dissection of frog, perch, worm lab.pdf
dissection of frog, perch, worm lab.pdf
dissection of frog, perch, worm lab.pdf
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
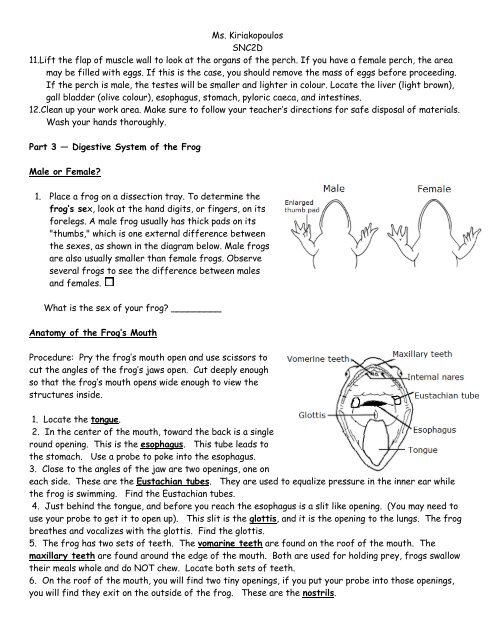
Ms. KiriakopoulosSNC2D11.Lift the flap <strong>of</strong> muscle wall to look at the organs <strong>of</strong> the <strong>perch</strong>. If you have a female <strong>perch</strong>, the areamay be filled with eggs. If this is the case, you should remove the mass <strong>of</strong> eggs before proceeding.If the <strong>perch</strong> is male, the testes will be smaller and lighter in colour. Locate the liver (light brown),gall bladder (olive colour), esophagus, stomach, pyloric caeca, and intestines.12.Clean up your work area. Make sure to follow your teacher’s directions for safe disposal <strong>of</strong> materials.Wash your hands thoroughly.Part 3 — Digestive System <strong>of</strong> the FrogMale or Female?1. Place a <strong>frog</strong> on a <strong>dissection</strong> tray. To determine the<strong>frog</strong>’s sex, look at the hand digits, or fingers, on itsforelegs. A male <strong>frog</strong> usually has thick pads on its"thumbs," which is one external difference betweenthe sexes, as shown in the diagram below. Male <strong>frog</strong>sare also usually smaller than female <strong>frog</strong>s. Observeseveral <strong>frog</strong>s to see the difference between malesand females.What is the sex <strong>of</strong> your <strong>frog</strong>? _________Anatomy <strong>of</strong> the Frog’s MouthProcedure: Pry the <strong>frog</strong>’s mouth open and use scissors tocut the angles <strong>of</strong> the <strong>frog</strong>’s jaws open. Cut deeply enoughso that the <strong>frog</strong>’s mouth opens wide enough to view thestructures inside.1. Locate the tongue.2. In the center <strong>of</strong> the mouth, toward the back is a singleround opening. This is the esophagus. This tube leads tothe stomach. Use a probe to poke into the esophagus.3. Close to the angles <strong>of</strong> the jaw are two openings, one oneach side. These are the Eustachian tubes. They are used to equalize pressure in the inner ear whilethe <strong>frog</strong> is swimming. Find the Eustachian tubes.4. Just behind the tongue, and before you reach the esophagus is a slit like opening. (You may need touse your probe to get it to open up). This slit is the glottis, and it is the opening to the lungs. The <strong>frog</strong>breathes and vocalizes with the glottis. Find the glottis.5. The <strong>frog</strong> has two sets <strong>of</strong> teeth. The vomarine teeth are found on the ro<strong>of</strong> <strong>of</strong> the mouth. Themaxillary teeth are found around the edge <strong>of</strong> the mouth. Both are used for holding prey, <strong>frog</strong>s swallowtheir meals whole and do NOT chew. Locate both sets <strong>of</strong> teeth.6. On the ro<strong>of</strong> <strong>of</strong> the mouth, you will find two tiny openings, if you put your probe into those openings,you will find they exit on the outside <strong>of</strong> the <strong>frog</strong>. These are the nostrils.