coastal and marine natural values of the kimberley - wwf - Australia
coastal and marine natural values of the kimberley - wwf - Australia
coastal and marine natural values of the kimberley - wwf - Australia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
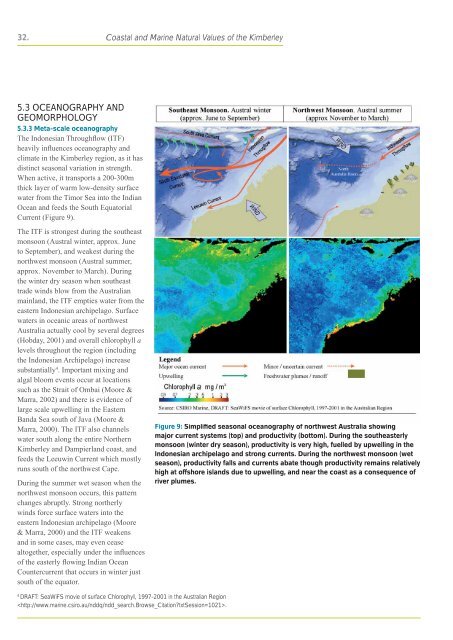
32. Coastal <strong>and</strong> Marine Natural Values <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Kimberley5.3 OCEANOGRAPHY ANDGEOMORPHOLOGY5.3.3 Meta-scale oceanographyThe Indonesian Throughflow (ITF)heavily influences oceanography <strong>and</strong>climate in <strong>the</strong> Kimberley region, as it hasdistinct seasonal variation in strength.When active, it transports a 200-300mthick layer <strong>of</strong> warm low-density surfacewater from <strong>the</strong> Timor Sea into <strong>the</strong> IndianOcean <strong>and</strong> feeds <strong>the</strong> South EquatorialCurrent (Figure 9).The ITF is strongest during <strong>the</strong> sou<strong>the</strong>astmonsoon (Austral winter, approx. Juneto September), <strong>and</strong> weakest during <strong>the</strong>northwest monsoon (Austral summer,approx. November to March). During<strong>the</strong> winter dry season when sou<strong>the</strong>asttrade winds blow from <strong>the</strong> <strong>Australia</strong>nmainl<strong>and</strong>, <strong>the</strong> ITF empties water from <strong>the</strong>eastern Indonesian archipelago. Surfacewaters in oceanic areas <strong>of</strong> northwest<strong>Australia</strong> actually cool by several degrees(Hobday, 2001) <strong>and</strong> overall chlorophyll alevels throughout <strong>the</strong> region (including<strong>the</strong> Indonesian Archipelago) increasesubstantially 4 . Important mixing <strong>and</strong>algal bloom events occur at locationssuch as <strong>the</strong> Strait <strong>of</strong> Ombai (Moore &Marra, 2002) <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>re is evidence <strong>of</strong>large scale upwelling in <strong>the</strong> EasternB<strong>and</strong>a Sea south <strong>of</strong> Java (Moore &Marra, 2000). The ITF also channelswater south along <strong>the</strong> entire Nor<strong>the</strong>rnKimberley <strong>and</strong> Dampierl<strong>and</strong> coast, <strong>and</strong>feeds <strong>the</strong> Leeuwin Current which mostlyruns south <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> northwest Cape.During <strong>the</strong> summer wet season when <strong>the</strong>northwest monsoon occurs, this patternchanges abruptly. Strong nor<strong>the</strong>rlywinds force surface waters into <strong>the</strong>eastern Indonesian archipelago (Moore& Marra, 2000) <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> ITF weakens<strong>and</strong> in some cases, may even ceasealtoge<strong>the</strong>r, especially under <strong>the</strong> influences<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> easterly flowing Indian OceanCountercurrent that occurs in winter justsouth <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> equator.Figure 9: Simplified seasonal oceanography <strong>of</strong> northwest <strong>Australia</strong> showingmajor current systems (top) <strong>and</strong> productivity (bottom). During <strong>the</strong> sou<strong>the</strong>asterlymonsoon (winter dry season), productivity is very high, fuelled by upwelling in <strong>the</strong>Indonesian archipelago <strong>and</strong> strong currents. During <strong>the</strong> northwest monsoon (wetseason), productivity falls <strong>and</strong> currents abate though productivity remains relativelyhigh at <strong>of</strong>fshore isl<strong>and</strong>s due to upwelling, <strong>and</strong> near <strong>the</strong> coast as a consequence <strong>of</strong>river plumes.4DRAFT: SeaWiFS movie <strong>of</strong> surface Chlorophyll, 1997-2001 in <strong>the</strong> <strong>Australia</strong>n Region.