SPH 4U FINAL REVIEW Units and Significant Digits 1. Express each ...
SPH 4U FINAL REVIEW Units and Significant Digits 1. Express each ...
SPH 4U FINAL REVIEW Units and Significant Digits 1. Express each ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
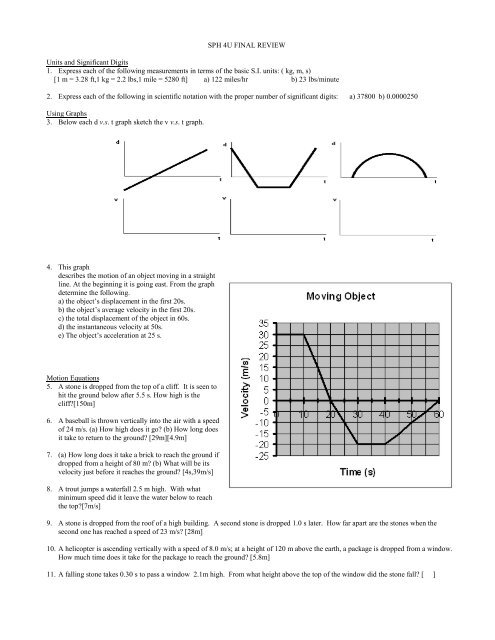
<strong>SPH</strong> <strong>4U</strong> <strong>FINAL</strong> <strong>REVIEW</strong><strong>Units</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Significant</strong> <strong>Digits</strong><strong>1.</strong> <strong>Express</strong> <strong>each</strong> of the following measurements in terms of the basic S.I. units: ( kg, m, s)[1 m = 3.28 ft,1 kg = 2.2 lbs,1 mile = 5280 ft] a ) 122 miles/hr b) 23 lbs/minute2. <strong>Express</strong> <strong>each</strong> of the following in scientific notation with the proper number of significant digits: a) 37800 b) 0.0000250Using Graphs3. Below <strong>each</strong> d v.s. t graph sketch the v v.s. t graph.4. This graphdescribes the motion of an object moving in a straightline. At the beginning it is going east. From the graphdetermine the following.a) the object’s displacement in the first 20s.b) the object’s average velocity in the first 20s.c) the total displacement of the object in 60s.d) the instantaneous velocity at 50s.e) The object’s acceleration at 25 s.Motion Equations5. A stone is dropped from the top of a cliff. It is seen tohit the ground below after 5.5 s. How high is thecliff?[150m]6. A baseball is thrown vertically into the air with a speedof 24 m/s. (a) How high does it go? (b) How long doesit take to return to the ground? [29m][4.9m]7. (a) How long does it take a brick to r<strong>each</strong> the ground ifdropped from a height of 80 m? (b) What will be itsvelocity just before it r<strong>each</strong>es the ground? [4s,39m/s]8. A trout jumps a waterfall 2.5 m high. With whatminimum speed did it leave the water below to r<strong>each</strong>the top?[7m/s]9. A stone is dropped from the roof of a high building. A second stone is dropped <strong>1.</strong>0 s later. How far apart are the stones when thesecond one has r<strong>each</strong>ed a speed of 23 m/s? [28m]10. A helicopter is ascending vertically with a speed of 8.0 m/s; at a height of 120 m above the earth, a package is dropped from a window.How much time does it take for the package to r<strong>each</strong> the ground? [5.8m]1<strong>1.</strong> A falling stone takes 0.30 s to pass a window 2.1m high. From what height above the top of the window did the stone fall? [ ]
12. A bus has stopped to pick up riders, as shown. A woman is running at aconstant velocity of + 4.0 m/s in an attempt to catch the bus. When she is 11 mfrom the door of the bus the bus pulls away with a constant acceleration of +20.75 m/s . From this point how much time does it take her to r<strong>each</strong> the door ofthe bus if she keeps running at the same velocity?13. A motorcycle travelling 90.0 km/h approaches a car travelling in the same direction at 80.0 km/h. When the motorcycle is 50 m behindthe car, the rider pushes down on the accelerator <strong>and</strong> passes the car 10.0 s later. What was the acceleration of the motorcycle? [ 0.45m/s 2 ]14. An unmarked police car travelling a constant 80 km/h is passed by a speeder travelling 100 km/h. Precisely l.0 s after the2speeder passes, the policeman steps on the accelerator; if the police car's acceleration is 2.0 m/s , how much time passes before thepolice car overtakes the speeder (assumed moving at constant speed)? [ 6.4 s]Relative Motiono15. A motorboat whose speed in still water is 9.5 km/h must aim at a 55 angle upstream in order to travel directly across the stream. (a)What is the speed of the current? (b) What is the resultant speed of the boat with respect to the shore?[7.8 km/hr,5.5 km/hr]o16. An air plane, whose air speed is 300 km/h, is supposed to fly in a straight path 30 N of E. But a steady 100 km/h wind is blowing fromothe north. In what direction should the plane head? [46.8 N of E] [hint cosine law is best for this question]Acceleration as a Vector17. An airplane is flying north at 200 m/s. It makes a gradual turn maintaining a constant speed. 