Next-Generation Sequencing: From Basic Research to Diagnostics ...
Next-Generation Sequencing: From Basic Research to Diagnostics ...
Next-Generation Sequencing: From Basic Research to Diagnostics ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
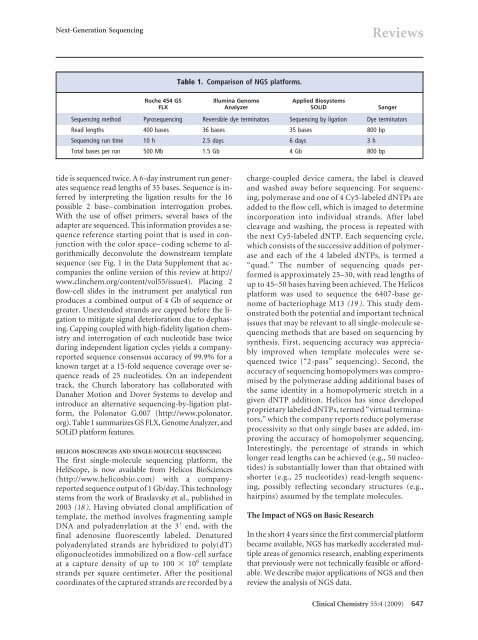
<strong>Next</strong>-<strong>Generation</strong> <strong>Sequencing</strong>ReviewsTable 1. Comparison of NGS platforms.Roche 454 GSFLXIllumina GenomeAnalyzerApplied BiosystemsSOLiDSanger<strong>Sequencing</strong> method Pyrosequencing Reversible dye termina<strong>to</strong>rs <strong>Sequencing</strong> by ligation Dye termina<strong>to</strong>rsRead lengths 400 bases 36 bases 35 bases 800 bp<strong>Sequencing</strong> run time 10 h 2.5 days 6 days 3 hTotal bases per run 500 Mb 1.5 Gb 4 Gb 800 bptide is sequenced twice. A 6-day instrument run generatessequence read lengths of 35 bases. Sequence is inferredby interpreting the ligation results for the 16possible 2 base–combination interrogation probes.With the use of offset primers, several bases of theadapter are sequenced. This information provides a sequencereference starting point that is used in conjunctionwith the color space–coding scheme <strong>to</strong> algorithmicallydeconvolute the downstream templatesequence (see Fig. 1 in the Data Supplement that accompaniesthe online version of this review at http://www.clinchem.org/content/vol55/issue4). Placing 2flow-cell slides in the instrument per analytical runproduces a combined output of 4 Gb of sequence orgreater. Unextended strands are capped before the ligation<strong>to</strong> mitigate signal deterioration due <strong>to</strong> dephasing.Capping coupled with high-fidelity ligation chemistryand interrogation of each nucleotide base twiceduring independent ligation cycles yields a companyreportedsequence consensus accuracy of 99.9% for aknown target at a 15-fold sequence coverage over sequencereads of 25 nucleotides. On an independenttrack, the Church labora<strong>to</strong>ry has collaborated withDanaher Motion and Dover Systems <strong>to</strong> develop andintroduce an alternative sequencing-by-ligation platform,the Polona<strong>to</strong>r G.007 (http://www.polona<strong>to</strong>r.org). Table 1 summarizes GS FLX, Genome Analyzer, andSOLiD platform features.HELICOS BIOSCIENCES AND SINGLE-MOLECULE SEQUENCINGThe first single-molecule sequencing platform, theHeliScope, is now available from Helicos BioSciences(http://www.helicosbio.com) with a companyreportedsequence output of 1 Gb/day. This technologystems from the work of Braslavsky et al., published in2003 (18). Having obviated clonal amplification oftemplate, the method involves fragmenting sampleDNA and polyadenylation at the 3 end, with thefinal adenosine fluorescently labeled. Denaturedpolyadenylated strands are hybridized <strong>to</strong> poly(dT)oligonucleotides immobilized on a flow-cell surfaceat a capture density of up <strong>to</strong> 100 10 6 templatestrands per square centimeter. After the positionalcoordinates of the captured strands are recorded by acharge-coupled device camera, the label is cleavedand washed away before sequencing. For sequencing,polymerase and one of 4 Cy5-labeled dNTPs areadded <strong>to</strong> the flow cell, which is imaged <strong>to</strong> determineincorporation in<strong>to</strong> individual strands. After labelcleavage and washing, the process is repeated withthe next Cy5-labeled dNTP. Each sequencing cycle,which consists of the successive addition of polymeraseand each of the 4 labeled dNTPs, is termed a“quad.” The number of sequencing quads performedis approximately 25–30, with read lengths ofup <strong>to</strong> 45–50 bases having been achieved. The Helicosplatform was used <strong>to</strong> sequence the 6407-base genomeof bacteriophage M13 (19). This study demonstratedboth the potential and important technicalissues that may be relevant <strong>to</strong> all single-molecule sequencingmethods that are based on sequencing bysynthesis. First, sequencing accuracy was appreciablyimproved when template molecules were sequencedtwice (“2-pass” sequencing). Second, theaccuracy of sequencing homopolymers was compromisedby the polymerase adding additional bases ofthe same identity in a homopolymeric stretch in agiven dNTP addition. Helicos has since developedproprietary labeled dNTPs, termed “virtual termina<strong>to</strong>rs,”which the company reports reduce polymeraseprocessivity so that only single bases are added, improvingthe accuracy of homopolymer sequencing.Interestingly, the percentage of strands in whichlonger read lengths can be achieved (e.g., 50 nucleotides)is substantially lower than that obtained withshorter (e.g., 25 nucleotides) read-length sequencing,possibly reflecting secondary structures (e.g.,hairpins) assumed by the template molecules.The Impact of NGS on <strong>Basic</strong> <strong>Research</strong>In the short 4 years since the first commercial platformbecame available, NGS has markedly accelerated multipleareas of genomics research, enabling experimentsthat previously were not technically feasible or affordable.We describe major applications of NGS and thenreview the analysis of NGS data.Clinical Chemistry 55:4 (2009) 647