Volume Representation by Gradient and Distance Fields - Spring ...
Volume Representation by Gradient and Distance Fields - Spring ...
Volume Representation by Gradient and Distance Fields - Spring ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
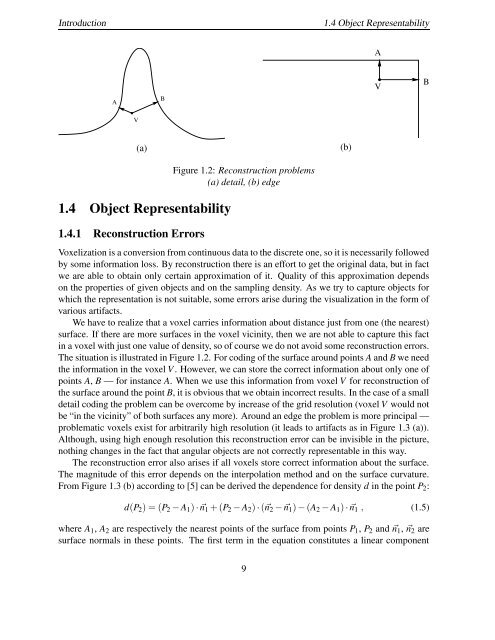
Introduction1.4 Object RepresentabilityAABVBV(a)(b)1.4 Object Representability1.4.1 Reconstruction ErrorsFigure 1.2: Reconstruction problems(a) detail, (b) edgeVoxelization is a conversion from continuous data to the discrete one, so it is necessarily followed<strong>by</strong> some information loss. By reconstruction there is an effort to get the original data, but in factwe are able to obtain only certain approximation of it. Quality of this approximation dependson the properties of given objects <strong>and</strong> on the sampling density. As we try to capture objects forwhich the representation is not suitable, some errors arise during the visualization in the form ofvarious artifacts.We have to realize that a voxel carries information about distance just from one (the nearest)surface. If there are more surfaces in the voxel vicinity, then we are not able to capture this factin a voxel with just one value of density, so of course we do not avoid some reconstruction errors.The situation is illustrated in Figure 1.2. For coding of the surface around points A <strong>and</strong> B we needthe information in the voxel V . However, we can store the correct information about only one ofpoints A, B — for instance A. When we use this information from voxel V for reconstruction ofthe surface around the point B, it is obvious that we obtain incorrect results. In the case of a smalldetail coding the problem can be overcome <strong>by</strong> increase of the grid resolution (voxel V would notbe “in the vicinity” of both surfaces any more). Around an edge the problem is more principal —problematic voxels exist for arbitrarily high resolution (it leads to artifacts as in Figure 1.3 (a)).Although, using high enough resolution this reconstruction error can be invisible in the picture,nothing changes in the fact that angular objects are not correctly representable in this way.The reconstruction error also arises if all voxels store correct information about the surface.The magnitude of this error depends on the interpolation method <strong>and</strong> on the surface curvature.From Figure 1.3 (b) according to [5] can be derived the dependence for density d in the point P 2 :d(P 2 ) = (P 2 − A 1 ) · ⃗n 1 + (P 2 − A 2 ) · (⃗n 2 − ⃗n 1 ) − (A 2 − A 1 ) · ⃗n 1 , (1.5)where A 1 , A 2 are respectively the nearest points of the surface from points P 1 , P 2 <strong>and</strong> ⃗n 1 , ⃗n 2 aresurface normals in these points. The first term in the equation constitutes a linear component9