Course outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
Course outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
Course outline - International Islamic University Malaysia, Staff ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
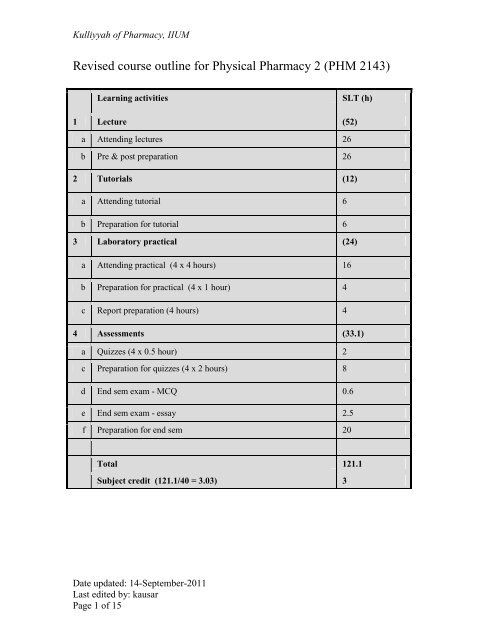
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMRevised course <strong>outline</strong> for Physical Pharmacy 2 (PHM 2143)Learning activitiesSLT (h)1 Lecture (52)a Attending lectures 26b Pre & post preparation 262 Tutorials (12)a Attending tutorial 6b Preparation for tutorial 63 Laboratory practical (24)a Attending practical (4 x 4 hours) 16b Preparation for practical (4 x 1 hour) 4c Report preparation (4 hours) 44 Assessments (33.1)a Quizzes (4 x 0.5 hour) 2c Preparation for quizzes (4 x 2 hours) 8d End sem exam - MCQ 0.6e End sem exam - essay 2.5f Preparation for end sem 20Total 121.1Subject credit (121.1/40 = 3.03) 3Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 1 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMINTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIACOURSE OUTLINEKulliyyahDepartmentProgrammePharmacyPharmaceutical TechnologyB. Pharm<strong>Course</strong> Title Physical Pharmacy 2<strong>Course</strong> Code PHM 2143StatusKulliyyah Required <strong>Course</strong>(Core course)Level 2000 (Year 2)Credit Hours 3Contact HoursPre-requisites(if any)Co-requisites(if any)InstructionalStrategiesTotal Student LearningTime (SLT).Face to Face Independent Total Guided andIndependent LearningLecture 26 26 52Tutorial 6 6 12Laboratory practical 16 8 24Assessment 5.1 28 33.1TOTAL 53.1 68 121.1 (120.6/40≈3 CH)Physical Pharmacy 1NilLecturesTutorialsLaboratory practicalDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 2 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUM<strong>Course</strong>AssessmentInstructor(s)SemesterOffered<strong>Course</strong> Synopsis<strong>Course</strong>ObjectivesLearningOutcomesLO Method %Continuous assessment 401,2,3,4 Lab practical 201,2,3 Quiz 20End-Semester Exam 601,2,3 MCQs (20 questions)20Duration: 40 mins.1,2,3 Short Essays 4 out of 520questions1,2,3 Long Essays 2 out of 320questionsDuration: 2 hours 30minsAsst. Prof. Dr. Kausar AhmadAsst. Prof. Dr. Juliana Md. JaffriAsst. Prof. Dr. MaryantoDr. Saifullah KhanProf. Zaidul Islam SarkerSemester 2This course is a continuation of Physical Pharmacy 1. The underlying principlesin drug preparation, their fluid properties and factors affecting the stability of thecolloidal systems will be emphasised.The course aims:1. To make the students understand the factors influencing the stability ofpharmaceutical emulsions and suspensions.2. To provide methods for monitoring processes and properties ofpharmaceutical preparations.3. To expose the students to the different types of mixing.4. To describe the uses of polymer in pharmaceuticals.5. To introduce students to methods in sizing.At the end of the course, students will be able to:1. Explain the different types of surfactants and polymers and how they canbe used to stabilise pharmaceuticals. (C2)2. Discuss procedures for the monitoring of the processes and properties ofpharmaceutical preparations. (A2)3. Explain rheology, Newtonian and non-Newtonian flow, mixing, andeffects of particle size on pharmaceuticals. (C2)4. Explain the findings in laboratory practical in the form of a report. (P2,CS3)Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 3 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 4 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMContent OutlinesWeeks Topics Task / Reading1 1 SurfactantsFlorence & Attwood (2006):22 1233 12Liquid crystalsIntroduction to Colloid 1Types of colloidal systems.Introduction to Colloid 2Types of emulsions.Tutorial 1 - ColloidStability of Colloid 1Factors affecting stability:electrical stabilisation, steric stabilisation.Stability of Colloid 2Destabilisation of colloidal systems:coalescence, flocculation.Aulton (2002)Dr. KausarSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Aulton (2002)Dr. KausarSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Aulton (2002)Dr. Kausar4 1235 12Characterisation of Colloid 1Microscopic and macroscopic observationsCharacterisation of Colloid 2Particle sizing, zeta potential, viscosity.Tutorial 2 - Stabilisation of ColloidalSystemsElectrical double layerElectrical double layer, repulsive effect ofdouble layer, potential energy of interaction.Electrokinetic PropertiesElectrokinetic phenomena, zeta potentialSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Aulton (2002)Dr. KausarSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Dr. KausarDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 