20.0 s later it completes the turn <strong>and</strong> ismoving east at 200 m/s. Find the magnitude of its average acceleration while making its turn, in metres per second squared.Projectile Motion18. A golf ball is launched from the roof of the school with a velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 30 ° above horizontal. If the roof is 40 mabove the ground calculate a) the ball’s time of flight, b) the ball’s horizontal displacement. [4.1 s, 71 m]19. A ball rolls off the top of a stairway with a horizontal velocity of 5.0 m/s. The steps are 30 cm high <strong>and</strong> 30 cm wide. Which step will theball hit first?20. During a tennis match, a player serves at 32.6 m/s, the ball leaving the racquet, 2.37 m above the court surface, horizontally. By howmuch does the ball clear the net, which is 12 m away <strong>and</strong> 0.90 m high?2<strong>1.</strong> Suppose the player serves the ball as in the previous question but the ball leaves the racquet at 5.0 ° below horizontal. Does the ballclear the net now?22. A garden hose, pointed at an angle of 25 ° above the horizontal, splashes water on a sunbather lying on the ground 4.4 m away in thehorizontal direction. If the hose is held <strong>1.</strong>4 m above the ground, at what speed does the water leave the hose? [ 5.8 m/s ]23. A golf ball is driven from a level fairway. At a time of 5.10 s later, the ball is travelling downward with a velocity of 48.6 m/s [22.2 °below horizontal]. Calculate the initial velocity of the golf ball. [55.0 m/s 35.1 ° above horiz.]24. If a projectile has a launch angle of 52.2 ° above the horizontal <strong>and</strong> an initial speed of 18.0 m/s, what is the highest barrier that theprojectile can clear? [ 10.3 m ]Equilibrium25. A 15 kg store sign is hung using two ropes as shown below. Determine the tensionin <strong>each</strong> rope.
26. A wire is stretched between the tops of two identical buildings. When a tight rope walker is at the middle of the wire, the tensionoin the wire is 3000 N. Each half of the wire makes an angle of 10.0 with respect to the horizontal. Draw a free-body diagram <strong>and</strong>find the weight of the performer.Forces27. A 90 kg man is about to run across an icy pond. The coefficient of static friction between his shoes <strong>and</strong> the ice is 0.160. What ishis maximum possible acceleration? (hint: how much force can he exert without slipping?)o28. A jeep (m = 1700 kg) is parked on a hill that is inclined at 30 with respect to the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the staticfrictional force exerted by the tires? What is the coefficient of static friction?29. A train engine pulls a carriage K <strong>and</strong> a caboose C. The mass of K is 9 times the mass of C. The engine supplies a force of 1000 Nto the K <strong>and</strong> C combination to shunt them backwards onto a different track. Use a free body diagram to find the force exerted bythe coupling between K <strong>and</strong> C. [ 100 N]30. A train locomotive is pulling two cars of the same mass behind it. Show that the tension in the coupling between the locomotive<strong>and</strong> the first car is twice that between the first car <strong>and</strong> the second car, independent of the acceleration rate of the train.3<strong>1.</strong> A ball on the end of a string is revolving in a vertical circle at a radius of <strong>1.</strong>10 m. If its speed is 3.75 m/s <strong>and</strong> its mass is 0.355 kg,calculate the tension in the string when the ball is (a) at the top of its path <strong>and</strong> (b) at the bottom of its path. [<strong>1.