Cheat Sheet for Exam #1 on Thermodynamics and ... - Chemistry
Cheat Sheet for Exam #1 on Thermodynamics and ... - Chemistry
Cheat Sheet for Exam #1 on Thermodynamics and ... - Chemistry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
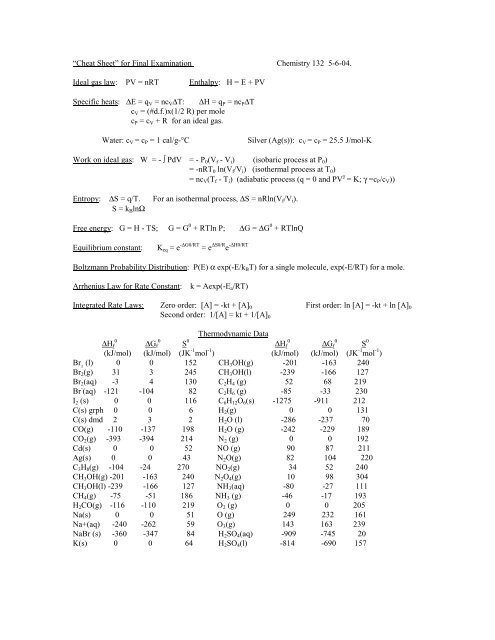
“<str<strong>on</strong>g>Cheat</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>Sheet</str<strong>on</strong>g>” <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> Final <str<strong>on</strong>g>Exam</str<strong>on</strong>g>inati<strong>on</strong> <strong>Chemistry</strong> 132 5-6-04.Ideal gas law: PV = nRT Enthalpy: H = E + PVSpecific heats: ∆E = q V = nc V ∆T: ∆H = q P = nc P ∆Tc V = (#d.f.)x(1/2 R) per molec P = c V + R <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> an ideal gas.Water: c V = c P = 1 cal/g-°CSilver (Ag(s)): c V = c P = 25.5 J/mol-KWork <strong>on</strong> ideal gas: W = - ∫ PdV = - P 0 (V f - V i ) (isobaric process at P 0 )= -nRT 0 ln(V f /V i ) (isothermal process at T 0 )= nc V (T f - T i ) (adiabatic process (q = 0 <strong>and</strong> PV γ = K; γ =c P /c V ))Entropy: ∆S = q/T. For an isothermal process, ∆S = nRln(V f /V i ).S = k B lnΩFree energy: G = H - TS; G = G 0 + RTln P; ∆G = ∆G 0 + RTlnQEquilibrium c<strong>on</strong>stant:K eq = e -∆G0/RT = e ∆S0/R e -∆H0/RTBoltzmann Probability Distributi<strong>on</strong>: P(E) α exp(-E/k B T) <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> a single molecule, exp(-E/RT) <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> a mole.Arrhenius Law <str<strong>on</strong>g>for</str<strong>on</strong>g> Rate C<strong>on</strong>stant:k = Aexp(-E a /RT)Integrated Rate Laws: Zero order: [A] = -kt + [A] 0 First order: ln [A] = -kt + ln [A] 0Sec<strong>on</strong>d order: 1/[A] = kt + 1/[A] 0Thermodynamic Data0∆H f0∆G f S 0 0∆H f0∆G f S 0(kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) (JK -1 mol -1 ) (kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) (JK -1 mol -1 )Br 2(l) 0 0 152 CH 3 OH(g) -201 -163 240Br 2 (g) 31 3 245 CH 3 OH(l) -239 -166 127Br 2 (aq) -3 4 130 C 2 H 4 (g) 52 68 219Br - (aq) -121 -104 82 C 2 H 6 (g) -85 -33 230I 2 (s) 0 0 116 C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) -1275 -911 212C(s) grph 0 0 6 H 2 (g) 0 0 131C(s) dmd 2 3 2 H 2 O (l) -286 -237 70CO(g) -110 -137 198 H 2 O (g) -242 -229 189CO 2 (g) -393 -394 214 