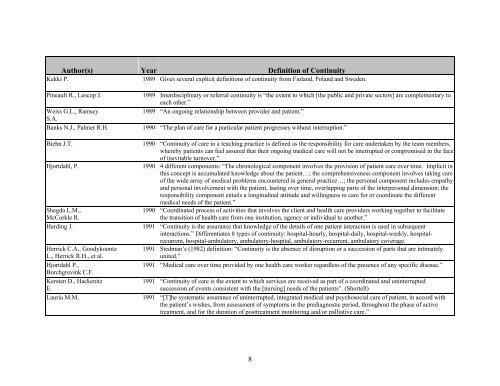
Author(s) Year Definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>Continuity</strong>Kekki P. 1989 Gives several explicit definitions <strong>of</strong> continuity from Finland, Poland and Sweden.Pineault R., Lescop J.Weiss G.L., RamseyS.A.Banks N.J., Palmer R.H.Biehn J.T.Hjortdahl, P.Shegda L.M.,McCorkle R.Harding J.Herrick C.A., GoodykoontzL., Herrick R.H., et al.Hjortdahl P.,Borchgrevink C.F.Kersten D., HackenitzE.Lauria M.M.1989 Interdisciplinary or referral continuity is “the extent to which [the public and private sectors] are complementary toeach other.”1989 “An ongoing relationship between provider and patient.”1990 “The plan <strong>of</strong> care for a particular patient progresses without interruption.”1990 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care in a teaching practice is defined as the responsibility for care undertaken by the team members,whereby patients can feel assured that their ongoing medical care will not be interrupted or compromised in the face<strong>of</strong> inevitable turnover.”1990 4 different components: “The chronological component involves the provision <strong>of</strong> patient care over time. Implicit inthis concept is accumulated knowledge about the patient…; the comprehensiveness component involves taking care<strong>of</strong> the wide array <strong>of</strong> medical problems encountered in general practice…; the personal component includes empathyand personal involvement with the patient, lasting over time, overlapping parts <strong>of</strong> the interpersonal dimension; theresponsibility component entails a longitudinal attitude and willingness to care for or coordinate the differentmedical needs <strong>of</strong> the patient.”1990 “Coordinated process <strong>of</strong> activities that involves the client and health care providers working together to facilitatethe transition <strong>of</strong> health care from one institution, agency or individual to another.”1991 “<strong>Continuity</strong> is the assurance that knowledge <strong>of</strong> the details <strong>of</strong> one patient interaction is used in subsequentinteractions.” Differentiates 8 types <strong>of</strong> continuity: hospital-hourly, hospital-daily, hospital-weekly, hospitalrecurrent,hospital-ambulatory, ambulatory-hospital, ambulatory-recurrent, ambulatory coverage.1991 Stedman’s (1982) definition: “<strong>Continuity</strong> is the absence <strong>of</strong> disruption or a succession <strong>of</strong> parts that are intimatelyunited.”1991 “Medical care over time provided by one health care worker regardless <strong>of</strong> the presence <strong>of</strong> any specific disease.”1991 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care is the extent to which services are received as part <strong>of</strong> a coordinated and uninterruptedsuccession <strong>of</strong> events consistent with the [nursing] needs <strong>of</strong> the patients”. (Shortell)1991 “[T]he systematic assurance <strong>of</strong> uninterrupted, integrated medical and psychosocial care <strong>of</strong> patient, in accord withthe patient’s wishes, from assessment <strong>of</strong> symptoms in the prediagnostic period, throughout the phase <strong>of</strong> activetreatment, and for the duration <strong>of</strong> posttreatment monitoring and/or palliative care.”8
Author(s) Year Definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>Continuity</strong>Semke J.1991 “A process involving the orderly, uninterrupted movement <strong>of</strong> patients among the diverse elements <strong>of</strong> the servicedelivery system.” (Bachrach 1991).Barbato A., TerzianE., Saraceno B., et al.Brekke J.S., TestM.A.Hjortdahl, P.Liaw ST., Litt J.,Radford A.White D.Anderson M.A., Helms L.Bachrach L.L.Commonwealth <strong>of</strong>AustraliaFreeman G.K.,Richards S.C.Gabel L.L., LucasJ.B., Westbury R.C.1992 “A process involving the uninterrupted movement <strong>of</strong> patients over time through the diverse elements <strong>of</strong> the servicedelivery system.” (Bachrach 1991)1992 2 dimensions: “cross-sectional ‘continuity refers to the need at any one point in time for the client to be involved ina system <strong>of</strong> care that is comprehensive and integrated.’” “Longitudinal continuity means care that is continuousand integrated over time.”1992 Traditional aspect <strong>of</strong> continuity: “Medical care provided over time by one health care worker.” Revised definition<strong>of</strong> continuity: “‘A sense <strong>of</strong> overall, direct or coordinative responsibility for the different medical needs <strong>of</strong> thepatient.’”1992 Five dimensions <strong>of</strong> the continuity environment: “firstly chronological continuity, which refers to care provided overtime to a defined population (also known as longitudinal continuity); secondly geographical continuity referring tosite continuity and/or provider continuity regardless <strong>of</strong> site (<strong>of</strong>fice, hospital, home)… Thirdly interdisciplinarycontinuity or the role <strong>of</strong> the general practitioner in tackling or coordinating the undifferentiated illnesses, themultifactorial causes and the range <strong>of</strong> services available. Fourthly interpersonal or relational continuity refers tocontinuity <strong>of</strong> process that involves the quality <strong>of</strong> relationships...Informational continuity refers to the medicalrecord as well as all forms <strong>of</strong> communication between the patient and provider.”1992 Gives several definitions from the literature including: “A broad number <strong>of</strong> strategies intended to ensure long-term,comprehensive support for people with mental health problems in managing day-to-day life in the “natural milieu”or non-institutional environment.” “ The coordination <strong>of</strong> diverse services required for the treatment <strong>of</strong> any type <strong>of</strong>chronic or complex illness.”1993 “Coordinating the delivery <strong>of</strong> ongoing health care services in a variety <strong>of</strong> health care settings.” “Discharge planning[is] a means <strong>of</strong> achieving continuity <strong>of</strong> care [and] is the process in which a patient’s continuing health needs areidentified and communicated to providers at the next level <strong>of</strong> care.”1993 Canadian definition <strong>of</strong> continuity <strong>of</strong> care: “A general practitioner or family physician who, in addition to medicaltasks, takes on direct responsibility for connecting patients with the mental health service system.”1993 “<strong>Continuity</strong> <strong>of</strong> care is the provision <strong>of</strong> long-term, barrier-free access to the necessary range <strong>of</strong> mental health,general health, social and disability services.”1993 “Seeing the same doctor each time.”1993 Long-term relationship with physician. Ten domains characterise continuity from patient perspective: 1)“familiarity with physician” 2) “physician's knowledge <strong>of</strong> patient” 3) “satisfaction with care” 4) “confidence inphysician” 5) “personal attributes <strong>of</strong> physician” 6) “friendship with physician” 7) “pr<strong>of</strong>essional growth <strong>of</strong> physician9