- Page 2:
31 Days BeforeYour CCNA ExamSecond
- Page 18:
ixThe TCP/IP Application Layer 21Th
- Page 22:
xiDuplex and Speed Mismatches 66Com
- Page 26:
xiiiDay 20: Host Addressing, DHCP,
- Page 30:
xvThe Cisco IOS File System 179IFS
- Page 34:
xviiRouter ID 235Modifying the OSPF
- Page 38:
xixTypes of ACLs 280ACL Identificat
- Page 42:
xxiDay 3: PPP Configuration and Tro
- Page 46:
xxiiiPart IX: Exam Day and Post-Exa
- Page 50:
xxv■■■■■Italic indicates
- Page 54:
xxviiand advancing their IT careers
- Page 58:
xxixA simlet is similar to a testle
- Page 62:
Part INetworking BasicsDay 31:Day 3
- Page 66:
Day 31Network Devices, Components,
- Page 70:
Day 31 5■■■Redundant componen
- Page 74:
Day 31 7LANs and WANsA local-area n
- Page 78:
Day 31 9Logical topologies refer to
- Page 82:
Day 31 11Figure 31-5An Example of t
- Page 86:
Day 30Network Models and Applicatio
- Page 90:
Day 30 15The following mnemonic phr
- Page 94:
Day 30 17Growth of Network-Based Ap
- Page 98:
Day 30 19Study ResourcesFor today
- Page 102:
Day 29Network Data Flow from End-to
- Page 106:
Day 29 23Figure 29-1TCP Header Fiel
- Page 110:
Day 29 25Flow ControlFlow control i
- Page 114:
Day 29 27The TCP/IP Network Access
- Page 118:
Day 29 29Using Layers to Troublesho
- Page 122:
Part IISwitching Concepts andConfig
- Page 126:
Day 28Connecting Switches and Ether
- Page 130:
Day 28 35Figure 28-3Ethernet Physic
- Page 134:
Day 28 37Figure 28-4TIA/EIA Standar
- Page 138:
Day 28 39Ethernet FramingThe physic
- Page 142:
Day 28 41Study ResourcesFor today
- Page 146:
Network Segmentation andSwitching C
- Page 150:
Day 27 45Figure 27-1Switch Forwardi
- Page 154:
Day 27 47Figure 27-2Sources for Cis
- Page 158:
Day 27 49Keyboard CommandWhat Happe
- Page 162:
Day 27 51Storing and Erasing Config
- Page 166:
Day 26Basic Switch Configuration an
- Page 170:
Day 26 55■■Although the enable
- Page 174:
Day 26 57Table 26-2Actions When Por
- Page 178:
Day 26 59Study ResourcesFor today
- Page 182:
Day 25Verifying and Troubleshooting
- Page 186:
Day 25 63By using the ping command
- Page 190:
Day 25 65Example 25-4Tracing the Ro
- Page 194:
Day 25 67Output queue: 0/40 (size/m
- Page 198:
Day 25 69Sending CDPv2 advertisemen
- Page 202:
Day 24Switching Technologies and VL
- Page 206:
Day 24 73■■■■Black hole VLA
- Page 210:
Day 24 75Figure 24-3Fields of the 8
- Page 214:
Day 24 77Notice in the figure that
- Page 218:
Day 24 79■■Multiple frame trans
- Page 222:
Day 24 81The main changes with RSTP
- Page 226:
Day 24 83Figure 24-8 shows a simple
- Page 230: Day 24 85Study ResourcesFor today
- Page 234: Day 23VLAN and Trunking Configurati
- Page 238: Day 23 89S2(config-vlan)#end%SYS-5-
- Page 242: Day 23 91Operational private-vlan:
- Page 246: Day 23 93Administrative Mode: trunk
- Page 250: Day 23 95Study ResourcesFor today
- Page 254: Day 22VTP and InterVLAN RoutingConf
- Page 258: Day 22 99Example 22-2Configuring th
- Page 262: Day 22 101Local updater ID is 0.0.0
- Page 266: Day 22 103b. The switches must have
- Page 270: Day 22 105To verify the configurati
- Page 274: Part IIIAddressing the NetworkDay 2
- Page 278: Day 21IPv4 Address SubnettingCCNA 6
- Page 284: 112 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exambo
- Page 288: 114 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamDe
- Page 292: 116 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam3.
