You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
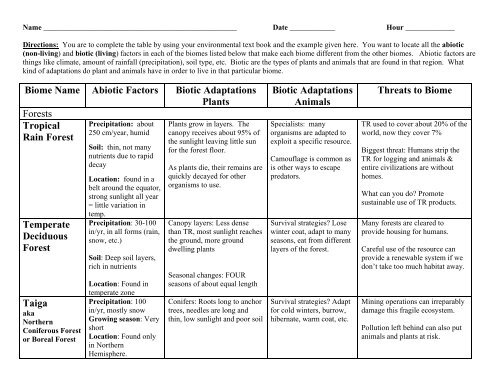
<strong>Name</strong> ___________________________________________________ Date ____________ Hour _____________Directions: You are to complete the table by using your environmental text book and the example given here. You want to locate all the abiotic(non-living) and biotic (living) factors in each of the biomes listed below that make each biome different from the other biomes. Abiotic factors arethings like climate, amount of rainfall (precipitation), soil type, etc. Biotic are the types of plants and animals that are found in that region. Whatkind of adaptations do plant and animals have in order to live in that particular biome.<strong>Biome</strong> <strong>Name</strong> Abiotic Factors Biotic AdaptationsPlantsForestsTropical Precipitation: about250 cm/year, humidRain ForestTemperateDeciduousForestTaigaakaNorthernConiferous Forestor Boreal ForestSoil: thin, not manynutrients due to rapiddecayLocation: found in abelt around the equator,strong sunlight all year= little variation intemp.Precipitation: 30-100in/yr, in all forms (rain,snow, etc.)Soil: Deep soil layers,rich in nutrientsLocation: Found intemperate zonePrecipitation: 100in/yr, mostly snowGrowing season: VeryshortLocation: Found onlyin NorthernHemisphere.Plants grow in layers. Thecanopy receives about 95% ofthe sunlight leaving little sunfor the forest floor.As plants die, their remains arequickly decayed for otherorganisms to use.Canopy layers: Less densethan TR, most sunlight reachesthe ground, more grounddwelling plantsSeasonal changes: FOURseasons of about equal lengthConifers: Roots long to anchortrees, needles are long andthin, low sunlight and poor soilBiotic AdaptationsAnimalsSpecialists: manyorganisms are adapted toexploit a specific resource.Camouflage is common asis other ways to escapepredators.Survival strategies? Losewinter coat, adapt to manyseasons, eat from differentlayers of the forest.Survival strategies? Adaptfor cold winters, burrow,hibernate, warm coat, etc.Threats to <strong>Biome</strong>TR used to cover about 20% of theworld, now they cover 7%Biggest threat: Humans strip theTR for logging and animals &entire civilizations are withouthomes.What can you do? Promotesustainable use of TR products.Many forests are cleared toprovide housing for humans.Careful use of the resource canprovide a renewable system if wedon’t take too much habitat away.Mining operations can irreparablydamage this fragile ecosystem.Pollution left behind can also putanimals and plants at risk.
<strong>Biome</strong> <strong>Name</strong> Abiotic Factors Biotic AdaptationsPlantsGrasslands, Chaparral, Deserts and TundraTropical Precipitation: 25-150 Grows in Tuftsin/yrGrassland:Resistance to DroughtSavannaTemperateGrasslands:Prairie andSteppeChaparralFire plays a large rolein this ecosystemLocation: Found intropics, near equator.Contain the greatestnumber of grazinganimals on Earth.Precipitation: less than50 in/year precipitationMountains:Mountains often play arole in climatecharacteristicsLocation: Found inRussia and the Ukraine.Location: Primarily incoastal areas withMediterraneanclimates. About 300 Nand S of the equator.Climate: hot, drysummers, mild, wetwinters. Slightvariations in seasonaltemperatures.Many plants have thorns andsharp leaves to protect againstpredation.Most abundant are plantscalled Bunch grasses, finebladed grasses that grow inclumps to preserve waterSod-forming grasses that won’tdry out or blow away in wind.Mostly low-lying shrubs andsmall trees.Many plants have leatheryleaves to resist water loss.Many plant species have oils inleaves to help them resistfire…the fire will take out“weaker” plants that don’tbelong.Biotic AdaptationsAnimalsFeeding strategy: Limitedfood leads to verticalfeedingReproduction: Reproduceduring rainy season—ensures more youngsurviveAdapt for short rainyseason—migrate asnecessaryMany migrate, hibernate orburrow during extremes intemp and precipitation.Camouflage: To avoidpredationFood: Many animals willchange their diet as theseason changes.Threats to <strong>Biome</strong>Invasive speciesChanges in fire managementBecause of their low elevation,some savannas are threatened byminor rises in sea level associatedwith global climate changeOvergrazing…nomadic tribes havestarted to spend more time in onelocation.Infrastructure development (roads,buildings, etc).Unmanaged hunting and poachingis destroying herds of animals.Human development—verydesirable climate for humans tolive.
<strong>Biome</strong> <strong>Name</strong> Abiotic Factors Biotic FactorsPlantsDesert Precipitation:
Decay is slow - Soil is acidic<strong>Biome</strong> <strong>Name</strong> Abiotic Factors Biotic AdaptationsPlantsRiversMarine EcosystemsEstuariesCoral ReefsOceanPolarEcosystemsAt headwaters, usuallycold and highlyoxygenated. As it flows,it will broaden out, warmup and this completelychanges the biota you’llfind.Definition: Fresh andsalt water meetLocation: Close toequator.Consistent watertemperatureShallow waterLow in NutrientsOpen ocean is one of theleast productive areas onearth, too little sunlightto support plant growth.Covers nearly ¾ of theEarth’s surface.Can be consideredmarine ecosystems sincethe base of food chain isphytoplanktonWill vary based on where inthe river they are.Very productive biomebecause it receives lots oflight and nutrients.N/APlants are micro andmacroscopic.Have floating plants.Antarctic--Penguins live here—onlycontinent not used byhumans.BioticAdaptationsAnimalsAt the headwaters,organisms need to hangon.Often used as nursery foryoung.Breeding area for manyfishZooplankton—sea’ssmallest herbivores.Deep ocean animals feedon detritus—floating debrisin the water column.Arctic--Relatively shallow, lots ofnutrients for large varietyof animals in food web,people, seals and polarbears found here.Threats to <strong>Biome</strong>Industry uses water to dispose ofwaste products.Runoff from homes and otherplaces causes changes in acidity,pollution, etc.Dams alter the flow of the water.Many ports are found onestuaries—pollutionHuman populationTemperature is important, too hotor too cold and the animals can’tlive there to create limestoneHuman intrusion (scuba diving) isdamaging if you touch/step on thereefPollution is also a concern.While the oceans are vast, they arebecoming more polluted.Overfishing and some fishingmethods are destroying fishinggrounds.Reserves of minerals draw humansto these fragile ecosystems.The main threat to wildlife hasbeen the increase in tourism—garbage left behind.