Getting the Upper Hand on Pain: Preventing Hand ... - IneedCE.com
Getting the Upper Hand on Pain: Preventing Hand ... - IneedCE.com
Getting the Upper Hand on Pain: Preventing Hand ... - IneedCE.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
c<strong>on</strong>servative CTS <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>rapies before c<strong>on</strong>sidering CTS surgery.<br />
Surgical patients treated three to five years after <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong>set of<br />
symptoms are less likely to have <strong>com</strong>plete symptom resoluti<strong>on</strong>.<br />
Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are important. 12 It is far<br />
easier to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome than to cure it.<br />
<strong>Pain</strong> Syndromes That Mimic Carpal Tunnel<br />
Syndrome<br />
Several problems may mimic CTS, including cervical<br />
radiculopathy, thoracic outlet syndrome, median nerve<br />
entrapment in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> forearm and trigger points, and poorly<br />
fitting gloves. (Fig. 5)<br />
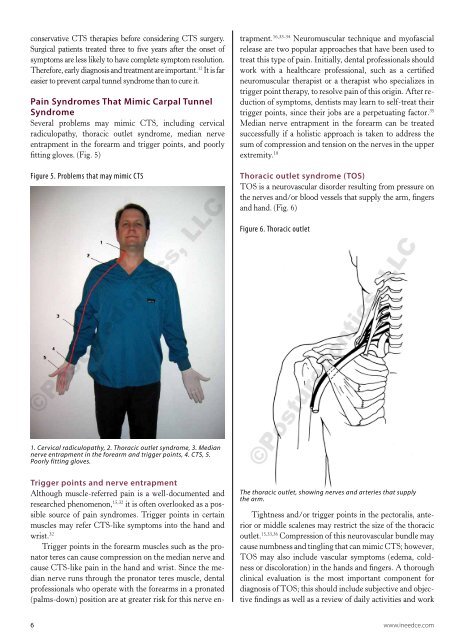
Figure 5. Problems that may mimic CTS<br />
1. Cervical radiculopathy, 2. Thoracic outlet syndrome, 3. Median<br />
nerve entrapment in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> forearm and trigger points, 4. CTS, 5.<br />
Poorly fitting gloves.<br />
Trigger points and nerve entrapment<br />
Although muscle-referred pain is a well-documented and<br />
researched phenomen<strong>on</strong>, 15,32 it is often overlooked as a possible<br />
source of pain syndromes. Trigger points in certain<br />
muscles may refer CTS-like symptoms into <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> hand and<br />
wrist. 32<br />
Trigger points in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> forearm muscles such as <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> pr<strong>on</strong>ator<br />
teres can cause <strong>com</strong>pressi<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> median nerve and<br />
cause CTS-like pain in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> hand and wrist. Since <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> median<br />
nerve runs through <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> pr<strong>on</strong>ator teres muscle, dental<br />
professi<strong>on</strong>als who operate with <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> forearms in a pr<strong>on</strong>ated<br />
(palms-down) positi<strong>on</strong> are at greater risk for this nerve en-<br />
trapment. 16,33-34 Neuromuscular technique and myofascial<br />
release are two popular approaches that have been used to<br />
treat this type of pain. Initially, dental professi<strong>on</strong>als should<br />
work with a healthcare professi<strong>on</strong>al, such as a certified<br />
neuromuscular <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>rapist or a <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>rapist who specializes in<br />
trigger point <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>rapy, to resolve pain of this origin. After reducti<strong>on</strong><br />
of symptoms, dentists may learn to self-treat <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>ir<br />
trigger points, since <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g>ir jobs are a perpetuating factor. 35<br />
Median nerve entrapment in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> forearm can be treated<br />
successfully if a holistic approach is taken to address <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
sum of <strong>com</strong>pressi<strong>on</strong> and tensi<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> nerves in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> upper<br />
extremity. 18<br />
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS)<br />
TOS is a neurovascular disorder resulting from pressure <strong>on</strong><br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> nerves and/or blood vessels that supply <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> arm, fingers<br />
and hand. (Fig. 6)<br />
Figure 6. Thoracic outlet<br />
The thoracic outlet, showing nerves and arteries that supply<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> arm.<br />
Tightness and/or trigger points in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> pectoralis, anterior<br />
or middle scalenes may restrict <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> size of <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> thoracic<br />
outlet. 15,33,36 Compressi<strong>on</strong> of this neurovascular bundle may<br />
cause numbness and tingling that can mimic CTS; however,<br />
TOS may also include vascular symptoms (edema, coldness<br />
or discolorati<strong>on</strong>) in <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> hands and fingers. A thorough<br />
clinical evaluati<strong>on</strong> is <str<strong>on</strong>g>the</str<strong>on</strong>g> most important <strong>com</strong>p<strong>on</strong>ent for<br />
diagnosis of TOS; this should include subjective and objective<br />
findings as well as a review of daily activities and work<br />
6 www.ineedce.<strong>com</strong>