Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
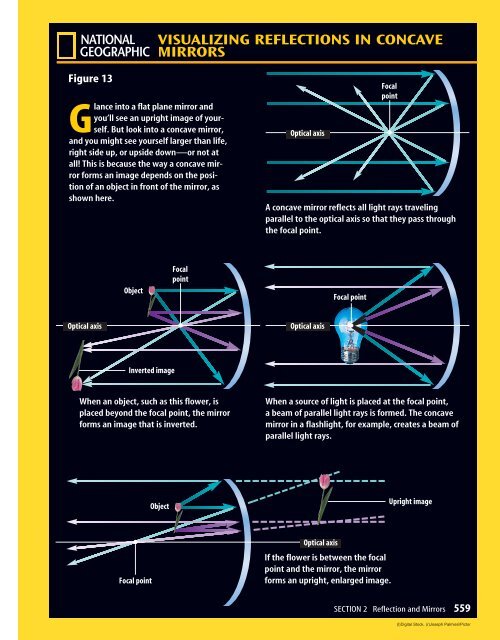
VISUALIZING REFLECTIONS IN CONCAVEMIRRORSFigure 13Glance into a flat plane mirror <strong>and</strong>you’ll see an upright image of yourself.But look into a concave mirror,<strong>and</strong> you might see yourself larger than life,right side up, or upside down—or not atall! This is because the way a concave mirrorforms an image depends on the positionof an object in front of the mirror, asshown here.Optical axisFocalpointA concave mirror reflects all light rays travelingparallel to the optical axis so that they pass throughthe focal point.ObjectFocalpointFocal pointOptical axisOptical axisInverted imageWhen an object, such as this flower, isplaced beyond the focal point, the mirrorforms an image that is inverted.When a source of light is placed at the focal point,a beam of parallel light rays is formed. The concavemirror in a flashlight, for example, creates a beam ofparallel light rays.ObjectUpright imageFocal pointOptical axisIf the flower is between the focalpoint <strong>and</strong> the mirror, the mirrorforms an upright, enlarged image.SECTION 2 Reflection <strong>and</strong> <strong>Mirrors</strong> 559(l)Digital Stock, (r)Joseph Palmieri/Pictor