APM Project Risk Management Single Subject Certificate Level 1 ...
APM Project Risk Management Single Subject Certificate Level 1 ...
APM Project Risk Management Single Subject Certificate Level 1 ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
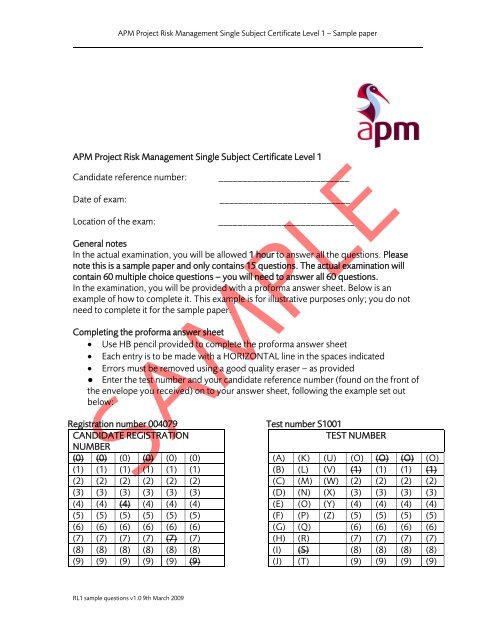
<strong>APM</strong> <strong>Project</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Single</strong> <strong>Subject</strong> <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>Level</strong> 1 – Sample paper<strong>APM</strong> <strong>Project</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Single</strong> <strong>Subject</strong> <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>Level</strong> 1Candidate reference number:Date of exam:Location of the exam:__________________________________________________________________________________General notesIn the actual examination, you will be allowed 1 hour to answer all the questions. Pleasenote this is a sample paper and only contains 15 questions. The actual examination willcontain 60 multiple choice questions – you will need to answer all 60 questions.In the examination, you will be provided with a proforma answer sheet. Below is anexample of how to complete it. This example is for illustrative purposes only; you do notneed to complete it for the sample paper.Completing the proforma answer sheet• Use HB pencil provided to complete the proforma answer sheet• Each entry is to be made with a HORIZONTAL line in the spaces indicated• Errors must be removed using a good quality eraser – as provided● Enter the test number and your candidate reference number (found on the front ofthe envelope you received) on to your answer sheet, following the example set outbelow:Registration number 004079Test number S1001CANDIDATE REGISTRATIONTEST NUMBERNUMBER(0) (0) (0) (0) (0) (0) (A) (K) (U) (O) (O) (O) (O)(1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (1) (B) (L) (V) (1) (1) (1) (1)(2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (C) (M) (W) (2) (2) (2) (2)(3) (3) (3) (3) (3) (3) (D) (N) (X) (3) (3) (3) (3)(4) (4) (4) (4) (4) (4) (E) (O) (Y) (4) (4) (4) (4)(5) (5) (5) (5) (5) (5) (F) (P) (Z) (5) (5) (5) (5)(6) (6) (6) (6) (6) (6) (G) (Q) (6) (6) (6) (6)(7) (7) (7) (7) (7) (7) (H) (R) (7) (7) (7) (7)(8) (8) (8) (8) (8) (8) (I) (S) (8) (8) (8) (8)(9) (9) (9) (9) (9) (9) (J) (T) (9) (9) (9) (9)RL1 sample questions v1.0 9th March 2009
<strong>APM</strong> <strong>Project</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Single</strong> <strong>Subject</strong> <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>Level</strong> 1 – Sample paper1) An opportunity is defined as:a. An appropriate option for dealing with a riskb. A risk with a potential beneficial outcomec. Something which may pose a riskd. A way of managing a threat to the project objectives2) Quantitative schedule risk analysis using Monte Carlo simulation can be used tocalculate:a. Earned valueb. Net present valuec. Criticality indexd. Three-point estimates3) A risk management plan should include:a. A Monte Carlo simulationb. Identified risks and control actionsc. The risk management organisationd. An event tree4) A benefit of project risk management is:a. It discourages the acceptance of financially unsound projectsb. <strong>Risk</strong>s can be transferred to other people at no costc. It will justify high contingencyd. The risks can all be managed by the project team5) ‘<strong>Risk</strong>y shift’ is evidenced by a tendency for the project team:a. To employ a wide range of risk management techniquesb. To be more risk-seeking than its constituent individualsc. To readily develop the capability to deal with high levels of uncertaintyd. To be more risk-averse than its constituent individuals6) The point on a probability distribution with the highest probability of occurrence iscalled the:a. Meanb. Medianc. Moded. QuartileRL1 sample questions v1.0 9th March 2009
<strong>APM</strong> <strong>Project</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Single</strong> <strong>Subject</strong> <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>Level</strong> 1 – Sample paper7) Which of the following is a correct and complete definition of project risk, accordingto the PRAM Guide?a. The exposure of outcomes to the consequences of variation in riskb. The exposure of projects to the consequences of variation in stakeholdersc. The exposure of stakeholders to the consequences of variation in outcomesd. The exposure of risks to the consequences of variation in projects8) A risk manager will get buy-in to the process from the project manager:a. By providing the appropriate toolsb. Through training, communication and allocation of appropriate resourcesc. By appealing to the managing director for supportd. By using Monte Carlo simulation9) Which of the following is NOT a risk identification technique?a. Brainstormingb. Assumptions analysisc. SWOT analysisd. Sensitivity analysis10) Most statistical simulations of project risk use which approach:a. PERTb. Ishikawa diagramsc. Net present value calculationd. Monte Carlo analysis11) The aim of risk identification is to:a. Identify only threatsb. Identify responsesc. Identify stakeholdersd. Identify all risksRL1 sample questions v1.0 9th March 2009
<strong>APM</strong> <strong>Project</strong> <strong>Risk</strong> <strong>Management</strong> <strong>Single</strong> <strong>Subject</strong> <strong>Certificate</strong> <strong>Level</strong> 1 – Sample paper12) Before assessing a risk you must first:a. Identify the risk response actionb. Identify the riskc. Manage the riskd. Calculate the contingency13) To determine whether a risk response is justified, a project manager needs toknow:a. How important it is to the clientb. The significance of the risk event concerned, relative to the project objectivesc. How late the project isd. Whether the sponsor is concerned about the risk14) ‘Power distance’ is one dimension that can be used to describe national culturaldifferences which can have an affect on attitude to risk. It can be best defined as:a. The prevalence of highly bureaucratic organisations with a high number ofhierarchical levels.b. The extent to which individuals are integrated into groups.c. The extent to which lower level members of a hierarchy accept the unequaldistribution of power.d. The sphere of influence attributed to an individual.15) A beta probability distribution is used to describe:a. An asymmetrical, continuous distributionb. A symmetrical, continuous distributionc. An asymmetrical, discrete distributiond. A symmetrical, discrete distributionAnswersQ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15A b c c a c c c b d d d b b c aRL1 sample questions v1.0 9th March 2009