Summary of Definitions of Continuity of Care
Summary of Definitions of Continuity of Care
Summary of Definitions of Continuity of Care
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
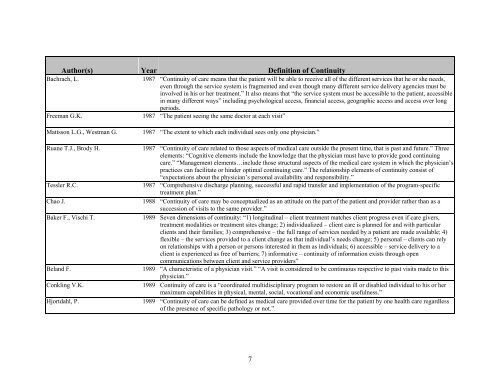
Author(s) Year Definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>Continuity</strong>Bachrach, L.1987 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care means that the patient will be able to receive all <strong>of</strong> the different services that he or she needs,even through the service system is fragmented and even though many different service delivery agencies must beinvolved in his or her treatment.” It also means that “the service system must be accessible to the patient, accessiblein many different ways” including psychological access, financial access, geographic access and access over longperiods.Freeman G.K.1987 “The patient seeing the same doctor at each visit”Mattsson L.G., Westman G. 1987 “The extent to which each individual sees only one physician.”Ruane T.J., Brody H. 1987 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care related to those aspects <strong>of</strong> medical care outside the present time, that is past and future.” Threeelements: “Cognitive elements include the knowledge that the physician must have to provide good continuingcare.” “Management elements…include those structural aspects <strong>of</strong> the medical care system in which the physician’spractices can facilitate or hinder optimal continuing care.” The relationship elements <strong>of</strong> continuity consist <strong>of</strong>“expectations about the physician’s personal availability and responsibility.”Tessler R.C.1987 “Comprehensive discharge planning, successful and rapid transfer and implementation <strong>of</strong> the program-specifictreatment plan.”Chao J. 1988 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care may be conceptualized as an attitude on the part <strong>of</strong> the patient and provider rather than as asuccession <strong>of</strong> visits to the same provider.”Baker F., Vischi T.1989 Seven dimensions <strong>of</strong> continuity: “1) longitudinal – client treatment matches client progress even if care givers,treatment modalities or treatment sites change; 2) individualized – client care is planned for and with particularclients and their families; 3) comprehensive – the full range <strong>of</strong> services needed by a patient are made available; 4)flexible – the services provided to a client change as that individual’s needs change; 5) personal – clients can relyon relationships with a person or persons interested in them as individuals; 6) accessible – service delivery to aclient is experienced as free <strong>of</strong> barriers; 7) informative – continuity <strong>of</strong> information exists through opencommunications between client and service providers”Beland F.1989 “A characteristic <strong>of</strong> a physician visit.” “A visit is considered to be continuous respective to past visits made to thisphysician.”Conkling V.K.1989 <strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care is a “coordinated multidisciplinary program to restore an ill or disabled individual to his or hermaximum capabilities in physical, mental, social, vocational and economic usefulness.”Hjortdahl, P.1989 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care can be defined as medical care provided over time for the patient by one health care regardless<strong>of</strong> the presence <strong>of</strong> specific pathology or not.”7