Routing protocols in wireless sensor networks
Routing protocols in wireless sensor networks
Routing protocols in wireless sensor networks
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Presently quite a lot of WSN <strong>protocols</strong> are available us<strong>in</strong>g different techniques<br />
to ensure proper rout<strong>in</strong>g of authentic data; each protocol has its own advantages<br />
and disadvantages <strong>in</strong> design.<br />
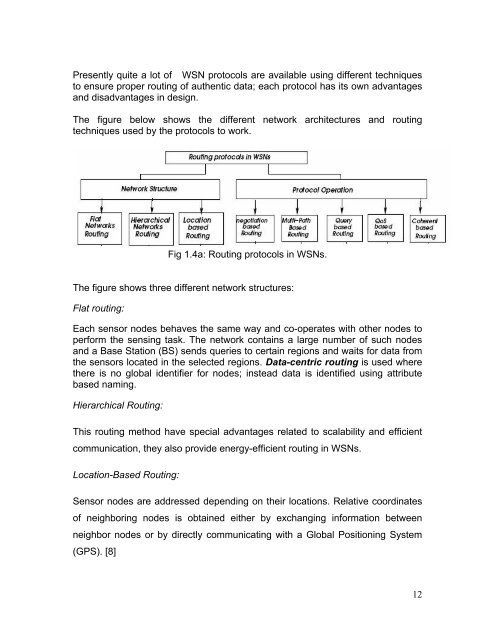
The figure below shows the different network architectures and rout<strong>in</strong>g<br />
techniques used by the <strong>protocols</strong> to work.<br />
Fig 1.4a: <strong>Rout<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>protocols</strong> <strong>in</strong> WSNs.<br />
The figure shows three different network structures:<br />
Flat rout<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
Each <strong>sensor</strong> nodes behaves the same way and co-operates with other nodes to<br />
perform the sens<strong>in</strong>g task. The network conta<strong>in</strong>s a large number of such nodes<br />
and a Base Station (BS) sends queries to certa<strong>in</strong> regions and waits for data from<br />
the <strong>sensor</strong>s located <strong>in</strong> the selected regions. Data-centric rout<strong>in</strong>g is used where<br />
there is no global identifier for nodes; <strong>in</strong>stead data is identified us<strong>in</strong>g attribute<br />
based nam<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Hierarchical <strong>Rout<strong>in</strong>g</strong>:<br />
This rout<strong>in</strong>g method have special advantages related to scalability and efficient<br />
communication, they also provide energy-efficient rout<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> WSNs.<br />
Location-Based <strong>Rout<strong>in</strong>g</strong>:<br />
Sensor nodes are addressed depend<strong>in</strong>g on their locations. Relative coord<strong>in</strong>ates<br />
of neighbor<strong>in</strong>g nodes is obta<strong>in</strong>ed either by exchang<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation between<br />
neighbor nodes or by directly communicat<strong>in</strong>g with a Global Position<strong>in</strong>g System<br />
(GPS). [8]<br />
12