dental biometrics used in forensic science - Call for papers= Asian ...
dental biometrics used in forensic science - Call for papers= Asian ...
dental biometrics used in forensic science - Call for papers= Asian ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
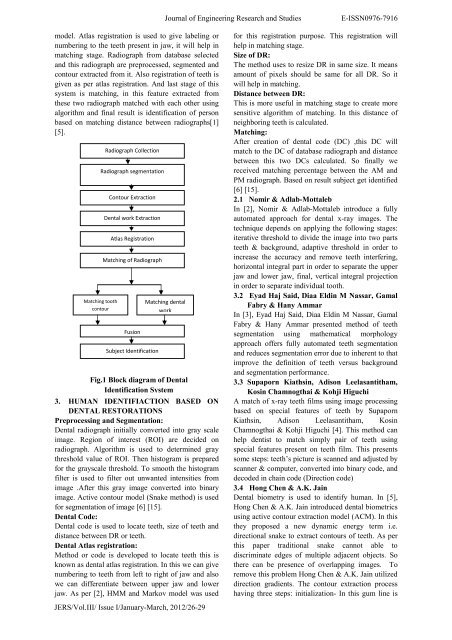
model. Atlas registration is <strong>used</strong> to give label<strong>in</strong>g or<br />
number<strong>in</strong>g to the teeth present <strong>in</strong> jaw, it will help <strong>in</strong><br />
match<strong>in</strong>g stage. Radiograph from database selected<br />
and this radiograph are preprocessed, segmented and<br />
contour extracted from it. Also registration of teeth is<br />
given as per atlas registration. And last stage of this<br />
system is match<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong> this feature extracted from<br />
these two radiograph matched with each other us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
algorithm and f<strong>in</strong>al result is identification of person<br />
based on match<strong>in</strong>g distance between radiographs[1]<br />
[5].<br />
Radiograph Collection<br />
Radiograph segmentation<br />
Match<strong>in</strong>g tooth<br />
contour<br />
Contour Extraction<br />
Dental work Extraction<br />
Atlas Registration<br />
Match<strong>in</strong>g of Radiograph<br />
Fusion<br />
Subject Identification<br />
Fig.1 Block diagram of Dental<br />
Identification System<br />
3. HUMAN IDENTIFIACTION BASED ON<br />
DENTAL RESTORATIONS<br />
Preprocess<strong>in</strong>g and Segmentation:<br />
Dental radiograph <strong>in</strong>itially converted <strong>in</strong>to gray scale<br />
image. Region of <strong>in</strong>terest (ROI) are decided on<br />
radiograph. Algorithm is <strong>used</strong> to determ<strong>in</strong>ed gray<br />
threshold value of ROI. Then histogram is prepared<br />
<strong>for</strong> the grayscale threshold. To smooth the histogram<br />
filter is <strong>used</strong> to filter out unwanted <strong>in</strong>tensities from<br />
image .After this gray image converted <strong>in</strong>to b<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
image. Active contour model (Snake method) is <strong>used</strong><br />
<strong>for</strong> segmentation of image [6] [15].<br />
Dental Code:<br />
Dental code is <strong>used</strong> to locate teeth, size of teeth and<br />
distance between DR or teeth.<br />
Dental Atlas registration:<br />
Method or code is developed to locate teeth this is<br />
known as <strong>dental</strong> atlas registration. In this we can give<br />
number<strong>in</strong>g to teeth from left to right of jaw and also<br />
we can differentiate between upper jaw and lower<br />
jaw. As per [2], HMM and Markov model was <strong>used</strong><br />
JERS/Vol.III/ Issue I/January-March, 2012/26-29<br />
Journal of Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Research and Studies E-ISSN0976-7916<br />
Match<strong>in</strong>g <strong>dental</strong><br />
work<br />
<strong>for</strong> this registration purpose. This registration will<br />
help <strong>in</strong> match<strong>in</strong>g stage.<br />
Size of DR:<br />
The method uses to resize DR <strong>in</strong> same size. It means<br />
amount of pixels should be same <strong>for</strong> all DR. So it<br />
will help <strong>in</strong> match<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Distance between DR:<br />
This is more useful <strong>in</strong> match<strong>in</strong>g stage to create more<br />