5 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUM6 127 1238 129 12310 123Particle Size 1Particle size distribution: Number andvolume averages, polydispersity.Particle Size 2Sizing: Coulter principle.Particle Size 3Sizing: Hydrodynamic chromatography,sieving, microscopy.Particle Size 4Sizing: Laser diffraction and photoncorrelation spectroscopy.Tutorial 3 - SizingPolymer Systems 1Types of polymers.Polymer Systems 2Thermal transitions in polymers.Polymer Systems 3Polymer properties.Polymer Systems 4Polymer solutions.Tutorial 4 - PolymerPractical 1: Emulsion formationPractical 2: Effect of viscosity on emulsionPractical 3: Effect of cation on emulsionFlorence & Attwood (2006)Aulton (2002)Dr. KausarAulton (2002)Dr. KausarSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Dr. KausarSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Dr. KausarDr. KausarDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 6 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUM11 12312 12313 1214 123Rheology 1Measurements and application of rheology inpharmacy, effect of rheological properties onbioavailability.Rheology 2Effect of aggregation/flocculation, influenceof emulsifier concentration, effect ofconcentration on viscosity.Tutorial 5 – RheologyRheology 3Newtonian fluids: viscosity values, boundarylayers, laminar & turbulent flows,measurement of flow.Rheology 4Non-Newtonian fluids: types of behaviouri.e. plastic, pseudoplastic & dilatant flow,determination of flow properties,viscoelasticity, suspensions.Practical 4: ViscometryMixing 1Theory of mixing, types of mixtures, mixingprocess.Mixing 2Mixing of powders: mechanisms of mixing,segregation, ordered mixing.Mixing 3Mixing of liquids and suspensions,mixing of semi-solids.Mixing 4Examples of industrial mixers.Tutorial 6 - MixingSinko (2011)Florence & Attwood (2006)Aulton (2002)Prof. ZaidulSinko (2011)Aulton (2002)Prof. ZaidulAulton (2002)Dr. JulianaAulton (2002)Dr. JulianaDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 7 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMReferencesRequiredAulton M.E. (2002). Pharmaceutics – The Science of Dosage Form Design (2 nd Ed.).Leicester: Churchill Livingstone.Florence A.T. and Attwood, D. (2006). Physicochemical Principles of Pharmacy (4 thed.). London: Pharmaceutical PressSinko, P. J. (2011). Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences (6 thed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott.RecommendedProposedStart Date(Semester)Batch ofStudents tobe AffectedOhannesian, L & Streeter, A. J. (2002). Handbook of pharmaceutical analysis. NewYork: Marcel Dekker.Vyas, S. P & Khar, R. K. (2002). Targeted and controlled drug delivery. New Delhi:CBS.Wise, D. L. (2000). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Controlled Release Technology.New York: Marcel Dekker.2011/20122011/2012Prepared by: Checked by: Approved by:Dr. Kausar Ahmad Dr. Juliana Md. Jaffri Prof. Dato’ Dr. Tariq Abd Razak<strong>Course</strong> Coordinator Head of Department DeanDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 8 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUM<strong>Course</strong> Assessment Matrix: PHM 2213Programme Outcomes<strong>Course</strong> Learning OutcomesPO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9Explain the different types of surfactants and polymers and howthey can be used to stabilise pharmaceuticals. (C2)Discuss procedures for the monitoring of the processes andproperties of pharmaceutical preparations. (A2)Explain rheology, Newtonian and non-Newtonian flow, mixing,and effects of particle size on pharmaceuticals. (C2)Explain the findings in laboratory practical in the form of a report.(P2, CS3)√ √ √√ √ √√ √ √√ √ √Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 9 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMThe educational outcomes of the programme conducted by the Kulliyyah of PharmacyAt the end of the programme, students should be able to:1. Knowledge: Demonstrate familiarity in all aspects of drugs beginning with their origin (synthetic or naturalproducts), medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, compounding or manufacturing and their usage.2. Practical Skills: Use relevant skills learnt as part of professional and personal growth for future pharmacists’roles and research in various settings.3. Social Skills and Responsibilities: Implement the concept of pharmaceutical care in a socially responsiblemanner for the progress of the nation and the Ummah.4. Values, Attitudes and Professionalism: Demonstrate commitment to ethics, autonomy and professionalism inpharmacy.5. Communication, Leadership and Team Skills: Apply effective communication