Fingerprint Image Enhancement Techniques and Performance ...
Fingerprint Image Enhancement Techniques and Performance ...
Fingerprint Image Enhancement Techniques and Performance ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
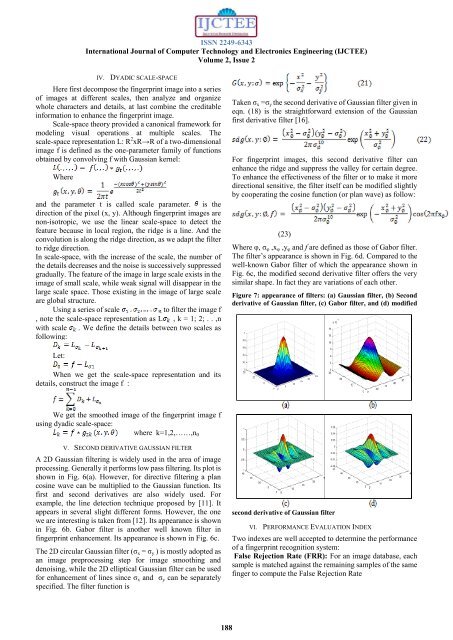
ISSN 2249-6343International Journal of Computer Technology <strong>and</strong> Electronics Engineering (IJCTEE)Volume 2, Issue 2IV. DYADIC SCALE-SPACEHere first decompose the fingerprint image into a seriesof images at different scales, then analyze <strong>and</strong> organizewhole characters <strong>and</strong> details, at last combine the creditableinformation to enhance the fingerprint image.Scale-space theory provided a canonical framework formodeling visual operations at multiple scales. Thescale-space representation L: R 2 xR→R of a two-dimensionalimage f is defined as the one-parameter family of functionsobtained by convolving f with Gaussian kernel:Where<strong>and</strong> the parameter t is called scale parameter. is thedirection of the pixel (x, y). Although fingerprint images arenon-isotropic, we use the linear scale-space to detect thefeature because in local region, the ridge is a line. And theconvolution is along the ridge direction, as we adapt the filterto ridge direction.In scale-space, with the increase of the scale, the number ofthe details decreases <strong>and</strong> the noise is successively suppressedgradually. The feature of the image in large scale exists in theimage of small scale, while weak signal will disappear in thelarge scale space. Those existing in the image of large scaleare global structure.Using a series of scaleto filter the image f, note the scale-space representation as L , k = 1; 2; . . ,nwith scale . We define the details between two scales asfollowing:Taken σ x =σ y the second derivative of Gaussian filter given ineqn. (18) is the straightforward extension of the Gaussianfirst derivative filter [16].For fingerprint images, this second derivative filter canenhance the ridge <strong>and</strong> suppress the valley for certain degree.To enhance the effectiveness of the filter or to make it moredirectional sensitive, the filter itself can be modified slightlyby cooperating the cosine function (or plan wave) as follow:(23)Where φ, σ φ ,x φ ,y φ <strong>and</strong> f are defined as those of Gabor filter.The filter’s appearance is shown in Fig. 6d. Compared to thewell-known Gabor filter of which the appearance shown inFig. 6c, the modified second derivative filter offers the verysimilar shape. In fact they are variations of each other.Figure 7: appearance of filters: (a) Gaussian filter, (b) Secondderivative of Gaussian filter, (c) Gabor filter, <strong>and</strong> (d) modifiedLet:When we get the scale-space representation <strong>and</strong> itsdetails, construct the image f :We get the smoothed image of the fingerprint image fusing dyadic scale-space:where k=1,2,……,n 0V. SECOND DERIVATIVE GAUSSIAN FILTERA 2D Gaussian filtering is widely used in the area of imageprocessing. Generally it performs low pass filtering. Its plot isshown in Fig. 6(a). However, for directive filtering a plancosine wave can be multiplied to the Gaussian function. Itsfirst <strong>and</strong> second derivatives are also widely used. Forexample, the line detection technique proposed by [11]. Itappears in several slight different forms. However, the onewe are interesting is taken from [12]. Its appearance is shownin Fig. 6b. Gabor filter is another well known filter infingerprint enhancement. Its appearance is shown in Fig. 6c.The 2D circular Gaussian filter (σ x = σ y ) is mostly adopted asan image preprocessing step for image smoothing <strong>and</strong>denoising, while the 2D elliptical Gaussian filter can be usedfor enhancement of lines since σ x <strong>and</strong> σ y can be separatelyspecified. The filter function issecond derivative of Gaussian filterVI. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION INDEXTwo indexes are well accepted to determine the performanceof a fingerprint recognition system:False Rejection Rate (FRR): For an image database, eachsample is matched against the remaining samples of the samefinger to compute the False Rejection Rate188