Principles of Linear Algebra With Maple The NewtonâRaphson ...
Principles of Linear Algebra With Maple The NewtonâRaphson ...
Principles of Linear Algebra With Maple The NewtonâRaphson ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
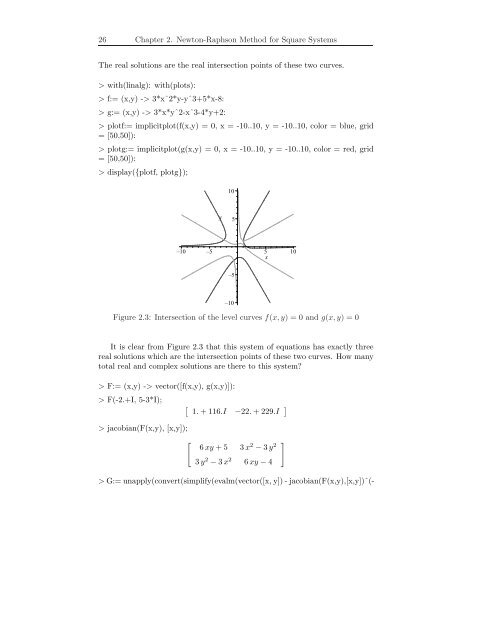
26 Chapter 2. Newton-Raphson Method for Square Systems<strong>The</strong> real solutions are the real intersection points <strong>of</strong> these two curves.> with(linalg): with(plots):> f:= (x,y) -> 3*xˆ2*y-yˆ3+5*x-8:> g:= (x,y) -> 3*x*yˆ2-xˆ3-4*y+2:> plotf:= implicitplot(f(x,y) = 0, x = -10..10, y = -10..10, color = blue, grid= [50,50]):> plotg:= implicitplot(g(x,y) = 0, x = -10..10, y = -10..10, color = red, grid= [50,50]):> display({plotf, plotg});10y5–10 –5 5 10x–5–10Figure 2.3: Intersection <strong>of</strong> the level curves f(x,y) = 0 and g(x,y) = 0It is clear from Figure 2.3 that this system <strong>of</strong> equations has exactly threereal solutions which are the intersection points <strong>of</strong> these two curves. How manytotal real and complex solutions are there to this system?> F:= (x,y) -> vector([f(x,y), g(x,y)]):> F(-2.+I, 5-3*I);[ 1.+116.I −22.+229.I]> jacobian(F(x,y), [x,y]);[6xy +5 3x 2 −3y 2]3y 2 −3x 26xy −4>G:=unapply(convert(simplify(evalm(vector([x,y])-jacobian(F(x,y),[x,y])ˆ(-