Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Raspberry Press Cake
Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Raspberry Press Cake
Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Raspberry Press Cake
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
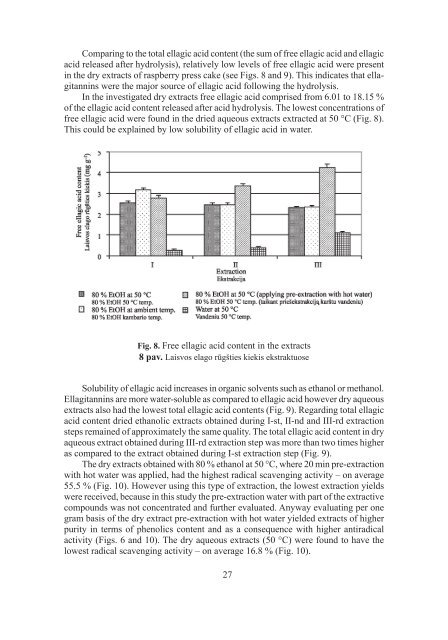
Comparing to the total ellagic acid content (the sum <strong>of</strong> free ellagic acid and ellagicacid released after hydrolysis), relatively low levels <strong>of</strong> free ellagic acid were presentin the dry extracts <strong>of</strong> raspberry press cake (see Figs. 8 and 9). This indicates that ellagitanninswere the major source <strong>of</strong> ellagic acid following the hydrolysis.In the investigated dry extracts free ellagic acid comprised <strong>from</strong> 6.01 to 18.15 %<strong>of</strong> the ellagic acid content released after acid hydrolysis. The lowest concentrations <strong>of</strong>free ellagic acid were found in the dried aqueous extracts extracted at 50 °C (Fig. 8).This could be explained by low solubility <strong>of</strong> ellagic acid in water.Fig. 8. Free ellagic acid content in the extracts8 pav. Laisvos elago rūgšties kiekis ekstraktuoseSolubility <strong>of</strong> ellagic acid increases in organic solvents such as ethanol or methanol.Ellagitannins are more water-soluble as compared to ellagic acid however dry aqueousextracts also had the lowest total ellagic acid contents (Fig. 9). Regarding total ellagicacid content dried ethanolic extracts obtained during I-st, II-nd and III-rd extractionsteps remained <strong>of</strong> approximately the same quality. The total ellagic acid content in dryaqueous extract obtained during III-rd extraction step was more than two times higheras compared to the extract obtained during I-st extraction step (Fig. 9).The dry extracts obtained with 80 % ethanol at 50 °C, where 20 min pre-extractionwith hot water was applied, had the highest radical scavenging activity – on average55.5 % (Fig. 10). However using this type <strong>of</strong> extraction, the lowest extraction yieldswere received, because in this study the pre-extraction water with part <strong>of</strong> the extractivecompounds was not concentrated and further evaluated. Anyway evaluating per onegram basis <strong>of</strong> the dry extract pre-extraction with hot water yielded extracts <strong>of</strong> higherpurity in terms <strong>of</strong> phenolics content and as a consequence with higher antiradicalactivity (Figs. 6 and 10). The dry aqueous extracts (50 °C) were found to have thelowest radical scavenging activity – on average 16.8 % (Fig. 10).27