Multiple Antigen Labeling - Vector Laboratories
Multiple Antigen Labeling - Vector Laboratories
Multiple Antigen Labeling - Vector Laboratories
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
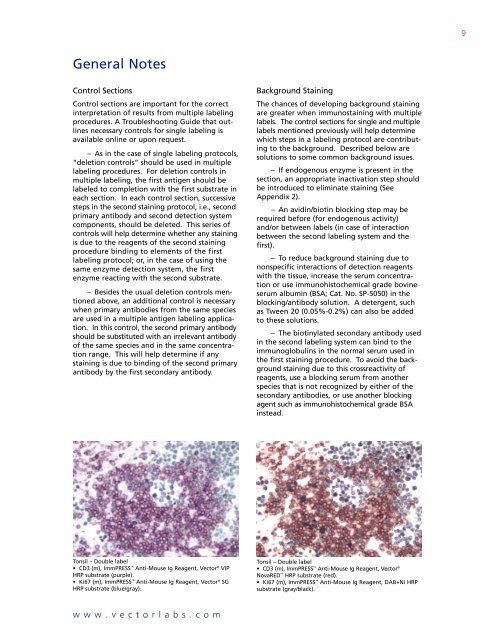
9General NotesControl SectionsControl sections are important for the correctinterpretation of results from multiple labelingprocedures. A Troubleshooting Guide that outlinesnecessary controls for single labeling isavailable online or upon request.– As in the case of single labeling protocols,“deletion controls” should be used in multiplelabeling procedures. For deletion controls inmultiple labeling, the first antigen should belabeled to completion with the first substrate ineach section. In each control section, successivesteps in the second staining protocol, i.e., secondprimary antibody and second detection systemcomponents, should be deleted. This series ofcontrols will help determine whether any stainingis due to the reagents of the second stainingprocedure binding to elements of the firstlabeling protocol; or, in the case of using thesame enzyme detection system, the firstenzyme reacting with the second substrate.– Besides the usual deletion controls mentionedabove, an additional control is necessarywhen primary antibodies from the same speciesare used in a multiple antigen labeling application.In this control, the second primary antibodyshould be substituted with an irrelevant antibodyof the same species and in the same concentrationrange. This will help determine if anystaining is due to binding of the second primaryantibody by the first secondary antibody.Background StainingThe chances of developing background stainingare greater when immunostaining with multiplelabels. The control sections for single and multiplelabels mentioned previously will help determinewhich steps in a labeling protocol are contributingto the background. Described below aresolutions to some common background issues.– If endogenous enzyme is present in thesection, an appropriate inactivation step shouldbe introduced to eliminate staining (SeeAppendix 2).– An avidin/biotin blocking step may berequired before (for endogenous activity)and/or between labels (in case of interactionbetween the second labeling system and thefirst).– To reduce background staining due tononspecific interactions of detection reagentswith the tissue, increase the serum concentrationor use immunohistochemical grade bovineserum albumin (BSA; Cat. No. SP-5050) in theblocking/antibody solution. A detergent, suchas Tween 20 (0.05%-0.2%) can also be addedto these solutions.– The biotinylated secondary antibody usedin the second labeling system can bind to theimmunoglobulins in the normal serum used inthe first staining procedure. To avoid the backgroundstaining due to this crossreactivity ofreagents, use a blocking serum from anotherspecies that is not recognized by either of thesecondary antibodies, or use another blockingagent such as immunohistochemical grade BSAinstead.Tonsil – Double label• CD3 (m), ImmPRESS Anti-Mouse Ig Reagent, <strong>Vector</strong> ® VIPHRP substrate (purple).• Ki67 (m), ImmPRESS Anti-Mouse Ig Reagent, <strong>Vector</strong> ® SGHRP substrate (blue/gray).Tonsil – Double label• CD3 (m), ImmPRESS Anti-Mouse Ig Reagent, <strong>Vector</strong> ®NovaRED HRP substrate (red).• Ki67 (m), ImmPRESS Anti-Mouse Ig Reagent, DAB+Ni HRPsubstrate (gray/black).www.vectorlabs.com