- Page 1 and 2:
Cropping Systems Simulation ModelUs
- Page 3 and 4:
❍■■■■■■■■Soil■
- Page 5 and 6:
AbstractCropSyst is a is a user-fri
- Page 8 and 9:
This will save the currently edited
- Page 10 and 11:
The simulation will create a subdir
- Page 12 and 13:
DOS parameter editorTo run CropSyst
- Page 14 and 15:
●LocationThe remaining main menu
- Page 16 and 17:
edited.Simulation descriptionA desc
- Page 18 and 19:
Chemical simulationWhen enabled, ch
- Page 20 and 21:
NH4 - Ammonium (kg N/ha initial N)N
- Page 22 and 23:
Soil profile initializationCropSyst
- Page 24 and 25:
Crop and management rotation tableC
- Page 26 and 27:
extension). Create the management f
- Page 28 and 29:
Residue water content (m³/kg)refer
- Page 30 and 31:
This is different than long term sc
- Page 32 and 33:
Additional requirementsIn order for
- Page 34 and 35:
Running CropSyst from the DOS comma
- Page 36 and 37:
●●●●●●Green area indexT
- Page 38 and 39:
Management parameter editorCropSyst
- Page 40 and 41:
To delete an entry in the table, se
- Page 42 and 43:
January and December the year will
- Page 44 and 45:
specified if automatic irrigation i
- Page 46 and 47:
Based on biomassIn this mode, clipp
- Page 48 and 49:
Clipping fateFor either the Based o
- Page 50 and 51:
Contouring factorLand Slope Pc valu
- Page 52 and 53:
Based on nitrogen balanceNeed descr
- Page 55 and 56:
Tillage and residue stubble operati
- Page 57 and 58:
105 Irrigated soil dry 5 -SCSCode D
- Page 59 and 60:
119 Heavy double disc irrig. 36" 85
- Page 61 and 62:
Crop classificationThe first parame
- Page 63 and 64:
Crop planting parametersPlanting mo
- Page 65 and 66:
SoybeanSunflowerWheatGrass (cropped
- Page 67 and 68:
Thermal time to cease temperature l
- Page 69 and 70:
❍Actual transpiration.
- Page 71 and 72:
Maximum leaf area index (LAI)The le
- Page 73 and 74:
Soybean 1.4-1.8 4 - 7Sunflower 1.7-
- Page 75 and 76:
eginning of grain filling X X -phys
- Page 77 and 78:
(mm/day) 10.0 - - - - - - - - - - 1
- Page 79 and 80:
Vernalization day requirement to co
- Page 81 and 82:
Crop harvestHarvest classificationT
- Page 83 and 84:
Crop residueThe amount of residue p
- Page 85 and 86:
Crop nitrogenNitrogen fixationFor l
- Page 87 and 88:
Crop salinityOsmotic potential for
- Page 89 and 90:
Crop dormancyAverage temperature fo
- Page 91 and 92:
Soil parameter editorThe soil entry
- Page 93 and 94:
Soil volatilizationVolatilization o
- Page 95 and 96:
SCS Curve number runoffCropSyst use
- Page 97 and 98:
Soil texturePercent Sand, Clay, Sil
- Page 99 and 100:
Soil layersThe number of soil layer
- Page 101 and 102:
Information Source:❍ soil propert
- Page 103 and 104:
weather files and specify the prefi
- Page 105 and 106:
●●Arnold and William, 1989 .For
- Page 107 and 108:
❍parameters tableFor other sites,
- Page 109 and 110:
Min relative humidity, wind speedFo
- Page 111 and 112: WindWind parameters are used by the
- Page 113 and 114: Daily weather FilesWeather files ar
- Page 115 and 116: General layout optionsCurrently the
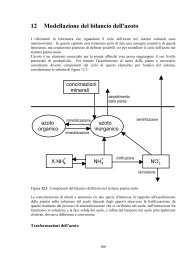
- Page 117 and 118: includes a balance for each chemica
- Page 119 and 120: Arc CropSyst CoöperatorThe Arc Cro
- Page 121 and 122: Using the ArcCS project editorThe p
- Page 123 and 124: The output page is used to specify
- Page 125 and 126: Questions●●What is a "combined
- Page 127 and 128: Note that only the numeric fields a
- Page 129 and 130: GIS Coverages/ThemesA GIS Coverage
- Page 131 and 132: 6940745.000000 21426.680000 71 70 2
- Page 133 and 134: 1.93 6.7 4 3 SOIL30.87 3.9 5 2 SOIL
- Page 135 and 136: ArcCS outputsA number of output fil
- Page 137 and 138: Error log fileA detailed error log
- Page 139 and 140: Visualizing Coöperator outputsOnce
- Page 142 and 143: Watershed wizardThe Watershed wizar
- Page 144 and 145: Graphics viewerThis utility is avai
- Page 146 and 147: Report viewerThis utility is availa
- Page 148 and 149: Batch run editorThe batch run edito
- Page 150 and 151: DOS version batch run editorLike th
- Page 152 and 153: Hints & Trouble Shooting:1.CROPSYST
- Page 154 and 155: Simulation modelThis model is a dai
- Page 156 and 157: Infiltration and soil water storage
- Page 158 and 159: PrecipitationPreciptation is taken
- Page 160 and 161: Potential evapotranspirationThe pot
- Page 164 and 165: Relhumid min % Is the minimum relat
- Page 166 and 167: λ (MJ/kg)is the latent heat of vap
- Page 168 and 169: Soil evaporationActual soil evapora
- Page 170 and 171: Runoff simulationsTwo water runoff
- Page 172 and 173: PAW * =nlΣPAW l [ Z l - Z l-1Z l]l
- Page 174 and 175: Row crops Terraced Good D 64 81 92R
- Page 176 and 177: Pasture or Range Straight row Good
- Page 178 and 179: REI' day is 0 if no daily precipita
- Page 180 and 181: contours that store moisture and re
- Page 182 and 183: greater than air dry water content
- Page 184 and 185: Original soil freezing modelThe soi
- Page 186 and 187: whereRFI1 (C- days ) is the require
- Page 188 and 189: The use of these equations is expla
- Page 190 and 191: Crop growth and developmentThe crop
- Page 192 and 193: Crop plantingCropSyst provides two
- Page 194 and 195: RootingRoot growth occurs soon afte
- Page 196 and 197: PhenologyThe stages of development
- Page 198 and 199: Above ground biomass accumulationCr
- Page 200 and 201: Crop TranspirationAs a function of
- Page 202 and 203: C Tc · K · (ψ l,sc - ψ l,wilt )
- Page 204 and 205: The fraction of GAI produced in eac
- Page 206 and 207: VernalizationVernalization in crops
- Page 208 and 209: Photo-periodPlant development may r
- Page 210 and 211: Residue surface (kg/m²) is the amo
- Page 212 and 213:
Nitrogen-dependent growthThe values
- Page 214 and 215:
CNU (kg/m²)is cumulative nitrogen
- Page 216 and 217:
UP max (kg N/day/m)is the maximum n
- Page 218 and 219:
Fix w is constrained to the range [
- Page 220 and 221:
C out (kg N/m³ water) is the nitro
- Page 222 and 223:
NRATE 35 = 0.8 (1/day) is the nitri
- Page 224 and 225:
Actual residue evaporationActual re
- Page 226 and 227:
Residue decompositionThe residue le
- Page 228 and 229:
Note: Subsurface residues (shallow,
- Page 230 and 231:
Irrigation management simulationAut
- Page 232 and 233:
Simulation of the affects of tillag
- Page 234 and 235:
steepness factor for the universal