N 2 (g) 0 0 192Cd(s) 0 0 52 NO (g) 90 87 211Ag(s) 0 0 43 N 2 O(g) 82 104 220C 3 H 8 (g) -104 -24 270 NO 2 (g) 34 52 240CH 3 OH(g) -201 -163 240 N 2 O 4 (g) 10 98 304CH 3 OH(l) -239 -166 127 NH 3 (aq) -80 -27 111CH 4 (g) -75 -51 186 NH 3 (g) -46 -17 193H 2 CO(g) -116 -110 219 O 2 (g) 0 0 205Na(s) 0 0 51 O (g) 249 232 161Na+(aq) -240 -262 59 O 3 (g) 143 163 239NaBr (s) -360 -347 84 H 2 SO 4 (aq) -909 -745 20K(s) 0 0 64 H 2 SO 4 (l) -814 -690 157
ElectrochemistryElectr<strong>on</strong>egativities∆G = -nFE C 2.5 H 2.1∆G = ∆G 0 + RTlnQ S 2.5 Cu 1.9E =E 0 - (0.0592/n) log 10 Q F 4.0 O 3.5log 10 K eq = nE 0 /0.0592 N 3.0W elec = q EZUMDAHL TABLE 11.1 HEREUseful c<strong>on</strong>stants <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>versi<strong>on</strong>s: 1 cal = 4.184 J 1 lit-atm = 101.3 JF = 96,485 coul/mole e = 1.6 x 10 -19 coul/electr<strong>on</strong> 1 Debye = 3.336 x 10 -30 coul-mc = 3 x 10 8 m/s k B = 1.38 x 10 -23 J/K R = 8.31 J/mole-KN 0 = 6.02 x 10 23 molecules/mole 1 amu = 1.66 x 10 -27 kg h = 6.63 x 10 -34 J-sε 0 = 8.85 x 10 -12 coul 2 /J-m m electr<strong>on</strong> = 9.1 x 10 -31 kg 1 Ampere = 1 coul/sec1 nm = 10 -9 m 1 Angstrom = 10 -10 mAverage b<strong>on</strong>d energies (KJ/mole)Atomic Radii (pm)N-H 391 C-N 305 N=O 607 Cs 265C≡C 839 C=N 615 N≡N 941 F 72H-H 432 I-I 149 C=C 614 C 91N-N 160 C-C 347 O=O 495 Cl 99O-H 467 C-O 358 C=O 799
Quantum Mechanicsphot<strong>on</strong> energy: Heisenberg Uncertainty: DeBroglie Wavelength:E = hν = hc/λ ∆p∆x ≥ h/4π λ = h/mvSchrödinger Equati<strong>on</strong> Hψ = Eψ : (-h 2 /8π 2 m)d 2 ψ/dψ 2 + V(x)ψ = EψH-atom: V = -Ze 2 /4πε 0 r E n = -Z 2 me 4 /(8n 2 h 2 ε 0 2 ) = 2.178 x 10 -18 (Z 2 /n 2 ) (in Joules) a 0 = 0.0529 nmSAMPLE HYDROGENICWAVEFUNCTIONS HERE.Dipole moment: µ = qRMelting Points <strong>and</strong> Heats of Fusi<strong>on</strong>: Intermolecular potentialMelting Point Enthalpy of Fusi<strong>on</strong> (KJ/mol) (Lennard-J<strong>on</strong>es)O 2 -218 0.45 V = - aR -6 + bR -12HCl -114 1.99HI -51 2.87CCl 4 -23 2.51CHCl 3 -64 9.2NaF 992 29.3NaCl 801 30.2ln ((P vap (T 1 ) /( P vap (T 2 )) = (∆H vap /R)(1/T 2 - 1/T 1 ) Clausius-Clayper<strong>on</strong> Equati<strong>on</strong>P = k H χ Henry’s Law: k H = 413 atm (CH 4 in water), 1640 atm (CO 2 in water), 43400 atm (O 2 in water)P(soluti<strong>on</strong>) = χ(solvent)P 0 (solvent) : Raoult’s Law