Integrating Business Process Improvement with Innovation ... - QAI
Integrating Business Process Improvement with Innovation ... - QAI
Integrating Business Process Improvement with Innovation ... - QAI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
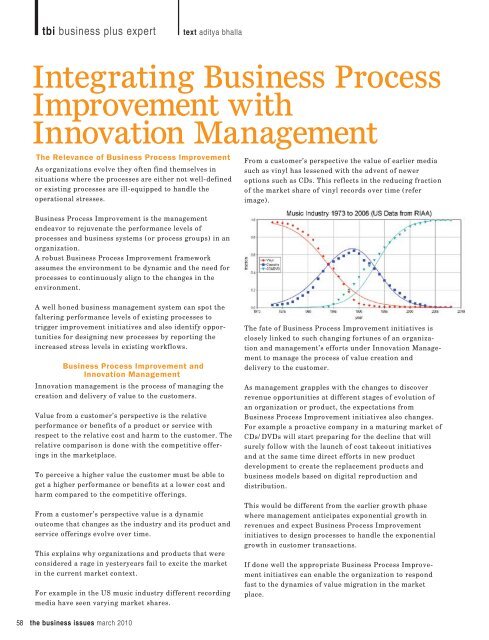
tbi business plus experttext aditya bhallaThe Relevance of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>As organizations evolve they often find themselves insituations where the processes are either not well-definedor existing processes are ill-equipped to handle theoperational stresses.From a customer’s perspective the value of earlier mediasuch as vinyl has lessened <strong>with</strong> the advent of neweroptions such as CDs. This reflects in the reducing fractionof the market share of vinyl records over time (referimage).<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> is the managementendeavor to rejuvenate the performance levels ofprocesses and business systems (or process groups) in anorganization.A robust <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> frameworkassumes the environment to be dynamic and the need forprocesses to continuously align to the changes in theenvironment.A well honed business management system can spot thefaltering performance levels of existing processes totrigger improvement initiatives and also identify opportunitiesfor designing new processes by reporting theincreased stress levels in existing workflows.<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> and<strong>Innovation</strong> Management<strong>Innovation</strong> management is the process of managing thecreation and delivery of value to the customers.Value from a customer’s perspective is the relativeperformance or benefits of a product or service <strong>with</strong>respect to the relative cost and harm to the customer. Therelative comparison is done <strong>with</strong> the competitive offeringsin the marketplace.To perceive a higher value the customer must be able toget a higher performance or benefits at a lower cost andharm compared to the competitive offerings.From a customer’s perspective value is a dynamicoutcome that changes as the industry and its product andservice offerings evolve over time.This explains why organizations and products that wereconsidered a rage in yesteryears fail to excite the marketin the current market context.For example in the US music industry different recordingmedia have seen varying market shares.The fate of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> initiatives isclosely linked to such changing fortunes of an organizationand management’s efforts under <strong>Innovation</strong> Managementto manage the process of value creation anddelivery to the customer.As management grapples <strong>with</strong> the changes to discoverrevenue opportunities at different stages of evolution ofan organization or product, the expectations from<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> initiatives also changes.For example a proactive company in a maturing market ofCDs/DVDs will start preparing for the decline that willsurely follow <strong>with</strong> the launch of cost takeout initiativesand at the same time direct efforts in new productdevelopment to create the replacement products andbusiness models based on digital reproduction anddistribution.This would be different from the earlier growth phasewhere management anticipates exponential growth inrevenues and expect <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>initiatives to design processes to handle the exponentialgrowth in customer transactions.If done well the appropriate <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>initiatives can enable the organization to respondfast to the dynamics of value migration in the marketplace.58 the business issues march 2010
<strong>Integrating</strong> <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> <strong>with</strong><strong>Innovation</strong> ManagementOrganizations and their products go through a growthcycle very similar to natural phenomenon such as life of aliving organism or the seasons of a year.This predictable pattern of evolution is very helpful as itforetells the changing priorities of management at eachstage of the evolution and the consequent impact on<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> initiatives.The image shows the rate of growth of revenues of anorganization or its products split across differentlife-cycle stages – Infancy, Growth, Maturity, andDecline.Each stage has its own characteristics, managementpriorities and impact on <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>initiatives.Infancy StageCharacteristics• Infancy Stage is characterized by the excitement ofgiving birth to a new venture.• In the early part it is not yet known what idea willsucceed in the marketplace.• It is only towards the end of infancy stage when thesurvival-of-the-fittest rule shows its results. Conceptsthat reach 10% of their growth potential are allowed togrow and others are killed or put on hold.Management Emphasis• Since a lot of ideas are competing for time and investmentmanagement lays a lot of emphasis on puttingsystems to manage the cycle of product and serviceinnovation.Focus of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>• <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> at this stage is focusedon two aspects1. Establish a structured framework forchannelizing the high levels of creativitytowards new product development.2. Design enabling processes that will support newproduct and service innovations in the marketplace.the business issues march 2010 59
