pdf - 395 K - Ecole des mines de Nantes
pdf - 395 K - Ecole des mines de Nantes
pdf - 395 K - Ecole des mines de Nantes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
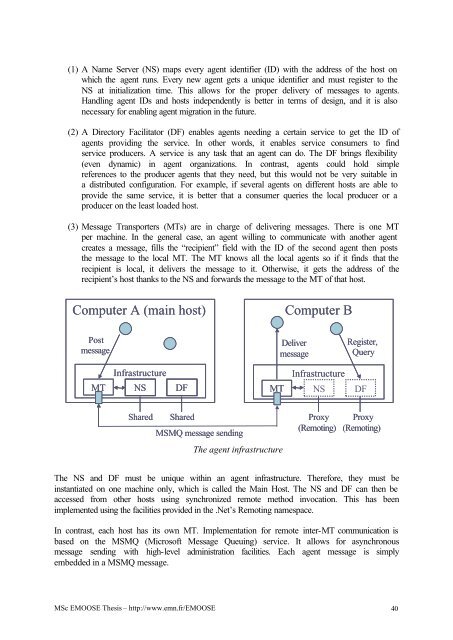
(1) A Name Server (NS) maps every agent i<strong>de</strong>ntifier (ID) with the address of the host onwhich the agent runs. Every new agent gets a unique i<strong>de</strong>ntifier and must register to theNS at initialization time. This allows for the proper <strong>de</strong>livery of messages to agents.Handling agent IDs and hosts in<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>ntly is better in terms of <strong><strong>de</strong>s</strong>ign, and it is alsonecessary for enabling agent migration in the future.(2) A Directory Facilitator (DF) enables agents needing a certain service to get the ID ofagents providing the service. In other words, it enables service consumers to findservice producers. A service is any task that an agent can do. The DF brings flexibility(even dynamic) in agent organizations. In contrast, agents could hold simplereferences to the producer agents that they need, but this would not be very suitable ina distributed configuration. For example, if several agents on different hosts are able toprovi<strong>de</strong> the same service, it is better that a consumer queries the local producer or aproducer on the least loa<strong>de</strong>d host.(3) Message Transporters (MTs) are in charge of <strong>de</strong>livering messages. There is one MTper machine. In the general case, an agent willing to communicate with another agentcreates a message, fills the “recipient” field with the ID of the second agent then poststhe message to the local MT. The MT knows all the local agents so if it finds that therecipient is local, it <strong>de</strong>livers the message to it. Otherwise, it gets the address of therecipient’s host thanks to the NS and forwards the message to the MT of that host.Computer A (main host)Computer BPostmessageDelivermessageRegister,QueryMTInfrastructureNSDFMTInfrastructureNSDFSharedSharedMSMQ message sendingThe agent infrastructureProxy(Remoting)Proxy(Remoting)The NS and DF must be unique within an agent infrastructure. Therefore, they must beinstantiated on one machine only, which is called the Main Host. The NS and DF can then beaccessed from other hosts using synchronized remote method invocation. This has beenimplemented using the facilities provi<strong>de</strong>d in the .Net’s Remoting namespace.In contrast, each host has its own MT. Implementation for remote inter-MT communication isbased on the MSMQ (Microsoft Message Queuing) service. It allows for asynchronousmessage sending with high-level administration facilities. Each agent message is simplyembed<strong>de</strong>d in a MSMQ message.MSc EMOOSE Thesis – http://www.emn.fr/EMOOSE 40