Practical-Manual-Scores-Algorithms-Haemostasis-Thrombosis
Practical-Manual-Scores-Algorithms-Haemostasis-Thrombosis
Practical-Manual-Scores-Algorithms-Haemostasis-Thrombosis
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
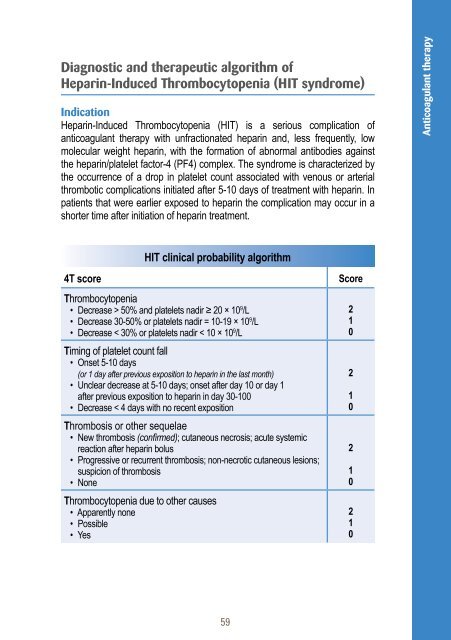
Diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm ofHeparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT syndrome)IndicationHeparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a serious complication ofanticoagulant therapy with unfractionated heparin and, less frequently, lowmolecular weight heparin, with the formation of abnormal antibodies againstthe heparin/platelet factor-4 (PF4) complex. The syndrome is characterized bythe occurrence of a drop in platelet count associated with venous or arterialthrombotic complications initiated after 5-10 days of treatment with heparin. Inpatients that were earlier exposed to heparin the complication may occur in ashorter time after initiation of heparin treatment.Anticoagulant therapyHIT clinical probability algorithm4T scoreThrombocytopenia• Decrease > 50% and platelets nadir ≥ 20 × 10 9 /L• Decrease 30-50% or platelets nadir = 10-19 × 10 9 /L• Decrease < 30% or platelets nadir < 10 × 10 9 /LTiming of platelet count fall• Onset 5-10 days(or 1 day after previous exposition to heparin in the last month)• Unclear decrease at 5-10 days; onset after day 10 or day 1after previous exposition to heparin in day 30-100• Decrease < 4 days with no recent exposition<strong>Thrombosis</strong> or other sequelae• New thrombosis (confirmed); cutaneous necrosis; acute systemicreaction after heparin bolus• Progressive or recurrent thrombosis; non-necrotic cutaneous lesions;suspicion of thrombosis• NoneThrombocytopenia due to other causes• Apparently none• Possible• YesScore21021021021059