</strong>1N,8.0N]32. What is the maximum speed with which a 1000 kg car can round a turn of radius 100 m on a flat road if the coefficient of frictionbetween the tires <strong>and</strong> the road is 0.50? Is the result independent of the mass of the car? [ v = 22 m/s , yes ]33. A 1400 kg car is travelling at 25 m/s on a circular hill of radius210 m. What is the normal force on this car at the top of the hill?34. What is the minimum speed a roller coaster must be travellingwhen upside down at the top of a circle if the passengers are notto fall out? Assume radius of curvature is 8.0 m. [ v = 8.9 m/s ]035. A curve of radius 50.0 m is banked at an angle of 16 . At what speed should a car be travelling to negociate the curve on a winterday when the icy road can be assumed to be frictionless? The car’s mass is 1200 kg. [ 12 m/s]36. In an amusement park, a 2.8 m radius “drum” rotates such that a person does not fall whenthe“floor” drops away.If the coefficient of friction between the person <strong>and</strong> the wall is 0.35, what is the maximum period of the rotation so thata person will not fall?237. A 5000-kg helicopter accelerates upwards at 0.50 m/s while lifting a 2000-kg car.4(a) What is the lift force exerted by the air on the propellers? [7.2 x 10 N ]4(b) What is the tension in the cable that connects car to helicopter? [ 2.1 x 10 N ]38. How much force is needed to accelerate a 6.0-g bullet from rest to 500 m/s over a distance of 0.70 m? [1100 N]39. Will (mass 90 kg) plans to quietly slip out of physics class by sliding down a 6.0 m long rope improvisedfrom panty hose. The rope will withst<strong>and</strong> a maximum load of 7.0 x 10² N.Calculate the minimum possible acceleration that Will can allow himself without breaking the rope.-440. A 0.10-gram spider is descending on a str<strong>and</strong> which supports it with a force of 5.6 x10 N. What is the2acceleration of the spider? Ignore air resistance. [ 4.2 m/s downward]
24<strong>1.</strong> The 4.0 kg block shown below is accelerating downwards at 3.0 m/s near the earth’s surface. What is the tension in therope attached to it?42. The mass shown at right is accelerating to the right due to the two forces acting on it. Whatis the size of the force F ?43. The system of masses shown below is accelerating to2the right at 2.0 m/s . If the tension in the rope atpoint P is 70 N, what is the coefficient of frictionbetween the masses <strong>and</strong> the surface?44. Three boxes are connected by a rope. The centre box sits on a table <strong>and</strong> the othertwo boxes are suspended from either side of the table by frictionless pulleys. Theobjects move, <strong>and</strong> the coefficient of kinetic friction between the middle object <strong>and</strong>the surface of the table is 0.100. a) what is the acceleration of the three masses? b)Find the tension in <strong>each</strong> of the two strings.45. A light rope is used to pull a 50 kg cart along a horizontal surface with no friction.oThe rope makes an angle of 60 to the horizontal. Calculate the tension in the rope2when the cart accelerates at 2 m/s . [ 200 N]046. A block of mass 10 kg is on a slope making an angle of 53 to the vertical. Calculate the coefficient of friction required to prevent itfrom sliding down the incline. [0.75]47. A 205 kg log is being pulled up a ramp by means of a rope that is parallel to the surface of the ramp. The ramp is inclined at an angle ofo30 with respect to the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the log <strong>and</strong> the ramp is 0.500, <strong>and</strong> the log has an acceleration of20.800 m/s . Find the tension in the rope. ( Hint: draw a free-body diagram)48. A man is st<strong>and</strong>ing on a scale in a moving elevator. If the reading on the scale is one half of what it is when the elevator is at rest, what isthe tension in the cable that supports the moving elevator. The mass of the man <strong>and</strong> the elevator is 500 kg.49. A space traveller weighs 500 N on earth. What will the traveller weigh on another planet whose radius is 0.5 times the radius of theearth <strong>and</strong> whose mass is 0.75 times that of earth?50. A spaceship makes a trip from earth to the moon, 380,000 km away. At what point in the trip will the gravitational field be zero? Themass of the moon is about 1/81 that of earth. [ 38 000 km from the moon]5<strong>1.</strong> Masses W, X, Y, <strong>and</strong> Z <strong>each</strong> have the same mass of + 4.0 kg. The sides of the square are 2.0 cm long. Calculate the net force on massW due to the other three masses. Draw a vector diagram.52. What is the magnitude of the electric force on a - 10 C charge if it is placed at point P in the diagram below?
