Hip & Knee Surgery - Orthoworld
Hip & Knee Surgery - Orthoworld
Hip & Knee Surgery - Orthoworld
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
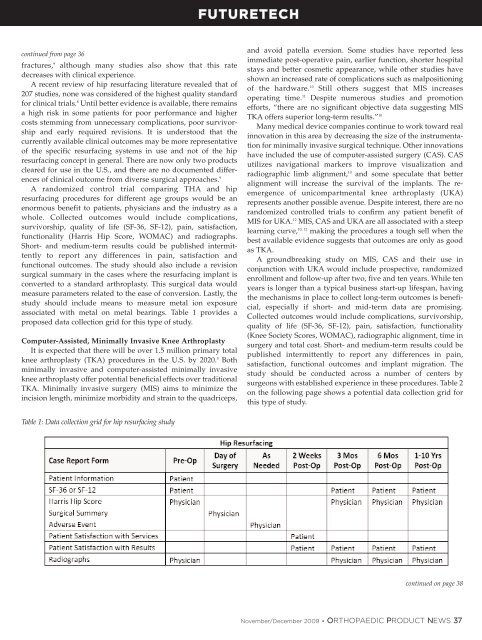
FUTURETECHcontinued from page 36fractures, 9 although many studies also show that this ratedecreases with clinical experience.A recent review of hip resurfacing literature revealed that of207 studies, none was considered of the highest quality standardfor clinical trials. 8 Until better evidence is available, there remainsa high risk in some patients for poor performance and highercosts stemming from unnecessary complications, poor survivorshipand early required revisions. It is understood that thecurrently available clinical outcomes may be more representativeof the specific resurfacing systems in use and not of the hipresurfacing concept in general. There are now only two productscleared for use in the U.S., and there are no documented differencesof clinical outcome from diverse surgical approaches. 9A randomized control trial comparing THA and hipresurfacing procedures for different age groups would be anenormous benefit to patients, physicians and the industry as awhole. Collected outcomes would include complications,survivorship, quality of life (SF-36, SF-12), pain, satisfaction,functionality (Harris <strong>Hip</strong> Score, WOMAC) and radiographs.Short- and medium-term results could be published intermittentlyto report any differences in pain, satisfaction andfunctional outcomes. The study should also include a revisionsurgical summary in the cases where the resurfacing implant isconverted to a standard arthroplasty. This surgical data wouldmeasure parameters related to the ease of conversion. Lastly, thestudy should include means to measure metal ion exposureassociated with metal on metal bearings. Table 1 provides aproposed data collection grid for this type of study.Computer-Assisted, Minimally Invasive <strong>Knee</strong> ArthroplastyIt is expected that there will be over 1.5 million primary totalknee arthroplasty (TKA) procedures in the U.S. by 2020. 5 Bothminimally invasive and computer-assisted minimally invasiveknee arthroplasty offer potential beneficial effects over traditionalTKA. Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) aims to minimize theincision length, minimize morbidity and strain to the quadriceps,and avoid patella eversion. Some studies have reported lessimmediate post-operative pain, earlier function, shorter hospitalstays and better cosmetic appearance, while other studies haveshown an increased rate of complications such as malpositioningof the hardware. 10 Still others suggest that MIS increasesoperating time. 11 Despite numerous studies and promotionefforts, “there are no significant objective data suggesting MISTKA offers superior long-term results.” 10Many medical device companies continue to work toward realinnovation in this area by decreasing the size of the instrumentationfor minimally invasive surgical technique. Other innovationshave included the use of computer-assisted surgery (CAS). CASutilizes navigational markers to improve visualization andradiographic limb alignment, 10 and some speculate that betteralignment will increase the survival of the implants. The reemergenceof unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA)represents another possible avenue. Despite interest, there are norandomized controlled trials to confirm any patient benefit ofMIS for UKA. 12 MIS, CAS and UKA are all associated with a steeplearning curve, 10, 12 making the procedures a tough sell when thebest available evidence suggests that outcomes are only as goodas TKA.A groundbreaking study on MIS, CAS and their use inconjunction with UKA would include prospective, randomizedenrollment and follow-up after two, five and ten years. While tenyears is longer than a typical business start-up lifespan, havingthe mechanisms in place to collect long-term outcomes is beneficial,especially if short- and mid-term data are promising.Collected outcomes would include complications, survivorship,quality of life (SF-36, SF-12), pain, satisfaction, functionality(<strong>Knee</strong> Society Scores, WOMAC), radiographic alignment, time insurgery and total cost. Short- and medium-term results could bepublished intermittently to report any differences in pain,satisfaction, functional outcomes and implant migration. Thestudy should be conducted across a number of centers bysurgeons with established experience in these procedures. Table 2on the following page shows a potential data collection grid forthis type of study.Table 1: Data collection grid for hip resurfacing studycontinued on page 38November/December 2009 • ORTHOPAEDIC PRODUCT NEWS 37