Resting Stages and the Population Dynamics of Harmful Algae in ...
Resting Stages and the Population Dynamics of Harmful Algae in ...
Resting Stages and the Population Dynamics of Harmful Algae in ...
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
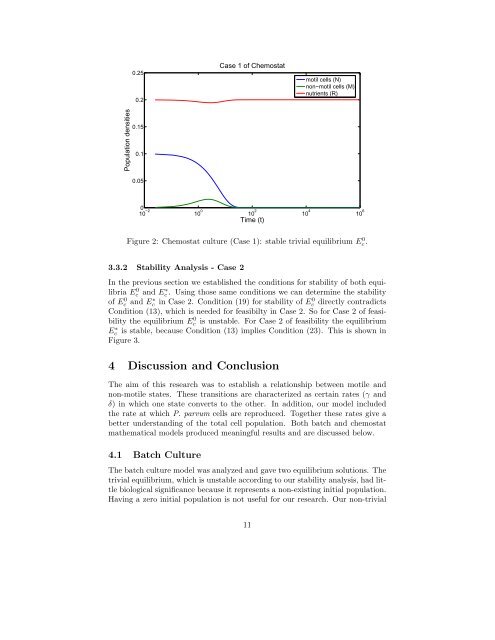
0.250.2Case 1 <strong>of</strong> Chemostatmotil cells (N)non−motil cells (M)nutrients (R)<strong>Population</strong> densities0.150.10.05010 −2 10 0 10 2Time (t)10 4 10 6Figure 2: Chemostat culture (Case 1): stable trivial equilibrium E 0 c .3.3.2 Stability Analysis - Case 2In <strong>the</strong> previous section we established <strong>the</strong> conditions for stability <strong>of</strong> both equilibriaEc 0 <strong>and</strong> Ec. ∗ Us<strong>in</strong>g those same conditions we can determ<strong>in</strong>e <strong>the</strong> stability<strong>of</strong> Ec 0 <strong>and</strong> E∗ c <strong>in</strong> Case 2. Condition (19) for stability <strong>of</strong> E0 c directly contradictsCondition (13), which is needed for feasibilty <strong>in</strong> Case 2. So for Case 2 <strong>of</strong> feasibility<strong>the</strong> equilibrium Ec 0 is unstable. For Case 2 <strong>of</strong> feasibility <strong>the</strong> equilibriumEc ∗ is stable, because Condition (13) implies Condition (23). This is shown <strong>in</strong>Figure 3.4 Discussion <strong>and</strong> ConclusionThe aim <strong>of</strong> this research was to establish a relationship between motile <strong>and</strong>non-motile states. These transitions are characterized as certa<strong>in</strong> rates (γ <strong>and</strong>δ) <strong>in</strong> which one state converts to <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r. In addition, our model <strong>in</strong>cluded<strong>the</strong> rate at which P. parvum cells are reproduced. Toge<strong>the</strong>r <strong>the</strong>se rates give abetter underst<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> total cell population. Both batch <strong>and</strong> chemostatma<strong>the</strong>matical models produced mean<strong>in</strong>gful results <strong>and</strong> are discussed below.4.1 Batch CultureThe batch culture model was analyzed <strong>and</strong> gave two equilibrium solutions. Thetrivial equilibrium, which is unstable accord<strong>in</strong>g to our stability analysis, had littlebiological significance because it represents a non-exist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>itial population.Hav<strong>in</strong>g a zero <strong>in</strong>itial population is not useful for our research. Our non-trivial11