Momentum <strong>and</strong> Impulse53. An atomic nucleus at rest decays radioactively into an alpha particle <strong>and</strong> a smaller nucleus. What will be the speed of this5recoiling nucleus if the speed of the alpha particle is 6.2 x 10 m/s? Assume the nucleus has a mass 57 times greater than that of4the alpha particle. [ <strong>1.</strong>09 x 10 m/s ]54. A 150-kg astronaut (including space suit) acquires a speed of 2.5 m/s by pushing off with his legs from a 2200-kg space capsule.(a) What is the change in speed of the space capsule? (b) If the push lasts 0.20 s, what was the average force exerted by <strong>each</strong> onthe other? As the reference frame, use the position of the capsule before the push. [ 0.17m/s, 1900N]55. A 15,000-kg railroad car travels alone on a level frictionless track with a constant speed of 30 m/s.A 5000-kg additional load is dropped onto the car. What then will be its speed? [23 m/s]56. A 140-kg tackler moving at 3.0 m/s meets head on (<strong>and</strong> tackles), a 90-kg halfback moving at 7.5 m/s. What will be their mutual speedimmediately after the collision? [<strong>1.</strong>1 m/s in direction of halfback ]57. An explosion blows a rock into three parts. Two pieces go off at right angles to <strong>each</strong> other, a 2.0 kg piece at 24 m/s [south] <strong>and</strong> a 4.0kg piece at 16.0 m/s [east]. The third piece flies off at 80 m/s. What is the mass of the third piece?58. A steel ball of mass 0.250 kg, moving with a velocity of 4.0 m/s strikes a second ball of mass 0.15 kg, initially at rest. The collision is aglancing one, causing the first ball to be deflected by an angle of 30 degrees, with a speed of 3.0 m/s. Determine the velocity of thesecond ball after the collision. Give both magnitude <strong>and</strong> direction.Kinetic Energy559. How much work (in joules) is done to accelerate a 1000 kg rocket sled on horizontal frictionless rails from 20 m/s to 40 m/s?[6x10 J]Elastic Collisions60. Two equal mass billiard balls undergo a perfectly elastic head-on collision. The speed of one ball was initially 2.0 m/s, <strong>and</strong> of the other3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. What will be their speeds after the collision? [ 3m/s,-2m/s]6<strong>1.</strong> A <strong>1.</strong>0 kg magnetized air puck moves across a level table at 0.18 m/s <strong>and</strong>, approaches head-on, a similarly magnetized air puck of mass0.50 kg approaching at 0.06 m/s. If the magnetic collision is repulsive <strong>and</strong> perfectly ELASTIC,a) determine the velocity of <strong>each</strong> puck after the collision.b) determine the speed of the two pucks at minimum separation.c) how much energy was stored as potential energy at minimum separation.Conservation of energy <strong>and</strong> momentum62. A 44-g bullet strikes a <strong>1.</strong>54-kg block of wood placed on a horizontal surface just in front of the gun. If the coefficient of kinetic frictionbetween the block <strong>and</strong> the surface is 0.28, <strong>and</strong> the impact drives the block a distance of 18.0 m before it comes to rest, what was themuzzle speed of the bullet? [358 m/s]63. A gun is fired vertically into a 3.40-kg block of wood directly above it. If the bullet has a mass of 62.0 g <strong>and</strong> a speed of 340 m/s, howhigh will the block rise into the air? [<strong>1.</strong>89m]64. A 5.0 kg block initially travelling at 11 m/s moves up a 30° incline as shown. A frictional forceof 9.4 N acts on the block as it moves up the incline. What maximum vertical height, h, will theblock r<strong>each</strong>?65. A 50 g bullet is fired horizontally, embedding itself in a 10 kg block initially at rest on a horizontal ice surface. The block slidesalong the ice, coming to rest in 2.0 s at a distance of 60 cm from its original position. Assuming that the frictional force stoppingthe block was constant, calculate the velocity of the bullet. Hint: Find a, then F, then W, then E , then vk66. A bullet of mass 15 g strikes <strong>and</strong> becomes embedded in a wooden block of mass 700 g, which is at reston a horizontal frictionless surface <strong>and</strong> is attached to a spring bumper. The impact compresses the spring, whose force constant is90 N/m by 25 cm.(a) What is the maximum potential energy of the spring? [2.81 J](b) Determine the velocity with which the block <strong>and</strong> bullet first begin to move? [2.8 m/s](c) What is the initial velocity of the bullet? [ 133.7 m/s](d) What is the initial kinetic energy of the bullet? [134 J](e) Explain any difference between (a) <strong>and</strong> (d).
