Communicating Phonics - The Communication Trust
Communicating Phonics - The Communication Trust
Communicating Phonics - The Communication Trust
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
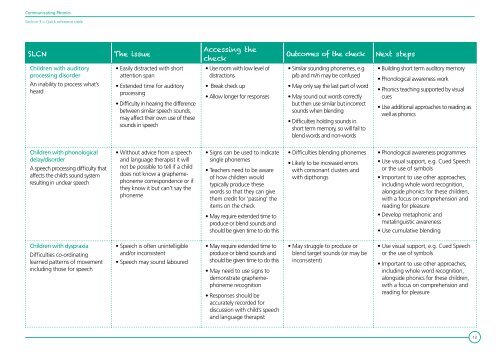
<strong>Communicating</strong> <strong>Phonics</strong>Section 3 > Quick reference tableSLCN<strong>The</strong> issueAccessing thecheckOutcomes of the checkNext stepsChildren with auditoryprocessing disorderAn inability to process what’sheard• Easily distracted with shortattention span• Extended time for auditoryprocessing• Difficulty in hearing the differencebetween similar speech sounds,may affect their own use of thesesounds in speech• Use room with low level ofdistractions• Break check up• Allow longer for responses• Similar sounding phonemes, e.g.p/b and m/n may be confused• May only say the last part of word• May sound out words correctlybut then use similar but incorrectsounds when blending• Difficulties holding sounds inshort term memory, so will fail toblend words and non-words• Building short term auditory memory• Phonological awareness work• <strong>Phonics</strong> teaching supported by visualcues• Use additional approaches to reading aswell as phonicsChildren with phonologicaldelay/disorderA speech processing difficulty thataffects the child’s sound systemresulting in unclear speech• Without advice from a speechand language therapist it willnot be possible to tell if a childdoes not know a graphemephonemecorrespondence or ifthey know it but can’t say thephoneme• Signs can be used to indicatesingle phonemes• Teachers need to be awareof how children wouldtypically produce thesewords so that they can givethem credit for ‘passing’ theitems on the check• Difficulties blending phonemes• Likely to be increased errorswith consonant clusters andwith dipthongs• Phonological awareness programmes• Use visual support, e.g. Cued Speechor the use of symbols• Important to use other approaches,including whole word recognition,alongside phonics for these children,with a focus on comprehension andreading for pleasure• May require extended time toproduce or blend sounds andshould be given time to do this• Develop metaphonic andmetalinguistic awareness• Use cumulative blendingChildren with dyspraxiaDifficulties co-ordinatinglearned patterns of movementincluding those for speech• Speech is often unintelligibleand/or inconsistent• Speech may sound laboured• May require extended time toproduce or blend sounds andshould be given time to do this• May need to use signs todemonstrate graphemephonemerecognition• Responses should beaccurately recorded fordiscussion with child’s speechand language therapist• May struggle to produce orblend target sounds (or may beinconsistent)• Use visual support, e.g. Cued Speechor the use of symbols• Important to use other approaches,including whole word recognition,alongside phonics for these children,with a focus on comprehension andreading for pleasure13