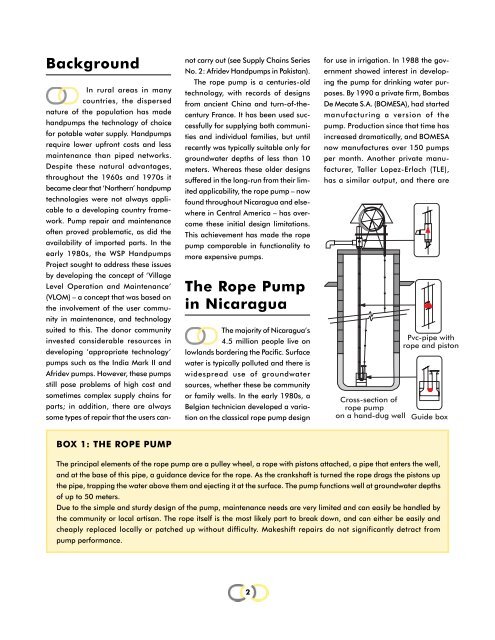
BackgroundIn rural areas in manycountries, the dispersednature of the population has madeh<strong>and</strong>pumps the technology of choicefor potable water supply. H<strong>and</strong>pumpsrequire lower upfront costs <strong>and</strong> lessmaintenance than piped networks.Despite these natural advantages,throughout the 1960s <strong>and</strong> 1970s itbecame clear that ‘Northern’ h<strong>and</strong>pumptechnologies were not always applicableto a developing country framework.<strong>Pump</strong> repair <strong>and</strong> maintenanceoften proved problematic, as did theavailability of imported parts. In theearly 1980s, the WSP H<strong>and</strong>pumpsProject sought to address these issuesby developing the concept of ‘VillageLevel Operation <strong>and</strong> Maintenance’(VLOM) – a concept that was based onthe involvement of the user communityin maintenance, <strong>and</strong> technologysuited to this. <strong>The</strong> donor communityinvested considerable resources indeveloping ‘appropriate technology’pumps such as the India Mark II <strong>and</strong>Afridev pumps. However, these pumpsstill pose problems of high cost <strong>and</strong>sometimes complex supply chains forparts; in addition, there are alwayssome types of repair that the users can-not carry out (see Supply Chains SeriesNo. 2: Afridev H<strong>and</strong>pumps in Pakistan).<strong>The</strong> rope pump is a centuries-oldtechnology, with records of designsfrom ancient China <strong>and</strong> turn-of-thecenturyFrance. It has been used successfullyfor supplying both communities<strong>and</strong> individual families, but untilrecently was typically suitable only forgroundwater depths of less than 10meters. Whereas these older designssuffered in the long-run from their limitedapplicability, the rope pump – nowfound throughout Nicaragua <strong>and</strong> elsewherein Central America – has overcomethese initial design limitations.This achievement has made the ropepump comparable in functionality tomore expensive pumps.<strong>The</strong> <strong>Rope</strong> <strong>Pump</strong>in Nicaragua<strong>The</strong> majority of Nicaragua’s4.5 million people live onlowl<strong>and</strong>s bordering the Pacific. Surfacewater is typically polluted <strong>and</strong> there iswidespread use of groundwatersources, whether these be communityor family wells. In the early 1980s, aBelgian technician developed a variationon the classical rope pump designfor use in irrigation. In 1988 the governmentshowed interest in developingthe pump for drinking water purposes.By 1990 a private firm, BombasDe Mecate S.A. (BOMESA), had startedmanufacturing a version of thepump. Production since that time hasincreased dramatically, <strong>and</strong> BOMESAnow manufactures over 150 pumpsper month. Another private manufacturer,Taller Lopez-Erlach (TLE),has a similar output, <strong>and</strong> there areCross-section ofrope pumpon a h<strong>and</strong>-dug wellPvc-pipe withrope <strong>and</strong> pistonGuide boxBOX 1: THE ROPE PUMP<strong>The</strong> principal elements of the rope pump are a pulley wheel, a rope with pistons attached, a pipe that enters the well,<strong>and</strong> at the base of this pipe, a guidance device for the rope. As the crankshaft is turned the rope drags the pistons upthe pipe, trapping the water above them <strong>and</strong> ejecting it at the surface. <strong>The</strong> pump functions well at groundwater depthsof up to 50 meters.Due to the simple <strong>and</strong> sturdy design of the pump, maintenance needs are very limited <strong>and</strong> can easily be h<strong>and</strong>led bythe community or local artisan. <strong>The</strong> rope itself is the most likely part to break down, <strong>and</strong> can either be easily <strong>and</strong>cheaply replaced locally or patched up without difficulty. Makeshift repairs do not significantly detract frompump performance.2