67. A 550-N crate rests on the floor. How much work is required to move it at constant speed (a) 2.0-M along the floor against a frictionforce of 150 N, <strong>and</strong> (b) 2.0-m vertically? [ 300 Nm, 1100 Nm]68. How much work did a horse do that pulled a 200-kg wagon 80 km along a level road if the effective coefficient of friction was 0.060?6[9.4 x 10 J]69. How far must a 200-kg pile driver fall if it is to do 13,000 J of work? [6.6m]70. How much work must be done to stop a 1000-kg car travelling at 100 km/h?7<strong>1.</strong> A 5.0-kg monkey swings from one branch to other 2.0 m higher. What is the change in its potential energy?72. (a)A spring of spring constant k is initially pressed a distance x o from its normal length. What is the change in potential energy if it isnow compressed by an amount x from equilibrium? (b) The spring is now stretched a distance x o from the normal length. What is the2 2change in potential energy as compared to when it is compressed by an amount x from normal length? [ ½ k(x - x ) , 0 ]73. Tarzan is running at top speed (8.0 m/s) <strong>and</strong> grabs a vine hanging vertically from a tall tree in the jungle. How high can he swingupwards? Does the length of the vine (or rope) affect your answer? [3.3 m/s, No]74. An object slides down a frictionless 30' incline 10 cm high. How fast is it going when it r<strong>each</strong>es the bottom?75. In the high jump, the kinetic energy of an athlete is transformed into gravitational potential energy without the aid of a pole. With whatminimum speed must the athlete leave the ground in order to lift his cg 2.20 m <strong>and</strong> cross the bar with a speed of 0.80 m/s? [6.6 m/s]76. A spring whose spring constant is 850 N/m is compressed 0.40 m. What speed can it give to a 0.30-kg ball when released?[ 21 m/s ]77. A 24-kg child descends a slide 5.0-m high <strong>and</strong> r<strong>each</strong>es the bottom with a speed of 2.9 m/s. How much heat wasgenerated in this process? [ 1075 J]78. Two railroad cars, <strong>each</strong> of mass 4200 kg <strong>and</strong> travelling 80 km/h, collide head-on <strong>and</strong> come to rest. How much energy6is released during this collision? [ 2.1 x 10 J]79. A 0.25-kg pine cone falls from a branch 20 m above the ground. (a) With what speed would it hit the ground if air resistancecould be ignored? (b) If it actually hits the ground with a speed of 9.0 m/s, what was the average force of air resistance exerted onit? [20 m/s, <strong>1.</strong>9 N]380. A stationary <strong>1.</strong>60 x 10 kg vehicle is taken from the surface of the moon <strong>and</strong> placed6into a circular orbit at a height of 2.0 x 10 m above the surface of the moon. Its speed in this orbit is3<strong>1.</strong>15 x 10 m/ s. How much work is required for this process?oo8<strong>1.</strong> Assume that a 1975 Pinto having a mass of 1200 kg is projected vertically upward from the earth’s surface with an initial kinetic9energy of 8.00 x 10 J. Determine the maximum distance from the center of the earth attained by the Pinto. (Note: Pintodoes not go into orbit)24 6 -11 2 2Me = 5.98 x 10 kg Re = 6.38 x 10 m G = 6.67 x Nm /kg82. Two people are fishing from small boats located 30 m apart. Waves pass through the water <strong>and</strong> <strong>each</strong> person’s boat bobs up <strong>and</strong> down15 times in <strong>1.</strong>0 minutes. At a time when one boat is on a crest, the other one is in a trough, <strong>and</strong> there is one crest between the two boats.What is the speed of the waves?83. A double slit produces an interference pattern at a wavelength of 550 nm on a screen 0.75 m away. The slit separation is 0.12 mm. What-3is the distance between adjacent maxima on the screen? [ 3.4 x 10 m]