sensitive algorithm of match<strong>in</strong>g. In this distance of<br />
neighbor<strong>in</strong>g teeth is calculated.<br />
Match<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
After creation of <strong>dental</strong> code (DC) ,this DC will<br />
match to the DC of database radiograph and distance<br />
between this two DCs calculated. So f<strong>in</strong>ally we<br />
received match<strong>in</strong>g percentage between the AM and<br />
PM radiograph. Based on result subject get identified<br />
[6] [15].<br />
2.1 Nomir & Adlab-Mottaleb<br />
In [2], Nomir & Adlab-Mottaleb <strong>in</strong>troduce a fully<br />
automated approach <strong>for</strong> <strong>dental</strong> x-ray images. The<br />
technique depends on apply<strong>in</strong>g the follow<strong>in</strong>g stages:<br />
iterative threshold to divide the image <strong>in</strong>to two parts<br />
teeth & background, adaptive threshold <strong>in</strong> order to<br />
<strong>in</strong>crease the accuracy and remove teeth <strong>in</strong>terfer<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
horizontal <strong>in</strong>tegral part <strong>in</strong> order to separate the upper<br />
jaw and lower jaw, f<strong>in</strong>al, vertical <strong>in</strong>tegral projection<br />
<strong>in</strong> order to separate <strong>in</strong>dividual tooth.<br />
3.2 Eyad Haj Said, Diaa Eld<strong>in</strong> M Nassar, Gamal<br />
Fabry & Hany Ammar<br />
In [3], Eyad Haj Said, Diaa Eld<strong>in</strong> M Nassar, Gamal<br />
Fabry & Hany Ammar presented method of teeth<br />
segmentation us<strong>in</strong>g mathematical morphology<br />
approach offers fully automated teeth segmentation<br />
and reduces segmentation error due to <strong>in</strong>herent to that<br />
improve the def<strong>in</strong>ition of teeth versus background<br />
and segmentation per<strong>for</strong>mance.<br />
3.3 Supaporn Kiaths<strong>in</strong>, Adison Leelasantitham,<br />
Kos<strong>in</strong> Chamnogthai & Kohji Higuchi<br />
A match of x-ray teeth films us<strong>in</strong>g image process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
based on special features of teeth by Supaporn<br />
Kiaths<strong>in</strong>, Adison Leelasantitham, Kos<strong>in</strong><br />
Chamnogthai & Kohji Higuchi [4]. This method can<br />
help dentist to match simply pair of teeth us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
special features present on teeth film. This presents<br />
some steps: teeth’s picture is scanned and adjusted by<br />
scanner & computer, converted <strong>in</strong>to b<strong>in</strong>ary code, and<br />
decoded <strong>in</strong> cha<strong>in</strong> code (Direction code)<br />
3.4 Hong Chen & A.K. Ja<strong>in</strong><br />
Dental biometry is <strong>used</strong> to identify human. In [5],<br />
Hong Chen & A.K. Ja<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>troduced <strong>dental</strong> <strong>biometrics</strong><br />
us<strong>in</strong>g active contour extraction model (ACM). In this<br />
they proposed a new dynamic energy term i.e.<br />
directional snake to extract contours of teeth. As per<br />
this paper traditional snake cannot able to<br />
discrim<strong>in</strong>ate edges of multiple adjacent objects. So<br />
there can be presence of overlapp<strong>in</strong>g images. To<br />
remove this problem Hong Chen & A.K. Ja<strong>in</strong> utilized<br />
direction gradients. The contour extraction process<br />
hav<strong>in</strong>g three steps: <strong>in</strong>itialization- In this gum l<strong>in</strong>e is