at least a dozen other small-scaleparticipants in the market.It is estimated that over 7,500pumps were sold <strong>and</strong> installed in Nicaraguain 1999, <strong>and</strong> that over half ofNicaragua’s rural population haveheard of the pump – a result apparentlydue to the extensive marketingthat the pump has received by themanufacturers. <strong>The</strong> marketing aswell as the receptive attitude of theNicaraguan government have beenimportant factors in the pump’s success.In the early 1990s the Nicaraguangovernment added the locally producedrope pump to the list of pumpsselected for use in the rural water sector,even though at that time the technologywas still under development.This is an example of the government’sattitude which facilitated the emergenceof the market for the rope pumpsdespite the fact that the other pumps,all imported, received support fromexternal agencies in all aspects of thedistribution <strong>and</strong> maintenance chains.SupplyBoth BOMESA <strong>and</strong> TLE manufacturea variety of pumps for communal <strong>and</strong>family use. TLE sells self-assembly kitsthat are put together <strong>and</strong> sold by localworkshops. Installation can be performedon request by either firm, buttends to be prohibitively expensive. Asa result, BOMESA provides an installationmanual <strong>and</strong> a short trainingcourse to customers. TLE, on the otherh<strong>and</strong>, maintains a network of installersthroughout the country whom theyrecommend to pump buyers. <strong>The</strong> buyerpays the installer directly.Dem<strong>and</strong>Dem<strong>and</strong> for the pumps comes fromthree sources: rural families, NGOsTHE HISTORY OFTHE ROPE PUMPIN NICARAGUAEarly 1980s: Belgian technici<strong>and</strong>evelops a variation on the classicalrope pump design.1988: <strong>The</strong> government developspump for drinking water purposes<strong>and</strong> post-hurricane dem<strong>and</strong>swells rapidly.1990: Bombas De Mecate S.A.(BOMESA) commences manufacturing,selling to low-incomerural families.1995: Private sector dem<strong>and</strong> hasbeen augmented by interest fromENACAL <strong>and</strong> NGOs. IRC report onNicaraguan <strong>Rope</strong> <strong>Pump</strong>.1996-98: Technology TransferDivision created within BOMESA –produces transfer kit.1999: Production surpasses 7,500pumps a year. Ghanaian authorities<strong>and</strong> others investigate transferpossibilities.<strong>and</strong> donors, <strong>and</strong> government organizations.During the first couple of yearsof production, private clients made upthe majority of BOMESA’s customers,while subsequently dem<strong>and</strong> fromdonors, NGOs <strong>and</strong> government hasexp<strong>and</strong>ed rapidly. Private clients, however,remain a significant source of revenuefor both major manufacturers.AffordabilityOne of the keys to the rapid spreadof the rope pump in Nicaragua hasbeen its low cost allied to its reliability<strong>and</strong> low maintenance needs. A studyperformed for the WSP found that theannual maintenance cost of the ropepump never exceeded $10 (<strong>and</strong> in factwas less than $5 in all but one areasurveyed). By comparison, the annualmaintenance cost for pumps in India –predominantly India Mark IIs – rangedbetween $59 <strong>and</strong> $107.<strong>The</strong> upfront cost of the rope pumpis also significantly less than for Afridevor India Mark II pumps. <strong>The</strong> same studyfound that in Nicaragua India Mark IIpumps sold for $750 (with similarprices for Afridev pumps) while theequivalent rope pump sold for $110.<strong>The</strong> imported pumps are harder toinstall <strong>and</strong> maintain <strong>and</strong> rely on importedparts, whose delivery may be problematic.<strong>The</strong>refore, in Nicaragua for wellsat a depth of less than 60 m, the ropepump has been preferred to eitherimported pump.In addition to its efficiency, lowcost <strong>and</strong> reliability, the rope pump’ssimple technology means that, givena rudimentary in-country manufacturingbase, it can be both produceddomestically <strong>and</strong> repaired locally,features which contribute greatlyto sustainability.<strong>The</strong> <strong>Rope</strong> <strong>Pump</strong>in Ghana<strong>The</strong> Government of Ghanalaunched the NationalCommunity <strong>Water</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sanitation</strong>Program in 1991 to accelerate accessof rural communities to sustainablewater <strong>and</strong> sanitation services. <strong>The</strong>agency responsible – the Community<strong>Water</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Sanitation</strong> Agency(CWSA) – works with the active participationof communities, NGOs <strong>and</strong>the private sector. Communitiesreceive government assistance in3