Trigonometric functions and circular measure - the Australian ...
Trigonometric functions and circular measure - the Australian ...
Trigonometric functions and circular measure - the Australian ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
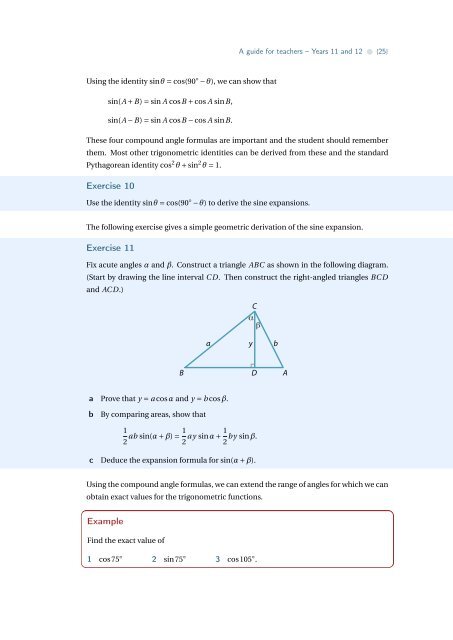
A guide for teachers – Years 11 <strong>and</strong> 12 • {25}Using <strong>the</strong> identity sinθ = cos(90 ◦ − θ), we can show thatsin(A + B) = sin A cosB + cos A sinB,sin(A − B) = sin A cosB − cos A sinB.These four compound angle formulas are important <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> student should remember<strong>the</strong>m. Most o<strong>the</strong>r trigonometric identities can be derived from <strong>the</strong>se <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ardPythagorean identity cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = 1.Exercise 10Use <strong>the</strong> identity sinθ = cos(90 ◦ − θ) to derive <strong>the</strong> sine expansions.The following exercise gives a simple geometric derivation of <strong>the</strong> sine expansion.Exercise 11Fix acute angles α <strong>and</strong> β. Construct a triangle ABC as shown in <strong>the</strong> following diagram.(Start by drawing <strong>the</strong> line interval C D. Then construct <strong>the</strong> right-angled triangles BC D<strong>and</strong> AC D.)CαβaybB D AabProve that y = a cosα <strong>and</strong> y = b cosβ.By comparing areas, show that12 ab sin(α + β) = 1 2 ay sinα + 1 by sinβ.2cDeduce <strong>the</strong> expansion formula for sin(α + β).Using <strong>the</strong> compound angle formulas, we can extend <strong>the</strong> range of angles for which we canobtain exact values for <strong>the</strong> trigonometric <strong>functions</strong>.ExampleFind <strong>the</strong> exact value of1 cos75 ◦ 2 sin75 ◦ 3 cos105 ◦ .