Fleksibilni Internet servisi na bazi kontrole kašnjenja i
Fleksibilni Internet servisi na bazi kontrole kašnjenja i
Fleksibilni Internet servisi na bazi kontrole kašnjenja i
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
RED has been designed to cooperate with TCP’s congestion control algorithm.<br />
TCP flows recognize packet losses as a sign of congestion and reduce their sending rate.<br />
RED begins to drop packets before the buffer overflows and, thus, provides an early<br />
feedback about congestion level on the output link and allows TCP flows to react in a<br />
timely manner. The interval where average queue sizes lie between qmin and qmax is called<br />
early drop region.<br />
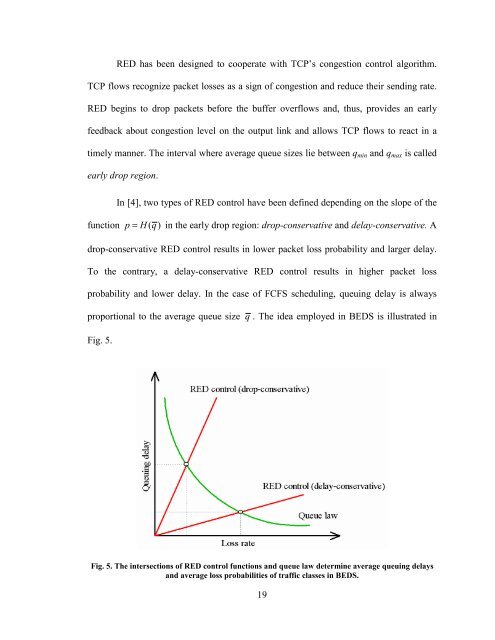
In [4], two types of RED control have been defined depending on the slope of the<br />
function p = H (q)<br />
in the early drop region: drop-conservative and delay-conservative. A<br />
drop-conservative RED control results in lower packet loss probability and larger delay.<br />
To the contrary, a delay-conservative RED control results in higher packet loss<br />
probability and lower delay. In the case of FCFS scheduling, queuing delay is always<br />
proportio<strong>na</strong>l to the average queue size q . The idea employed in BEDS is illustrated in<br />
Fig. 5.<br />
Fig. 5. The intersections of RED control functions and queue law determine average queuing delays<br />
and average loss probabilities of traffic classes in BEDS.<br />
19