84. A nonreflective coating of magnesium flouride ( n = <strong>1.</strong>38) covers the glass ( n = <strong>1.</strong>52 ) of a camera lens. Assuming the coating preventsreflection of yellow-green light ( = 565 nm), determine the minimum nonzero thickness that the coating can have.-285. A parallel beam of 400 nm light falls on two small slits 4.9 x 10 mm apart. How far apart are the fringes on the screen 2.0 m away?86. If the first nodal line in a single slit diffraction pattern occurs at an angle of 15 degrees for light with a wavelenght of 580 nm, what isthe width of the slit? (2.2 m)-387. An air wedge 9.8 cm long is separated at one end by a piece of paper <strong>1.</strong>9 x 10 cm thick. The distance between centres of the first <strong>and</strong>-7eighth successive dark b<strong>and</strong>s is <strong>1.</strong>23 cm. What is the wave lenght of the light being used? (6.8 x 10 )Look over your tests: Error in measurement.The Exam: 38 multiple Choice ( 8 @ 2 marks ) 46 marks9 problems 47 marksMotionForcesEquilibriumRelative MotionProjectile MotionImpulseMomentum in 2 -DEnergy <strong>and</strong> MomentumLight
Simple Forces F = maGravitationFrictionalF = F F is the normal forcef N NCentripetalBanked CurvesHookes’ Law F = kxMomentumImpulse p = F tElectricityp = mvElastic CollisionsEnergyWork W = Fd = |F| |d| cos Kinetic2Potentialelastic E e = ½ kx where k is the spring constantgravitationalE = mgh close to earth’s surface < 100 kmg-11 2 2or , G = 6.67 x 10 Nm /kgWaves <strong>and</strong> Lightindex of refractionuniversal wave equationYoung’s Double Slit (minimum)Single Slit (minimum)Air Wedge (minimums)
Useful Math Equationspercent error = (absolute error / accepted value) x 100 %percentage difference = (difference of measurements / average of measurements) x 100 %DATA TABLEEarthMoonSunradius ......................................................................................... = 6.38 x10 6 mradius of orbit about Sun ........................................................... = <strong>1.</strong> 50 x104period of rotation....................................................................... = 8. 6 x 10 s7period of revolution about Sun.................................................. = 3.16 x 10 smass........................................................................................... = 5. 98 x10radius .........................................................................................= <strong>1.</strong> 74 x10 6 mradius of orbit about Earth ........................................................ = 3. 84 x10 8 m6period of rotation....................................................................... = 2.36 x10 s6period of revolution about Earth ............................................... = 2.36 x10 s22mass........................................................................................... = 7. 35 x10 kg30mass........................................................................................... = <strong>1.</strong> 98 x10 kgElementary charge .................................................................................. e = <strong>1.</strong>60 x 10Charge on a proton same as electron but positiveMass of electron...................................................................................... m e = 9.11 x 10Mass of proton ........................................................................................ m p = <strong>1.</strong>67 x 10Mass of neutron ...................................................................................... m p = <strong>1.</strong>68 x 10Absolute zero .......................................................................................... = -27C8Speed of light ..........................................................................................c = 3.00 x 10 m/s0Speed of sound (air 20 ) .......................................................................... v = 343 m/sConversions-19 -101 Watt = 1 J/s 1 eV = <strong>1.</strong>60 x 10 J 1 angstrom = 1 x 10 m121 mile = <strong>1.</strong>609 km 1 light-year = 9.460 x 10 km 1 inch = 2.540 cm2411mkg-19-34C-27-27kgkgkg