moj seminar P ... - F9
moj seminar P ... - F9
moj seminar P ... - F9
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
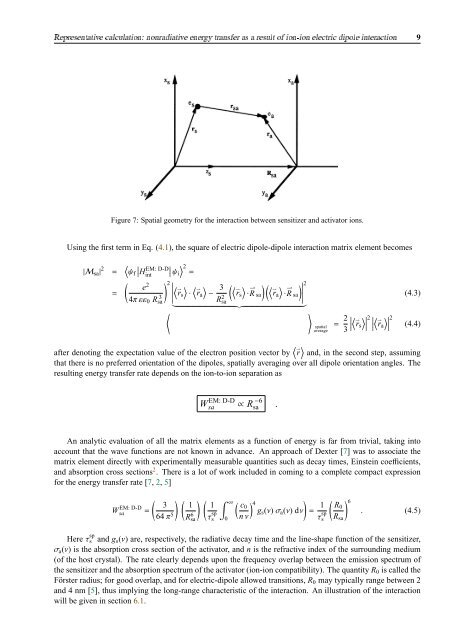
Representative calculation: nonradiative energy transfer as a result of ion-ion electric dipole interaction 9Figure 7: Spatial geometry for the interaction between sensitizer and activator ions.Using the first term in Eq. (4.1), the square of electric dipole-dipole interaction matrix element becomes|M sa | 2 = 〈 ∣ψ ∣∣H EM: D-D〉 2f ∣intψ i =(e 2 ) 2 ∣ ∣∣∣∣∣ 〈 ⇀〉 〈 ⇀〉 3(〈 ⇀〉 ) ⇀(〈 ⇀〉 ) ∣ 2 ⇀ ∣∣∣∣=4π εε 0 Rsa3 r s · r a −R 2 r s · R sa r a · R sasa}{{}〈 〉spatialaverage= 2 〈 ⇀〉∣ ∣∣∣ 2 ∣ 〈∣ r s ∣∣ ⇀〉∣ ∣∣∣ 2r a3(4.3)(4.4)after denoting the expectation value of the electron position vector by 〈 ⇀r 〉 and, in the second step, assumingthat there is no preferred orientation of the dipoles, spatially averaging over all dipole orientation angles. Theresulting energy transfer rate depends on the ion-to-ion separation asEM: D-DWsa∝ Rsa −6 .An analytic evaluation of all the matrix elements as a function of energy is far from trivial, taking intoaccount that the wave functions are not known in advance. An approach of Dexter [7] was to associate thematrix element directly with experimentally measurable quantities such as decay times, Einstein coefficients,and absorption cross sections 2 . There is a lot of work included in coming to a complete compact expressionfor the energy transfer rate [7, 2, 5](EM: D-DWsa =364 π 5 ) ( 1R 6 sa) ( 1τ sps∫ ∞0( c0) 4gs (ν) σ a (ν) dν)n ν= 1 ( ) 6 R0τ sp . (4.5)s R saHere τ sps and g s (ν) are, respectively, the radiative decay time and the line-shape function of the sensitizer,σ a (ν) is the absorption cross section of the activator, and n is the refractive index of the surrounding medium(of the host crystal). The rate clearly depends upon the frequency overlap between the emission spectrum ofthe sensitizer and the absorption spectrum of the activator (ion-ion compatibility). The quantity R 0 is called theFörster radius; for good overlap, and for electric-dipole allowed transitions, R 0 may typically range between 2and 4 nm [5], thus implying the long-range characteristic of the interaction. An illustration of the interactionwill be given in section 6.1.