Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 6 - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 6 - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 TEST Chapter 6 - Pearson Australia Media ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
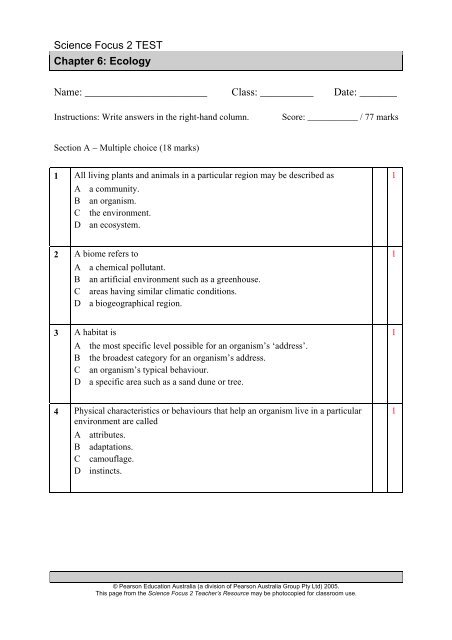
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: EcologyName: _______________________ Class: __________ Date: _______Instructions: Write answers in the right-hand column.Score: ___________ / 77 marksSection A − Multiple choice (18 marks)1 All living plants and animals in a particular region may be described asA a community.B an organism.C the environment.D an ecosystem.12 A biome refers toA a chemical pollutant.B an artificial environment such as a greenhouse.C areas having similar climatic conditions.D a biogeographical region.13 A habitat isA the most specific level possible for an organism’s ‘address’.B the broadest category for an organism’s address.C an organism’s typical behaviour.D a specific area such as a sand dune or tree.14 Physical characteristics or behaviours that help an organism live in a particularenvironment are calledA attributes.B adaptations.C camouflage.D instincts.1© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology5 Which of the following is an abiotic factor that influences where an organismcan live?A Humidity.B Predation.C Human intervention.D Competition from other organisms.16 Salinity is a measure ofA the number of organisms in a particular region.B the acidity of soil.C the amount of water vapour in the air.D the salt content of water.7 The original source of all energy used by organisms isA plants.B water.C glucose.D the Sun.8 A secondary consumer isA a plant.B an animal that eats plants.C an animal that eats an animal that eats plants.D an omnivore.9 Each ‘link’ in a food chain isA a plant.B an animal.C an organism.D a carnivore.10 Communities with high biodiversity are more likely to survive environmentalchanges because theyA contain more than one type of food source for the organisms within them.B have denser plant growth, which insulates the community from suchchanges.C are generally popular tourist attractions and are protected by law.D consist of large numbers of only a few species.11111© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology11 The number of producers in a food chain isA less than the number of producers.B the same as the number of consumers.C greater than the number of consumers.D possibly any of the above, depending on the organisms involved.12 A decomposer isA an animal that eats another animal.B a plant that loses its leaves in winter.C an organism which breaks down organic matter so it is recycled.D an animal that uses sound as its main method of communication.13 The interaction between a remora (a type of sucker fish) and a shark to which itattaches is an example of commensalism becauseA the remora benefits, but the shark is harmed.B the remora benefits, but the shark is unaffected.C the remora is unaffected, but the shark is harmed.D both fish benefit from their relationship.14 The impact of humans on the ecosystem increased suddenly after theA environmental convolution.B mechanical inspiration.C climatic illusion.D industrial revolution.15 A pollutant isA a substance created by human activity that harms the environment.B a natural or artificial substance that makes the environment unhealthy forsome organisms.C a gas such as sulfur dioxide that is able to reach the atmosphere.D something produced when a fossil fuel is burnt.16 The greenhouse effect occurs because gases released into the atmosphere causeA plants to grow too quickly and rob the atmosphere of vital gases.B heat to be trapped on the Earth.C the hole in the ozone layer to increase in size.D the atmosphere to become too thin and allow more energy to escape fromthe Earth.17 Which of the following are introduced species as far as <strong>Australia</strong> is concerned?A Rabbit.B Carp.C Pig.D All of the above.1111111© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology18 Frogs in <strong>Australia</strong> are considered to be environmental indicators becauseA they are the most common <strong>Australia</strong>n animal and so may be easily caughtand studied.B they are at the bottom of the food chain.C they breathe through their skin and depend on water, so pollutants tend toaffect them strongly.D they change colour in response to pollutants.1Section B − Written answers (59 marks)1 Classify the following in order fromsmallest to largest:biome, microhabitat, biosphere, habitat,biogeographical region32 Match each of the following with one ofthe regions given in the previousquestion.a Just under the surface of somedesert sand.b The part of our planet where lifeexists.c Grassland.d A tussock of grass.e <strong>Australia</strong>.53 Identify two examples ofa organisms.b the non-living environment.44 Describe the characteristics of anorganism which lives most of its lifeunder the desert sand.2© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology5 Animal species suffer reductions inpopulations during or immediately aftera fire. Identify how some escape thefire.36 Identifya an animal and describe twophysical adaptations.b an animal (it may be the sameone as above) and describe twobehavioural adaptations.7 Describe how each of the followingaffects organisms. Give a specificexamples.a Temperature.b Humidity.c Light availability.d Acidity.448 Clarify each of the following factorsthat affect where an organism can live.a Competition.b Dispersal.c Predation.d Human intervention.4© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology9 Identify a biotic factor and an abioticfactor (in that order) that may affect akookaburra.310 Classify each of the following as aherbivore, carnivore or omnivore.a Crocodile.b Deer.c Blue-tongue lizard.11 Draw arrows identifying the linksbetween the following animals in apossible food web.snake, garden skink, kookaburra, fly33© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology12 a Explain why a food web is moreaccurate than a food chain.b Use arrows to identify severalconnections in the food webbelow.413 Choose one of the terms listed todescribe each of the followinginteractions.mutualism, competition, amensalism,herbivory, parasitism, predationa A small bird picks insects from arhinoceros’s hide.b Wallabies using a particular routerepeatedly eventually wear a trailin the bush.c A tick burrows into the skin of astumpy tail lizard, causing minorskin irritation.d A koala eats the leaves on abranch of a gum tree.4© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology14 a Use the graph below to estimatewhat the human population wasin the year 2000.b Predict the range of values thatthe population will lie between inthe year 2020.315 Identify four types of waterway andocean pollution.416 Describe the cause of two of the typesof pollution in the previous question.2© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.
<strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 <strong>TEST</strong><strong>Chapter</strong> 6: Ecology17 Outline the problems caused by twodifferent introduced species.218 Propose two ways of encouragingconservation of our native plants andanimals.2© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource may be photocopied for classroom use.