Course Outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
Course Outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
Course Outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
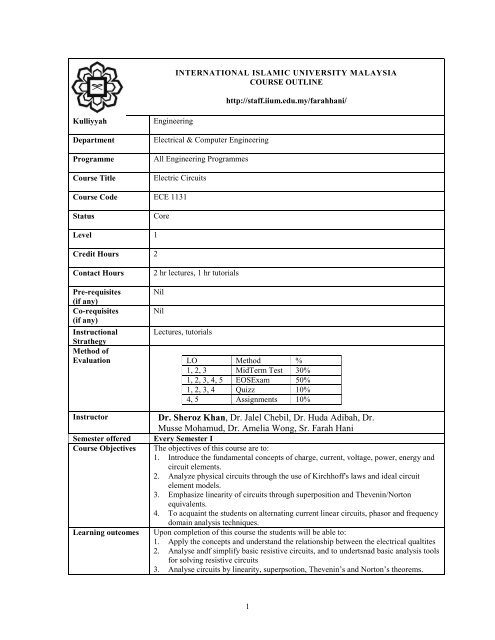
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIACOURSE OUTLINEhttp://staff.iium.edu.my/farahhani/KulliyyahDepartmentProgramme<strong>Course</strong> TitleEngineeringElectrical & Computer EngineeringAll Engineering ProgrammesElectric Circuits<strong>Course</strong> Code ECE 1131StatusCoreLevel 1Credit Hours 2Contact Hours2 hr lectures, 1 hr tutorialsPre-requisites Nil(if any)Co-requisites Nil(if any)Instructional Lectures, tutorialsStrathegyMethod ofEvaluation LO Method %1, 2, 3 MidTerm Test 30%1, 2, 3, 4, 5 EOSExam 50%1, 2, 3, 4 Quizz 10%4, 5 Assignments 10%InstructorSemester offered<strong>Course</strong> ObjectivesLearning outcomesDr. Sheroz Khan, Dr. Jalel Chebil, Dr. Huda Adibah, Dr.Musse Mohamud, Dr. Amelia Wong, Sr. Farah HaniEvery Semester IThe objectives of this course are to:1. Introduce the fundamental concepts of charge, current, voltage, power, energy andcircuit elements.2. Analyze physical circuits through the use of Kirchhoff's laws and ideal circuitelement models.3. Emphasize linearity of circuits through superposition and Thevenin/Nortonequivalents.4. To acquaint the students on alternating current linear circuits, phasor and frequencydomain analysis techniques.Upon completion of this course the students will be able to:1. Apply the concepts and understand the relationship between the electrical qualtites2. Analyse andf simplify basic resistive circuits, and to undertsnad basic analysis toolsfor solving resistive circuits3. Analyse circuits by linearity, superpsotion, Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorems.1
<strong>Course</strong> Synopsis<strong>Course</strong> <strong>Outline</strong>s /Contents4. Analyze circuits with energy storage elements.5. Analyze and simplify AC circuits using phasor and frequency domain analysistechniques.Kirchhoff voltage and current laws; Resistors in series and parallel; Delta-wye and wyedeltaconversions; Circuit theorems and analysis for resistive circuits; Maximum powertransfer theorem; Inductance and capacitance; Sinusoidal excitation of RLC circuits,phasors and phasor diagrams, ac steady-state circuit analysis using phasors; Averageand rms values of ac signals; Power calculations and power factor.Week Topics ReadingAssignment1 Basic concepts: electrical quantities - charge, current;difference between voltage and current; dc and ac voltageand current; circuit elements.Chapter 1Quizz 12, 3 Basic laws: Ohm’s law and resistivity, Kirchhoff’s laws,series resistors and voltage division, parallel resistors andcurrent division, Wye-Delta and Delta-Wyetransformation.4, 5 Methods of analysis: nodal analysis, nodal analysis withvoltage sources, mesh analysis with current source.Chapter 2Quizz 2Chapter 3Quizz 3Mid-Term Exam Friday, March 23, 2012; 0810pm6, 7, 8 Circuit theorems: source transformations, linearityproperty and superposition theorem, Thevenin’s andNorton’s theorems, maximum power transfer theorem andtheir applicationsChapter 4ReferencesProposed Start Date(Semester)Batch of Students tobe Affected9, 10 Capacitors and inductors: capacitors, series and parallelcapacitors, inductors, series and parallel inductors,practical problems and applications.11, 12,13Alternating current circuits: sinusoids, phasors, phasorsrelation for circuit elements, impedance, admittance,Kirchhoff’s laws in frequency domain, ac nodal and meshanalysis, superposition theorem, Thevenin’s and Norton’sequivalent circuits, practical problems and applications,maximum power transfer and matching theorem.14 AC power analysis: instantaneous and average power,active (or rms power ) and reactive power, apparentpower, power factor and its correction, powermeasurement in single phase circuits, practical problemsand applications.Chapter 6Chapter 9Chapter 10Quizz 4Chapter 11Quizz 5Required:Alexander, C. K. & Sadiku, M. N. O., (2007), Fundamentals of Electric Circuits,McGraw Hill.Recommended:Wilson, J. W. & Riedel, S., A., Electric Circuits, (2006), 6 th Edition Prentice Hall.Dorf, R. C. & Svoboda, J. A, (2006), Introduction to Electric Circuits, 6 th Edition, JohnWiley & Sons.Semester I, 2007-20082005 intake and onwards2
Outcome 1Outcome 2Outcome 3Outcome 4Outcome 5Outcome 6Outcome 7Outcome 8Outcome 9Outcome 10Outcome 11Outcome 12Outcome 13COURSE ASSESSMENT MATRIX: ECE 1131<strong>Course</strong> Number and NameComputer and Information Engineering Program Learning OutcomesECE11131: Electric CircuitsLO1. Apply the concepts andunderstand the relationshipbetween the electrical qualtitesLO2. Analyse andf simplify basicresistive circuits, and toundertsnad basic analysis toolsfor solving resistive circuitsLO3. Analyse circuits by linearity,superpsotion, Thevenin’s andNorton’s theorems.LO4. Analyze circuits with energystorage elements.LO5. Analyze and simplify ACcircuits using phasor andfrequency domain analysisWeightage3 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 03 0 1 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 03 0 2 2 2 2 0 1 0 0 0 03 0 3 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 03 0 3 2 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 015 0 10 8 4 2 4 2 2 0 0 0Index of Computer and Information Engineering Program Leaning Outcomes1. The ability to acquire and apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering fundamentals.2. To have abroad based education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global and scientificcontext.3. The ability to have in depth understanding and technical competency in Computer and Information / CommunicationEngineering.4. The ability to undertake problem identification, formulation and solution.5. The ability to design a component, system and process for operational performance.6. The ability to design and conduction experiments as well as to analyze and interpret data.7. The ability to understand the principles of sustainable design and development.8. The ability to effectively communicate orally, in writing and using multimedia tools.9. The ability to function effectively as an individual and in group with the capacity to be a leader or a manager as well as aneffective team leader member.10. The ability to recognize the need of life long learning and possess the ability to pursue independent learning forprofessional development.11. The ability to understand the social, cultural, global and environmental responsibilities of a professional engineer and theneed for a sustainable development.12. The ability to understand and commit to professional and ethical responsibilities.13. The ability to understand the expectations of an engineer who practices in an industrial or governmental organization.3