Science Focus 2 - Coursebook Answers - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 - Coursebook Answers - Pearson Australia Media ...
Science Focus 2 - Coursebook Answers - Pearson Australia Media ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
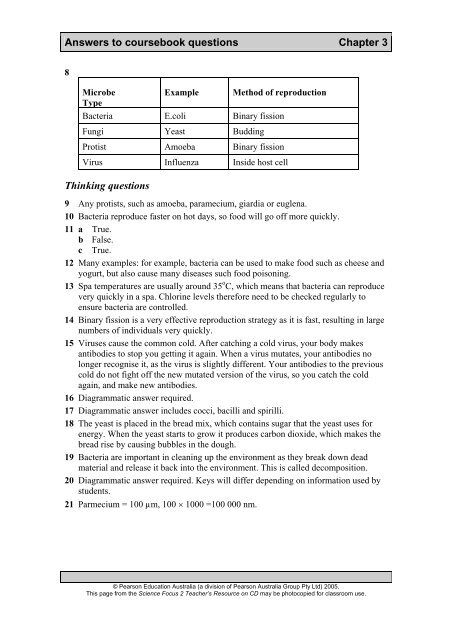
<strong>Answers</strong> to coursebook questions Chapter 38MicrobeExample Method of reproductionTypeBacteria E.coli Binary fissionFungi Yeast BuddingProtist Amoeba Binary fissionVirus Influenza Inside host cellThinking questions9 Any protists, such as amoeba, paramecium, giardia or euglena.10 Bacteria reproduce faster on hot days, so food will go off more quickly.11 a True.b False.c True.12 Many examples: for example, bacteria can be used to make food such as cheese andyogurt, but also cause many diseases such food poisoning.13 Spa temperatures are usually around 35 o C, which means that bacteria can reproducevery quickly in a spa. Chlorine levels therefore need to be checked regularly toensure bacteria are controlled.14 Binary fission is a very effective reproduction strategy as it is fast, resulting in largenumbers of individuals very quickly.15 Viruses cause the common cold. After catching a cold virus, your body makesantibodies to stop you getting it again. When a virus mutates, your antibodies nolonger recognise it, as the virus is slightly different. Your antibodies to the previouscold do not fight off the new mutated version of the virus, so you catch the coldagain, and make new antibodies.16 Diagrammatic answer required.17 Diagrammatic answer includes cocci, bacilli and spirilli.18 The yeast is placed in the bread mix, which contains sugar that the yeast uses forenergy. When the yeast starts to grow it produces carbon dioxide, which makes thebread rise by causing bubbles in the dough.19 Bacteria are important in cleaning up the environment as they break down deadmaterial and release it back into the environment. This is called decomposition.20 Diagrammatic answer required. Keys will differ depending on information used bystudents.21 Parmecium = 100 µm, 100 × 1000 =100 000 nm.© <strong>Pearson</strong> Education <strong>Australia</strong> (a division of <strong>Pearson</strong> <strong>Australia</strong> Group Pty Ltd) 2005.This page from the <strong>Science</strong> <strong>Focus</strong> 2 Teacher’s Resource on CD may be photocopied for classroom use.