Covalent Bonding
Covalent Bonding
Covalent Bonding
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
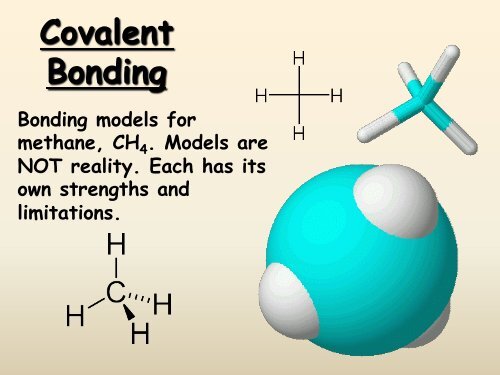
<strong>Covalent</strong><strong>Bonding</strong><strong>Bonding</strong> models formethane, CH 4 . Models areNOT reality. Each has itsown strengths andlimitations.
q Students know atoms combine to formmolecules by sharing electrons to formcovalent or metallic bonds or by exchangingelectrons to form ionic bonds.q Students know how to draw Lewis dotstructures.
Molecule <strong>Covalent</strong> Bond–Nonmetal toNonmetalSharing e -
Formation of a <strong>Covalent</strong> BondMost atoms have lower potential energywhen they are bonded to other atoms thanthey have as they are independentparticles. The figure below shows potential energychanges during the formation of a hydrogen-hydrogenbond.
Formation of a <strong>Covalent</strong> Bond• The electron of one atomand proton of the otheratom attract one another.• The two nuclei and twoelectrons repel eachother.• These two forces cancelout to form a covalentbond at a length wherethe potential energy is ata minimum.
Formation of a <strong>Covalent</strong> Bond
Characteristics of the <strong>Covalent</strong> BondThe distance between two bondedatoms at their minimum potentialenergy (the average distancebetween two bonded atoms) is thebond length.
Characteristics of the <strong>Covalent</strong> BondIn forming a covalent bond, the hydrogenatoms release energy. The same amountof energy must be added to separate thebonded atoms.Bond energy is the energy required tobreak a chemical bond and form neutralisolated atoms.
Bond EnergyClick below to watch the Visual Concept.Visual Concept
The Octet Rule and<strong>Covalent</strong> Compoundsv <strong>Covalent</strong> compounds tend to form so thateach atom, by sharing electrons, has an octetof electrons in its highest occupied energy level.v <strong>Covalent</strong> compounds involve atoms ofnonmetals only.v The term “molecule” is used exclusively forcovalent bonding (ionic bonds are referred to asformula units)
The Octet RuleClick below to watch the Visual Concept.Visual Concept
The Octet Rule:The Diatomic Fluorine MoleculeFF1s2s2pEach hasseven valenceelectrons1s2s2pF F
The Octet Rule:The Diatomic Oxygen MoleculeOO1s2s2pEach has sixvalenceelectrons1s2s2pO O
NThe Octet Rule:The Diatomic Nitrogen MoleculeN1s2s2pEach has fivevalenceelectrons1s2s2pN N
Diatomic Elements7 elements on the periodictable: They are most stablein pairs!H 2 Cl 2N 2 Br 2O 2 I 2F 2
Lewis Structuresq Lewis structures show how valence electronsare arranged among atoms in a molecule.q Lewis structures Reflect the central ideathat stability of a compound relates tonoble gas electron configuration.q Shared electrons pairs are covalent bondsand can be represented by two dots (:) orby a single line ( - )
Lewis StructuresClick below to watch the Visual Concept.Visual Concept
Lewis StructuresThe pair of dots representing ashared pair of electrons in acovalent bond are replaced by along dash.example:HH
Draw the Lewis structure ofiodomethane, CH 3 I.
Multiple <strong>Covalent</strong> BondsA double bond, is a covalent bond in whichtwo pairs of electrons are shared betweentwo atoms.Double bonds are often found inmolecules containing carbon, nitrogen,and oxygen.
Multiple <strong>Covalent</strong> BondsA triple bond, is a covalent bond in whichthree pairs of electrons are sharedbetween two atoms. Carbon & Nitrogenexample 1—diatomic nitrogen:example 2—ethyne, C 2 H 2 :
The HONC Rule" Hydrogen (and Halogens) form one covalentbond" Oxygen forms two covalent bonds" One double bond, or two single bonds" Nitrogen forms three covalent bonds" One triple bond, or three single bonds, or onedouble bond and a single bond" Carbon forms four covalent bonds." Two double bonds, or four single bonds, or a tripleand a single, or a double and two singles
carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen:remember that double bondsare possiblecarbon and nitrogen:remember that triple bondsbetween pairs of these atomsare possible.
Draw the Lewis structurefor methanal, CH 2 O,which is also known asformaldehyde.
Lewis Structure Check List1. Count the number of e- needed.2. Begin with a skeletal structure.a. Element with lowestelectronegativity goes in thecenter.b. Carbon is always in the center.c. Hydrogen and Halogens are never inthe center.
3. Add lone pairs of electrons.4. Check octet for each element:exceptions: hydrogen,beryllium, and boron5. Count electrons for correctnumber required.
Practice• Draw the Lewis DotStructures for:* CCl 4* CO* SO 2
Resonance" Occurs when more than one valid Lewisstructure can be written for a particularmolecule." These are resonance structures.The actual structure is an average ofthe resonance structures.
Resonance in SO 3