supplement ii to the japanese pharmacopoeia fifteenth edition - NIHS
supplement ii to the japanese pharmacopoeia fifteenth edition - NIHS
supplement ii to the japanese pharmacopoeia fifteenth edition - NIHS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
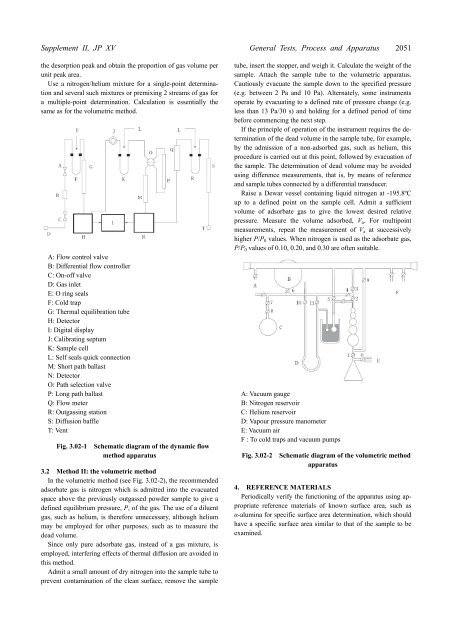
Supplement II, JP XV General Tests, Process and Apparatus 2051<strong>the</strong> desorption peak and obtain <strong>the</strong> proportion of gas volume perunit peak area.Use a nitrogen/helium mixture for a single-point determinationand several such mixtures or premixing 2 streams of gas fora multiple-point determination. Calculation is essentially <strong>the</strong>same as for <strong>the</strong> volumetric method.A: Flow control valveB: Differential flow controllerC: On-off valveD: Gas inletE: O ring sealsF: Cold trapG: Thermal equilibration tubeH: Detec<strong>to</strong>rI: Digital displayJ: Calibrating septumK: Sample cellL: Self seals quick connectionM: Short path ballastN: Detec<strong>to</strong>rO: Path selection valveP: Long path ballastQ: Flow meterR: Outgassing stationS: Diffusion baffleT: VentFig. 3.02-1Schematic diagram of <strong>the</strong> dynamic flowmethod apparatus3.2 Method II: <strong>the</strong> volumetric methodIn <strong>the</strong> volumetric method (see Fig. 3.02-2), <strong>the</strong> recommendedadsorbate gas is nitrogen which is admitted in<strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> evacuatedspace above <strong>the</strong> previously outgassed powder sample <strong>to</strong> give adefined equilibrium pressure, P, of <strong>the</strong> gas. The use of a diluentgas, such as helium, is <strong>the</strong>refore unnecessary, although heliummay be employed for o<strong>the</strong>r purposes, such as <strong>to</strong> measure <strong>the</strong>dead volume.Since only pure adsorbate gas, instead of a gas mixture, isemployed, interfering effects of <strong>the</strong>rmal diffusion are avoided inthis method.Admit a small amount of dry nitrogen in<strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> sample tube <strong>to</strong>prevent contamination of <strong>the</strong> clean surface, remove <strong>the</strong> sampletube, insert <strong>the</strong> s<strong>to</strong>pper, and weigh it. Calculate <strong>the</strong> weight of <strong>the</strong>sample. Attach <strong>the</strong> sample tube <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> volumetric apparatus.Cautiously evacuate <strong>the</strong> sample down <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> specified pressure(e.g. between 2 Pa and 10 Pa). Alternately, some instrumentsoperate by evacuating <strong>to</strong> a defined rate of pressure change (e.g.less than 13 Pa/30 s) and holding for a defined period of timebefore commencing <strong>the</strong> next step.If <strong>the</strong> principle of operation of <strong>the</strong> instrument requires <strong>the</strong> determinationof <strong>the</strong> dead volume in <strong>the</strong> sample tube, for example,by <strong>the</strong> admission of a non-adsorbed gas, such as helium, thisprocedure is carried out at this point, followed by evacuation of<strong>the</strong> sample. The determination of dead volume may be avoidedusing difference measurements, that is, by means of referenceand sample tubes connected by a differential transducer.Raise a Dewar vessel containing liquid nitrogen at -195.8ºCup <strong>to</strong> a defined point on <strong>the</strong> sample cell. Admit a sufficientvolume of adsorbate gas <strong>to</strong> give <strong>the</strong> lowest desired relativepressure. Measure <strong>the</strong> volume adsorbed, V a . For multipointmeasurements, repeat <strong>the</strong> measurement of V a at successivelyhigher P/P 0 values. When nitrogen is used as <strong>the</strong> adsorbate gas,P/P 0 values of 0.10, 0.20, and 0.30 are often suitable.A: Vacuum gaugeB: Nitrogen reservoirC: Helium reservoirD: Vapour pressure manometerE: Vacuum airF : To cold traps and vacuum pumpsFig. 3.02-2Schematic diagram of <strong>the</strong> volumetric methodapparatus4. REFERENCE MATERIALSPeriodically verify <strong>the</strong> functioning of <strong>the</strong> apparatus using appropriatereference materials of known surface area, such asα-alumina for specific surface area determination, which shouldhave a specific surface area similar <strong>to</strong> that of <strong>the</strong> sample <strong>to</strong> beexamined.