skills in the delivery ofpharmaceutical care, perform patient counselling and monitoring and show leadership qualities in working as ateam.6. Problem Solving and Scientific Skills: Analyse the common signs and symptoms, laboratory findings and drugsin the identification and resolution of drug related problem and management of common disorders involvingvarious body systems.7. Information Management and Lifelong Learning Skills: Use the necessary learning skills in informationmanagement and apply effective strategies for lifelong self-improvement.8. Managerial and Entrepreneurial Skills: Apply basic managerial and entrepreneurial skills for pharmacists incompounding or manufacturing, business, administration and management.9. Islamization: Apply <strong>Islamic</strong> principles as part of professional ethics for pharmacists and analyse scientificissues from the <strong>Islamic</strong> perspective.Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 10 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMProgramme Aims<strong>Course</strong> Learning OutcomesA1 A2 A3 A4Explain the different types of surfactants and polymers and how theycan be used to stabilise pharmaceuticals. (C2)Discuss procedures for the monitoring of the processes and propertiesof pharmaceutical preparations. (A2)Explain rheology, Newtonian and non-Newtonian flow, mixing, andeffects of particle size on pharmaceuticals. (C2)Explain the findings in laboratory practical in the form of a report.(P2, CS3)√√√√√√√√Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 11 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMProgramme Aims1. To enable students to become competent and competitive professionals who are life-long learners in the field ofpharmacy.2. To inculcate commitment to Islam and its values in the students so that they abide by the <strong>Islamic</strong> code ofconduct in both their personal and professional life.3. To develop the potentials of the students for participation in the overall nation-building so that they maycontribute towards the well-being and development of the nation.4. To produce pharmacists who are patient focused in providing pharmaceutical care services and who will be ableto specialize in any field of pharmacy.Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 12 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMTable 1: Summary of Student Learning TimeLearning activitiesSLT (h)Learning activitiesSLT (h)1 Lecture (52)4 Assessments (33.1)a Attending lectures 26a Quizzes (4 x 0.5 hour) 2b Pre & post preparation 26b Preparation for quiz (4 x 2 hours) 82 Tutorials (12)a Attending tutorial 6d End sem exam - 20 MCQs 0.6b Preparation for tutorial 6e End sem exam - essay 2.53 Laboratory practical (24)f Preparation for end sem 20a Attending practical (4 x 4 hours) 16b Preparation for practical (4 x 1 hour) 4Total 121.1c Report preparation (4 hours) 4Subject credit121.1/40 = 3.033Date updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 13 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 14 of 15
Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, IIUMTable 2: Record of changes to course <strong>outline</strong>No Date Description of changes made Changed by1 10/8/09 1. Change End of Semester Long Essay Questions to answer TWO out of THREE Kausarquestions instead of TWO out of FOUR questions. Action taken followingexternal examiner’s report, which was again mentioned during Kulliyyah Boardmeeting 5/8/09.2. Revised name of lecturers involved.2 17/8/09 Add a summary of Student Learning Time Kausar3 11/5/10 1. Revise course objectives and learning outcomes (after briefing by Dr. Badri) Kausar2. Add 0.5 hour to essay exam in mid-sem and end sem exams.3. Revised matrix of learning outcome versus programme outcome4 11/6/10 1. Follow MQA format as per PHM3142 (provided as example):Kausara. SLT at first pageb. SLT indicated in contact hoursc. Include programme aims and matrix2. Remove Size Exclusion Chromatography as per Academic Review 20105 21/6/10 Revise Programme Aims item no. 4 as per instruction from Deputy Dean via e-mail Kausar17/6/10.6 20/10/10 Replace mid semester exam with continuous assessment Kausar7 17/3/11 1. Restructure sequence of lectures and laboratory practicalKausar2. <strong>Course</strong> code in red to indicate changes made during the academic review (toshift the course from semester 2 to semester 1)8 30/6/11 1. References of latest editionKausar2. Change course code from PHM2213 to PHM21439 14/9/11 1. Prof. Zaidul replacing Dr. Saifullah for the teaching of topics in rheology.2. Remove chapters and pages from references.KausarDate updated: 14-September-2011Last edited by: kausarPage 15 of 15