European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied ... - MGNet
European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied ... - MGNet
European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied ... - MGNet
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
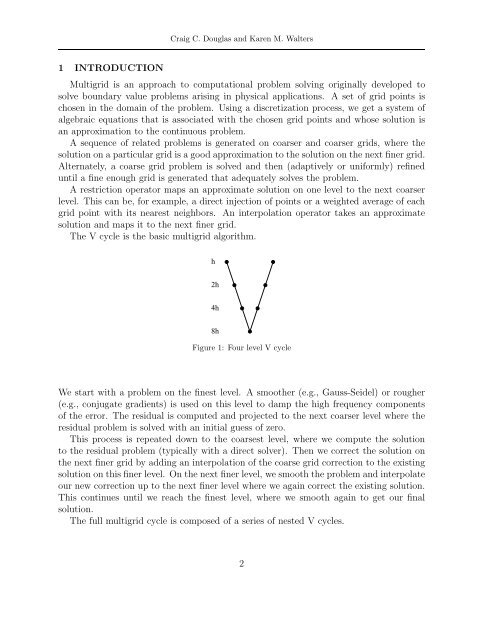
Craig C. Douglas and Karen M. Walters1 INTRODUCTIONMultigrid is an approach to computati<strong>on</strong>al problem solv<strong>in</strong>g orig<strong>in</strong>ally developed tosolve boundary value problems aris<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> physical applicati<strong>on</strong>s. A set of grid po<strong>in</strong>ts ischosen <strong>in</strong> the doma<strong>in</strong> of the problem. Us<strong>in</strong>g a discretizati<strong>on</strong> process, we get a system ofalgebraic equati<strong>on</strong>s that is associated with the chosen grid po<strong>in</strong>ts and whose soluti<strong>on</strong> isan approximati<strong>on</strong> to the c<strong>on</strong>t<strong>in</strong>uous problem.A sequence of related problems is generated <strong>on</strong> coarser and coarser grids, where thesoluti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> a particular grid is a good approximati<strong>on</strong> to the soluti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> the next f<strong>in</strong>er grid.Alternately, a coarse grid problem is solved and then (adaptively or uniformly) ref<strong>in</strong>eduntil a f<strong>in</strong>e enough grid is generated that adequately solves the problem.A restricti<strong>on</strong> operator maps an approximate soluti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong>e level to the next coarserlevel. This can be, for example, a direct <strong>in</strong>jecti<strong>on</strong> of po<strong>in</strong>ts or a weighted average of eachgrid po<strong>in</strong>t with its nearest neighbors. An <strong>in</strong>terpolati<strong>on</strong> operator takes an approximatesoluti<strong>on</strong> and maps it to the next f<strong>in</strong>er grid.The V cycle is the basic multigrid algorithm.h2h4h8hFigure 1: Four level V cycleWe start with a problem <strong>on</strong> the f<strong>in</strong>est level. A smoother (e.g., Gauss-Seidel) or rougher(e.g., c<strong>on</strong>jugate gradients) is used <strong>on</strong> this level to damp the high frequency comp<strong>on</strong>entsof the error. The residual is computed and projected to the next coarser level where theresidual problem is solved with an <strong>in</strong>itial guess of zero.This process is repeated down to the coarsest level, where we compute the soluti<strong>on</strong>to the residual problem (typically with a direct solver). Then we correct the soluti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong>the next f<strong>in</strong>er grid by add<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>terpolati<strong>on</strong> of the coarse grid correcti<strong>on</strong> to the exist<strong>in</strong>gsoluti<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> this f<strong>in</strong>er level. On the next f<strong>in</strong>er level, we smooth the problem and <strong>in</strong>terpolateour new correcti<strong>on</strong> up to the next f<strong>in</strong>er level where we aga<strong>in</strong> correct the exist<strong>in</strong>g soluti<strong>on</strong>.This c<strong>on</strong>t<strong>in</strong>ues until we reach the f<strong>in</strong>est level, where we smooth aga<strong>in</strong> to get our f<strong>in</strong>alsoluti<strong>on</strong>.The full multigrid cycle is composed of a series of nested V cycles.2