tbi business plus experttext aditya bhallaGrowth StageCharacteristics• Growth is about ramping up fast to meet the exponentialgrowth in sales.• It is also about learning from the customer experiencesto improve the offerings.Management Emphasis• Management emphasis is on maximizing the growth ofrevenues to grab a sizeable market share.• There is a lot of emphasis on learning from the experiencesof customers and creating a feedback loop to theproduct development life-cycle.Focus of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>• There are two areas that <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>focuses its efforts on.1. Design processes that are scalable to handle thehumungous demand from customers.• This is the first time that the processes are stretched tothe maximum and it is time to revisit the underlyingassumptions in the original design of the processes.• Since skilled resources may not be readily availablethere is pressure to attain scalability through technologicalinnovations as enablers.1. Research and Development on product variants.• <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> improvement efforts are also directedat improving the process of collecting the voice ofcustomer to identify latent business opportunities suchas new areas of application of the product or service.Maturity StageCharacteristics• Maturity stage is characterized by a certain psychologicalinertia gripping the organization. Organizationculture does not encourage questioning the practicesthat have proven to work in the past.• The mindset is of sustaining the benefits and milkingthe cash cow.Management Emphasis• The emphasis is on reaping profits from successfulproducts. A lot of the entrepreneur spirit characterizedof Infancy stage is missing at this stage.• Wasteful practices suffer benign neglect as everyone isenjoying the financial boom.Management risks exhibiting the “boiled frog”syndrome and fail to notice the falling growth rateassuming it to be a temporary offset and hoping forrevival.Focus of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>• Unfortunately <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> initia-tives suffer the maximum in this phase of the evolution.• Jargons seem to replace meaningful action. The role of<strong>Business</strong> Excellence or <strong>Process</strong> Excellence teams isreduced to ensuring that “more of the same” is delivered.There is a strong resistance to change wastefulpractices as they are justified by the high profits andthe need to generate higher sales.• The focus of the <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> is moretowards obtaining certifications around process orbusiness excellence and increased emphasis on controlssuch as inspection and testing to retain current levels ofperformance.Decline StageCharacteristics• As the reality of shrinking market shares finally snapsmanagement out of its inertia, the first reactions are ofblame and panic.• A back-to-basics mindset eventually sets in leading toshrinking of operations.Management Emphasis• Management starts pushing for cost-takeout as one ofthe core initiatives by culling wasteful practices.• Another area of focus is of phasing out products on thedecline and finding replacement products.Focus of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>• Work on <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Innovation</strong> reaches a crescendo and<strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong> sees a revival <strong>with</strong>renewed focus on trimming wasteful practices andsimplifying processes for servicing customers.• At the same time new product development initiativesare revived <strong>with</strong> the entrepreneurial spirit and thestructured approach to find replacement products.There is no more infighting on account of cannibalizationof successful products as was witnessed in theMaturity Stage.Transition stage to new S-curveCharacteristics• This phase represents the phasing out of the earlierofferings or business model and the beginning of a newgrowth curve of the replacement offerings or businessmodel.Management Emphasis• Management focus is on managing a smooth transitionby squeezing out remaining revenues <strong>with</strong> minimuminvestment on old offerings.• In parallel the organization resources are diverted towardsexperimenting <strong>with</strong> newer offerings to help them cross theinfancy threshold of 10% of the revenue potential.60 the business issues march 2010
Focus of <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>• The Transition stage is about replacing the old <strong>with</strong> thenew in the most elegant manner.• <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> re-engineering on old processes canafford dramatic simplification of processes to meet thereducing market demand of the offerings <strong>with</strong> minimalcost.• In parallel the efforts characterized of Infancy stage areset in motion for the new offerings.ConclusionIf done well integrating <strong>Business</strong> <strong>Process</strong> <strong>Improvement</strong>initiatives <strong>with</strong> <strong>Innovation</strong> Management at each stage ofthe evolutionary growth curve can enable the organizationto respond fast to the dynamics of value migration inthe market place <strong>with</strong> the most appropriate actions.ABOUT THEAUTHORAditya Bhalla is Practice Manager <strong>with</strong> <strong>QAI</strong> GlobalServices <strong>Innovation</strong> Practice and President TRIZ Associationof Asia. He is one of the two persons in South Asia tobe certified as MATRIZ Level 3, I-TRIZ Inventive ProblemSolving and Anticipatory Failure Determination, SixSigma MBB and Lean Practitioner and Post GraduateDiploma in Patents Law. He is full member of AmericanSociety of Quality (ASQ), member Altshuller InstituteUSA, and registered volunteer for Financial ServicesVolunteer Corps (FSVC) USA.His articles on innovation, lean, and Six Sigma have beenpublished in magazines such as Altshuller Institute, ASQQuality Progress, Quality Digest, ASQ Six Sigma Forum,TRIZ Journal, IDG Outsourcing World and OUTSOURC-ING. He is on the book review panel of Pearson Vue(owners of Addison Wesley, Penguin brands).His clients include Cognizant, Government of Singapore,Globe Telecom (Philippines), Citibank (South Asia), andmany others. He can be contacted atadityabhalla@yahoo.comABOUT <strong>QAI</strong><strong>QAI</strong> is a leading global consulting and workforce developmentorganization addressing ‘Operational Excellence' inKnowledge intensive service organizations throughmulti-faceted interventions which include consulting,training, benchmarking, assessments and knowledgebased products. <strong>QAI</strong> is currently servicing over 200clients in 30 countries and our regional bases are locatedin US, India, UK, China, Singapore, Malaysia and Canada.The unique blend of services enables clients using oneservice to benefit form our experience, knowledge base,network, and learning in other services. <strong>QAI</strong> believes incontributing to the development of the 'Nations ofSoftware and BPO Excellence' by working closely <strong>with</strong>government bodies, government funded agencies,research institutions, defense organizations, softwareparks, local industry associations, and World Bankfunded projects in several countries. For more detailsvisit www.qaiglobal.com or mail us atcustomer_relations@qaiglobal.comthe business issues march 2010 61