Revision Checklist â IGCSE MATHEMATICS FOUNDATION TIER
Revision Checklist â IGCSE MATHEMATICS FOUNDATION TIER
Revision Checklist â IGCSE MATHEMATICS FOUNDATION TIER
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
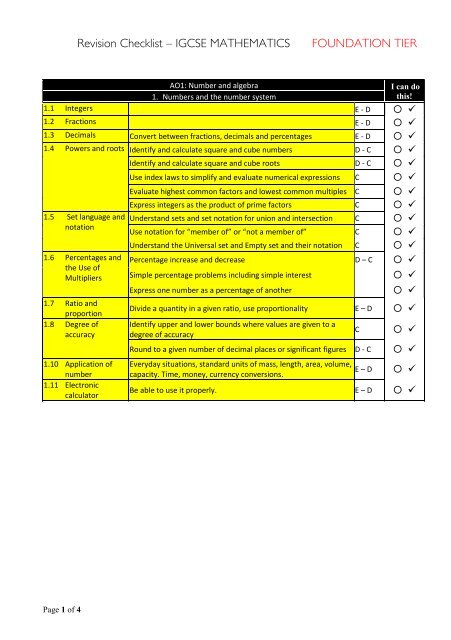
<strong>Revision</strong> <strong>Checklist</strong> – <strong>IGCSE</strong> <strong>MATHEMATICS</strong><strong>FOUNDATION</strong> <strong>TIER</strong>AO1: Number and algebra1. Numbers and the number systemI can dothis!1.1 Integers E - D ◦ 1.2 Fractions E - D ◦ 1.3 Decimals Convert between fractions, decimals and percentages E - D ◦ 1.4 Powers and roots Identify and calculate square and cube numbers D - C ◦ Identify and calculate square and cube roots D - C ◦ Use index laws to simplify and evaluate numerical expressions C ◦ Evaluate highest common factors and lowest common multiples C ◦ Express integers as the product of prime factors C ◦ 1.5 Set language andnotation1.6 Percentages andthe Use ofMultipliers1.7 Ratio andproportion1.8 Degree ofaccuracy1.10 Application ofnumber1.11 ElectroniccalculatorUnderstand sets and set notation for union and intersection C ◦ Use notation for “member of” or “not a member of” C ◦ Understand the Universal set and Empty set and their notation C ◦ Percentage increase and decrease D – C ◦ Simple percentage problems including simple interestExpress one number as a percentage of another◦ ◦ Divide a quantity in a given ratio, use proportionality E – D ◦ Identify upper and lower bounds where values are given to adegree of accuracyC◦ Round to a given number of decimal places or significant figures D - C ◦ Everyday situations, standard units of mass, length, area, volume,capacity. Time, money, currency conversions.E – D◦ Be able to use it properly. E – D ◦ Page 1 of 4
<strong>Revision</strong> <strong>Checklist</strong> – <strong>IGCSE</strong> <strong>MATHEMATICS</strong><strong>FOUNDATION</strong> <strong>TIER</strong>2.1 Use of symbols2.2 AlgebraicmanipulationAO1: Number and algebra2. Equations, formulae and identitiesI can dothis!Use index notation involving positive integer powers C ◦ Expand the product of two linear expressions C ◦ Collect like terms E - D ◦ Multiply out a single bracket E - D ◦ 2.3 Expressions andformulae Substituting values into a formula C ◦ 2.4 Linear equations Sole with integer or fractional coefficients in one unknown, whichmay appear on both sides of the equation.E – DSet up simple equations from given data (eg perimeter of a shape)2.6 Simultaneousequations2.8 Inequalities◦ Calculate the exact solution of two unknowns C ◦ Define regions defined by inequalities on a graph C ◦ Understand inequality symbols and number line conventions C ◦ Solve linear inequalities in one unknown and represent thesolution on a number lineC◦ AO1: Number and algebra3. Sequences, functions and graphs3.1 Sequences Find a pattern in a linear sequence and generate subsequentterms3.3 GraphsCI can dothis!◦ Calculate the gradient of a straight line C ◦ Interpret information from linear and non-linear graphs E – D ◦ Understand 2D Cartesian coordinates D - C ◦ Calculate the gradient of a straight line C ◦ Recognise that equations of the form are straight lines C ◦ Generate points and plot linear and quadratic functions on agraphPage 2 of 4
<strong>Revision</strong> <strong>Checklist</strong> – <strong>IGCSE</strong> <strong>MATHEMATICS</strong><strong>FOUNDATION</strong> <strong>TIER</strong>4.1 AnglesAO2: Shape, space and measures4. GeometryI can dothis!Alternate, corresponding and interior angles D - C ◦ 4.2 Polygons Interior angles and their sum, exterior angles and their sumProperties of quadrilaterals incl. kite, rhombus, trapezium,parallelogram, congruenceE – D◦ 4.3 Symmetry Lines of symmetry, order of rotational symmetry E – D ◦ 4.4 Measures Distance, speed, time. Degrees, bearings. Clocks. E – D ◦ 4.5 Constructions Scale drawingBisector of an angle, perpendicular bisector of a line.4.6 Circle Properties Recognise radius, diameter, circumference, tangent, arc, sector,chord, segment.Understand the properties of chords and tangents4.7 Geometrical Provide reasons using standard geometrical statements toreasoning support angles found in a geometrical context4.8 Trigonometry and Understand and use sine, cosine and tangent including obtusePythagoras’ anglestheoremCCCC◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Use Pythagoras's theorem in 2D C ◦ Use trigonometric methods to solve 2D problems C ◦ 4.9 Mensuration Area and perimeter (includes circles) E -C ◦ 4.10 3D shapes andvolumeRecognise solids and the terms face, edge, vertex D - C ◦ Calculate volumes of prisms and simple surface areas D - C Convert between volume measures C ◦ 4.11 Similarity Understand that the areas of similar figures are in the ratio of thesquare of their corresponding sidesC◦ Interpret maps and scale drawings E - C ◦ 5.2 TransformationgeometryAO2: Shape, space and measuresVectors and transformation geometryReflections, rotation, translations and enlargementsD - CI can dothis!◦ Page 3 of 4
<strong>Revision</strong> <strong>Checklist</strong> – <strong>IGCSE</strong> <strong>MATHEMATICS</strong><strong>FOUNDATION</strong> <strong>TIER</strong>6.1 Graphicalrepresentation ofdata6.2 StatisticalmeasuresAO3: Handling data6. StatisticsI can dothis!Pictograms, bar charts and pie charts C ◦ Interpretation of statistical diagrams C ◦ Frequency tables and tallies C ◦ Mean, mode and median D ◦ Range C ◦ Estimate the mean from grouped data C ◦ Identify the modal class from grouped data C ◦ 6.3 Probability Simple probability C ◦ Sample space for one or two events C ◦ Estimate probability from data, expected frequency C ◦ Addition rule for mutually exclusive events C ◦ Page 4 of 4