(ALMOST) ALL THE BACTERIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
(ALMOST) ALL THE BACTERIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
(ALMOST) ALL THE BACTERIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
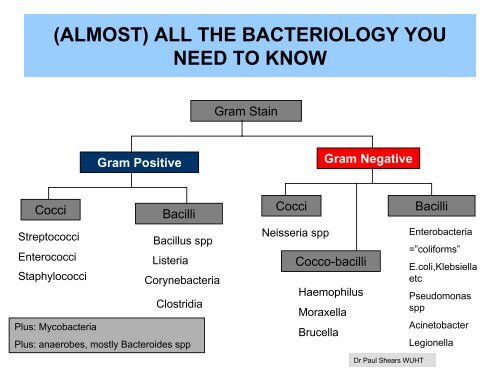
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIAG+ve cocciG+ve bacilliStreptococci:Alpha and beta haemolysisα: S.pneumoniae, S.”viridans”β: Lancefield groups:GpA: S.pyogenesGpB: S.agalactiaeGpD: now EnterococciEnterococci.. VREStaphylococci:Coagulase test:Coag+ve: S.aureus“All” others Coag –ve=CNSCNS usually non -pathogenic unless longlines/immunocompromisedetcMRSA: Meticillin(=flucloxacillin) resistantS.aureus i.e. Coag +veAltered penicillin bindingprotein coded by Mec AgenePVL MSSA and MRSA!Globally cause a variety ofdiseases but relatively uncommonin UK practice: (except nowC.difficile)Listeria monocytogenesCorynebacteria, “diphtheroids”Bacillus spp. Usually contaminantsClostridia (anaerobic)C.welchii. C.tetani, C.difficileDr Paul Shears WUHT
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIAGRAM +VE COCCI IN CHAINSEg StreptococciGRAM +VE COCCI IN CLUSTERSEg StaphylococciGRAM +VE BACILLIEg CorynebacteriaGRAM +VE BACILLIEg Bacillus sppDr Paul Shears WUHT
ALPHA AND BETA HAEMOLYTICSTREP<strong>TO</strong>COCCISTREP<strong>TO</strong>COOCI INCUBATED ON BLOOD AGARAlpha haemolysis: greenishtinge around coloniesBeta haemolysis: clear zonearound coloniesBacterial growthOptochin disc to distinguishS.pneumoniae (optochin sensitive)from other α haemolytic streptococciBeta haemolytic streptococci are divided intoLancefield groups based on their surface antigens:Gp A; S.pyogenesGp B: S.agalactiaeAnd othersDr Paul Shears WUHT
GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIAGram negative bacilliGram negative cocciN.meningitidisN.gonnorhoeaGram negative cocco-bacilliHaemophilus influenzae,parainfluenzaeBordatella pertussisMoraxella catarrhalisBrucella spp.Enterobacteriaceae:E.coli, Klebsiella spp, Salmonella, Shigellaplus Enterobacter, Serratia, Citrobacter: nowcomplicated by new resistance mechanisms, particularlyESBL’s: extended spectrum beta lactamases giveresistance to most cephalosporins, plus+/- tazocin:Increased need to use ertapenem or meropenemPseudomonas spp. Plus Stenotrophomonas maltophilia,BurkholderiaAcinetobacter sppLegionellaCampylobacter , Vibrio sppHelicobacter spp.Dr Paul Shears WUHT
GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIAGRAM –VE COCCIGram –ve cocci are often difficult to seeagainst a background of pink stainingpolymorph leucocytesPolymorphsGRAM – VE BACILLIGram –ve cocciprobablemeningo cocciDr Paul Shears WUHT
MICROBIOLOGY, INFECTIONS, TREATMENT ANDINFECTION CONTROL•Need to know basic microbiology of common infections to diagnose patients andgive appropriate antimicrobial treatment•Health care related infections are NOT something separate from individual patientinfections, they are patients with health care related infections•Knowledge of the causes of infection, an antimicrobial formulary, and knowledge ofhow infections are transmitted means that we SHOULD be able to reduce thenumber of patients with health care associated infections,•As clinicians, look at HCAI from the view point of patient care, not DH targets orinappropriate bureaucracy.•Health and Social Care Act 2008: You need to be aware of this.Dr Paul Shears WUHT
CURRENT PROBLEM PATHOGENS• Meticillin resistant S.aureus• Panton Valentine Leucocidin producing MSSA and MRSA• Vancomycin resistant enterococci• Clostridium difficile• Multi resistant Gram negative bacteria• Treatment of systemic fungal infections