Sunflower Production - NDSU Agriculture - North Dakota State ...
Sunflower Production - NDSU Agriculture - North Dakota State ...
Sunflower Production - NDSU Agriculture - North Dakota State ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
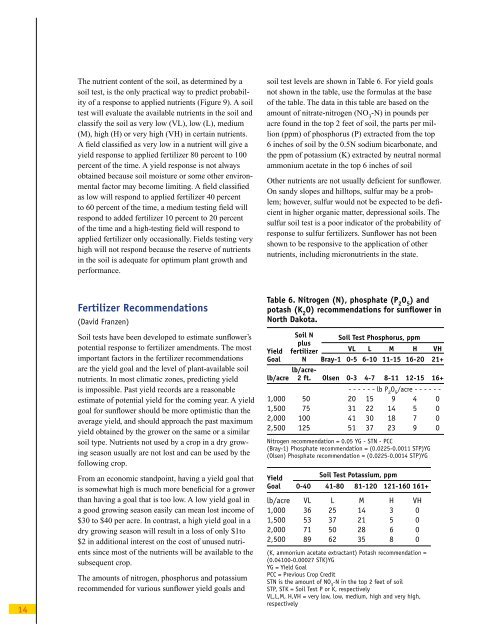
The nutrient content of the soil, as determined by asoil test, is the only practical way to predict probabilityof a response to applied nutrients (Figure 9). A soiltest will evaluate the available nutrients in the soil andclassify the soil as very low (VL), low (L), medium(M), high (H) or very high (VH) in certain nutrients.A field classified as very low in a nutrient will give ayield response to applied fertilizer 80 percent to 100percent of the time. A yield response is not alwaysobtained because soil moisture or some other environmentalfactor may become limiting. A field classifiedas low will respond to applied fertilizer 40 percentto 60 percent of the time, a medium testing field willrespond to added fertilizer 10 percent to 20 percentof the time and a high-testing field will respond toapplied fertilizer only occasionally. Fields testing veryhigh will not respond because the reserve of nutrientsin the soil is adequate for optimum plant growth andperformance.soil test levels are shown in Table 6. For yield goalsnot shown in the table, use the formulas at the baseof the table. The data in this table are based on theamount of nitrate-nitrogen (NO 3-N) in pounds peracre found in the top 2 feet of soil, the parts per million(ppm) of phosphorus (P) extracted from the top6 inches of soil by the 0.5N sodium bicarbonate, andthe ppm of potassium (K) extracted by neutral normalammonium acetate in the top 6 inches of soilOther nutrients are not usually deficient for sunflower.On sandy slopes and hilltops, sulfur may be a problem;however, sulfur would not be expected to be deficientin higher organic matter, depressional soils. Thesulfur soil test is a poor indicator of the probability ofresponse to sulfur fertilizers. <strong>Sunflower</strong> has not beenshown to be responsive to the application of othernutrients, including micronutrients in the state.14Fertilizer Recommendations(David Franzen)Soil tests have been developed to estimate sunflower’spotential response to fertilizer amendments. The mostimportant factors in the fertilizer recommendationsare the yield goal and the level of plant-available soilnutrients. In most climatic zones, predicting yieldis impossible. Past yield records are a reasonableestimate of potential yield for the coming year. A yieldgoal for sunflower should be more optimistic than theaverage yield, and should approach the past maximumyield obtained by the grower on the same or a similarsoil type. Nutrients not used by a crop in a dry growingseason usually are not lost and can be used by thefollowing crop.From an economic standpoint, having a yield goal thatis somewhat high is much more beneficial for a growerthan having a goal that is too low. A low yield goal ina good growing season easily can mean lost income of$30 to $40 per acre. In contrast, a high yield goal in adry growing season will result in a loss of only $1to$2 in additional interest on the cost of unused nutrientssince most of the nutrients will be available to thesubsequent crop.The amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassiumrecommended for various sunflower yield goals andTable 6. Nitrogen (N), phosphate (P 2O 5) andpotash (K 2O) recommendations for sunflower in<strong>North</strong> <strong>Dakota</strong>.Soil N Soil Test Phosphorus, ppmplusYield fertilizer VL L M H VHGoal N Bray-1 0-5 6-10 11-15 16-20 21+lb/acrelb/acre2 ft. Olsen 0-3 4-7 8-11 12-15 16+- - - - - - lb P 2O 5/acre - - - - - -1,000 50 20 15 9 4 01,500 75 31 22 14 5 02,000 100 41 30 18 7 02,500 125 51 37 23 9 0Nitrogen recommendation = 0.05 YG - STN - PCC(Bray-1) Phosphate recommendation = (0.0225-0.0011 STP)YG(Olsen) Phosphate recommendation = (0.0225-0.0014 STP)YGYieldSoil Test Potassium, ppmGoal 0-40 41-80 81-120 121-160 161+lb/acre VL L M H VH1,000 36 25 14 3 01,500 53 37 21 5 02,000 71 50 28 6 02,500 89 62 35 8 0(K, ammonium acetate extractant) Potash recommendation =(0.04100-0.00027 STK)YGYG = Yield GoalPCC = Previous Crop CreditSTN is the amount of NO 3-N in the top 2 feet of soilSTP, STK = Soil Test P or K, respectivelyVL,L,M, H,VH = very low, low, medium, high and very high,respectively