Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
Light Mirrors and Lenses (3379.0K) - McGraw-Hill Higher Education
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
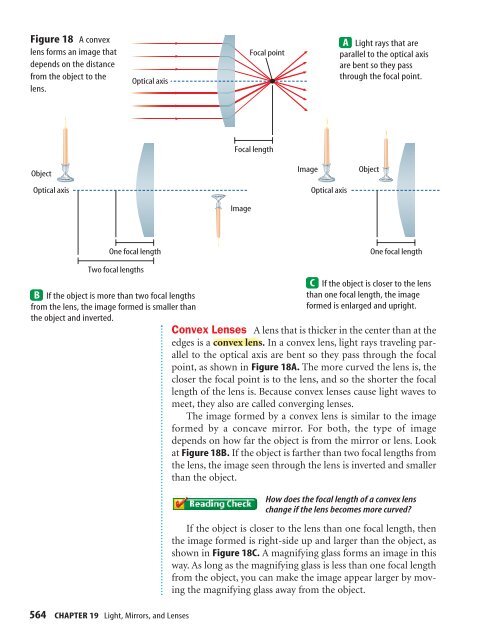
Figure 18 A convexlens forms an image thatdepends on the distancefrom the object to thelens.Optical axisFocal point<strong>Light</strong> rays that areparallel to the optical axisare bent so they passthrough the focal point.Focal lengthObjectOptical axisImageOptical axisObjectImageOne focal lengthOne focal lengthTwo focal lengthsIf the object is more than two focal lengthsfrom the lens, the image formed is smaller thanthe object <strong>and</strong> inverted.If the object is closer to the lensthan one focal length, the imageformed is enlarged <strong>and</strong> upright.Convex <strong>Lenses</strong> A lens that is thicker in the center than at theedges is a convex lens. In a convex lens, light rays traveling parallelto the optical axis are bent so they pass through the focalpoint, as shown in Figure 18A. The more curved the lens is, thecloser the focal point is to the lens, <strong>and</strong> so the shorter the focallength of the lens is. Because convex lenses cause light waves tomeet, they also are called converging lenses.The image formed by a convex lens is similar to the imageformed by a concave mirror. For both, the type of imagedepends on how far the object is from the mirror or lens. Lookat Figure 18B. If the object is farther than two focal lengths fromthe lens, the image seen through the lens is inverted <strong>and</strong> smallerthan the object.How does the focal length of a convex lenschange if the lens becomes more curved?If the object is closer to the lens than one focal length, thenthe image formed is right-side up <strong>and</strong> larger than the object, asshown in Figure 18C. A magnifying glass forms an image in thisway. As long as the magnifying glass is less than one focal lengthfrom the object, you can make the image appear larger by movingthe magnifying glass away from the object.564 CHAPTER 19 <strong>Light</strong>, <strong>Mirrors</strong>, <strong>and</strong> <strong>Lenses</strong>