- Page 296: 118 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 300: 120 31 Days Before Your CCNA Examov
- Page 304: This page intentionally left blank
- Page 308: 124 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 312: 126 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRe
- Page 316: 128 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCo
- Page 320: 130 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTo
- Page 324: 132 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 328: 134 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTh
- Page 332:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 336:
138 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamAn
- Page 340:
140 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamWh
- Page 344:
142 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 348:
144 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 352:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 356:
148 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamPa
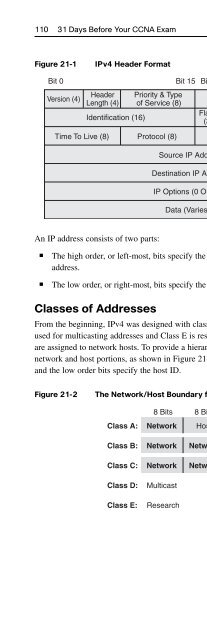
- Page 360:
150 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCl
- Page 364:
152 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCl
- Page 368:
154 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamIn
- Page 372:
156 31 Days Before Your CCNA Examth
- Page 376:
158 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 380:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 384:
162 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 388:
164 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRo
- Page 392:
166 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 396:
168 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 400:
170 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamAs
- Page 404:
172 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamOu
- Page 408:
174 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 412:
176 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 416:
178 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRe
- Page 420:
180 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRo
- Page 424:
182 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCo
- Page 428:
184 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 432:
186 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 436:
188 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamNo
- Page 440:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 444:
192 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 448:
194 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamAn
- Page 452:
196 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 456:
198 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRI
- Page 460:
200 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTo
- Page 464:
202 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 468:
204 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamNo
- Page 472:
206 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamDe
- Page 476:
208 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 480:
210 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamRe
- Page 484:
212 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEI
- Page 488:
214 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamDU
- Page 492:
216 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 496:
218 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 500:
220 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 504:
222 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 508:
224 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 512:
226 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 516:
228 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTh
- Page 520:
230 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 524:
232 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 528:
234 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 532:
236 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTo
- Page 536:
238 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 540:
240 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamOS
- Page 544:
242 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamNu
- Page 548:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 552:
246 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam3.
- Page 556:
248 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam2.
- Page 560:
250 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamIf
- Page 564:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 568:
254 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 572:
256 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamWi
- Page 576:
258 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamWi
- Page 580:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 584:
262 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamWi
- Page 588:
264 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 592:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 596:
268 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 600:
270 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamA
- Page 604:
272 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 608:
274 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 612:
276 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 616:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 620:
280 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 624:
282 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 628:
284 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 632:
286 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTh
- Page 636:
288 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 640:
290 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTh
- Page 644:
292 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 648:
294 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamPr
- Page 652:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 656:
298 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 660:
300 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam1.
- Page 664:
302 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 668:
304 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTh
- Page 672:
306 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 676:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 680:
310 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 684:
312 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 688:
314 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamDe
- Page 692:
316 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 696:
318 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 700:
320 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 704:
322 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamVP
- Page 708:
324 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamHa
- Page 712:
326 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 716:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 720:
330 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 724:
332 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 728:
334 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamPP
- Page 732:
336 31 Days Before Your CCNA Examwo
- Page 736:
338 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFr
- Page 740:
340 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 744:
342 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exammo
- Page 748:
344 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 752:
346 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCo
- Page 756:
348 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamEx
- Page 760:
350 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam
- Page 764:
352 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFo
- Page 768:
354 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamFi
- Page 772:
356 31 Days Before Your CCNA Examip
- Page 776:
358 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 780:
360 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCC
- Page 784:
362 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamHQ
- Page 788:
364 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamTa
- Page 792:
366 31 Days Before Your CCNA Exam20
- Page 796:
368 31 Days Before Your CCNA Examvt
- Page 800:
370 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamVL
- Page 804:
372 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSt
- Page 808:
374 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamCC
- Page 812:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 816:
378 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamSu
- Page 820:
380 31 Days Before Your CCNA ExamYo
- Page 824:
382 applications, network-based app
- Page 828:
384 commandsshow ip route, 11, 152,
- Page 832:
386 DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuratio
- Page 836:
388 forward explicit congestion not
- Page 840:
390 IP multicastIP multicast, 72ip
- Page 844:
392 neighbor adjacency issues, trou
- Page 848:
394 PVC (permanent virtual circuit)
- Page 852:
396 static routing, dynamic routing
- Page 856:
398 URL prefixes for specifying fil
- Page 860:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 866:
CCNA Countdown CalendarThe lines af