( )<br />
4<br />
10<br />
15<br />
P( )<br />
5.2<br />
10<br />
1.2<br />
10<br />
9<br />
4 10<br />
15<br />
9<br />
<br />
[Wm<br />
[Wm<br />
2<br />
2<br />
m<br />
m<br />
1<br />
1<br />
]<br />
]<br />
Where the wavelength is expressed in meters.<br />
a) What are the standard test conditions (STC) under which the nominal<br />
performance of solar cells are measured?<br />
b) Calculate the irradiance I of the solar simulator. What are the difference(s)<br />
between the spectrum of the solar simulator and the standard test conditions?<br />
c) What is the photon flux of the solar simulator?<br />
In figure 2, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) as a function of the wavelength of<br />
solar cell A under short circuited (V= 0 V) condition is presented.<br />
d) What is the band gap in eV of the absorber layer of the solar cell A?<br />
e) Calculate the short circuit current density J SC in mA·cm -2 if the solar cell is<br />
measured under the solar simulator.<br />
f) Solar cell B has a different absorber layer in reference to solar cell A. Above the<br />
band gap solar cell B has an EQE=0.70 and remains constant. Solar cell B has a
<strong>PHOTOVOLTAIC</strong> <strong>TECHNOLOGIES</strong> (<strong>ET4377</strong>): <strong>INSTRUCTION</strong> 2<br />
LIGHT MANAGEMENT<br />
J SC = 17.8 mA·cm -2 under the solar simulator shown in Figure 1. What is the band<br />
gap of this material?<br />
Question 2:<br />
The Rayleigh film<br />
Figure 3<br />
a) Consider the interface between two media with refractive index n=a and n=b<br />
(Figure 3b). What are the Fresnel coefficients R and T expressed in a and b for<br />
irradiance for light with an incident angle of i =0 (perpendicular)?<br />
b) Consider the situation in Fig. 3b. A third medium with refractive index n = x is<br />
placed between the other two media. What are the effective Fresnel coefficients R<br />
and T expressed in a, b and x for irradiance for light with an incident angle of<br />
i =0 (perpendicular)?<br />
c) Proof that the minimum reflection and maximum transmission is obtained for<br />
x ab . Hint: use the function T(x) derived at question 2b. (Which conditions<br />
should be valid to have a maximum for T(x)?)<br />
Question 3:<br />
The AR coating.<br />
Figure 4
<strong>PHOTOVOLTAIC</strong> <strong>TECHNOLOGIES</strong> (<strong>ET4377</strong>): <strong>INSTRUCTION</strong> 2<br />
LIGHT MANAGEMENT<br />
In Figure 4 the light beam traveling in the z-direction is shown. The interface between<br />
media 1 and 2 is positioned at z=0. The interface between media 2 and 3 is positioned at<br />
z=d. The Fresnel coefficients at the interfaces are t 12 , r 12 , t 23 and r 12 . A light beam<br />
described by:<br />
Ei<br />
(z) E0<br />
cos( t<br />
kz) z 0<br />
is traveling in the z-direction and is incident on the interface at z=0.<br />
a) Give the expression E R<br />
(z a)<br />
for the reflected light beam at z=-a.<br />
b) Give the expression E T<br />
(z b)<br />
for the transmitted light beam at z=b.<br />
c) For which optical thickness is (z a)<br />
minimized?<br />
E R<br />
Question 4: The critical angle<br />
glass<br />
glass<br />
glass<br />
TCO<br />
TCO<br />
TCO<br />
1<br />
•n-a-Si:H<br />
absorber<br />
2<br />
absorber<br />
3<br />
absorber<br />
back reflector<br />
back reflector<br />
back reflector<br />
Figure 5<br />
Consider the thin film silicon solar cells as depicted in Figure 5. The interfaces between<br />
the various layers are not textured but flat. The transparent conductive oxide layer is<br />
Aluminum-doped Zinc-oxide. The back reflector is a magic layer, which reflects all the<br />
light transmitted through the silicon absorber layer under a certain angle r back in to the<br />
cell. The refractive index for Si layer n Si =4.3, transparent conductive oxide n ZnO =1.86,<br />
n glass =1.51 and n Air =1.<br />
a) What is the minimum angle for the refraction at the r to have all light reflected<br />
and the Si-ZnO interface?<br />
b) What is the minimum angle for the refraction at the r to have all light reflected<br />
and the ZnO-glass interface?<br />
c) What is the minimum angle for the refraction at the r to have all light reflected<br />
and the glass-air interface?<br />
d) For which r angles does the light not escape the Si, ZnO and glass?
<strong>PHOTOVOLTAIC</strong> <strong>TECHNOLOGIES</strong> (<strong>ET4377</strong>): <strong>INSTRUCTION</strong> 2<br />
LIGHT MANAGEMENT<br />
Fresnel coefficient<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
r<br />
i<br />
2<br />
t<br />
1<br />
i<br />
2<br />
t<br />
1<br />
p<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
r<br />
t<br />
2<br />
i<br />
1<br />
t<br />
2<br />
i<br />
1<br />
S<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
t<br />
2<br />
i<br />
1<br />
t<br />
2<br />
i<br />
1<br />
S<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
R<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
i<br />
2<br />
t<br />
1<br />
i<br />
2<br />
t<br />
1<br />
p<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
)<br />
cos(<br />
n<br />
R<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
2<br />
1<br />
2<br />
1<br />
p<br />
o<br />
i<br />
n<br />
n<br />
n<br />
n<br />
R<br />
0<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
2<br />
1<br />
2<br />
1<br />
p<br />
n<br />
n<br />
n<br />
4n<br />
T<br />
<br />
<br />
)<br />
n<br />
n<br />
arcsin(<br />
1<br />
2<br />
,critic<br />
i <br />
Snell’s law:<br />
r<br />
i<br />
t<br />
2<br />
i<br />
1 sin<br />
)<br />
(<br />
n<br />
)sin<br />
(<br />
n<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Irradiance, photon flux and short current density<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
d<br />
)<br />
P(<br />
I<br />
hc<br />
)<br />
P(<br />
)<br />
(<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
0<br />
0<br />
d<br />
hc<br />
)<br />
P(<br />
)d<br />
(<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
0<br />
0<br />
SC<br />
d<br />
)<br />
EQE(<br />
hc<br />
)<br />
P(<br />
q<br />
)d<br />
)EQE(<br />
(<br />
q<br />
0 V)<br />
(V<br />
J