Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Adults - Wirral University Teaching ...
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Adults - Wirral University Teaching ...
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Adults - Wirral University Teaching ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Appendix I - <strong>Therapeutic</strong> drug monitoringIntroduction<strong>Therapeutic</strong> <strong>Drug</strong> <strong>Monitoring</strong> aims to individualise drug therapy and avoid both sub-therapeutic andtoxic plasma drug concentrations. A number of factors influence drug concentration and a singlesample will only reflect the concentration at the sampling time.When a new drug is introduced, ‘steady state’ will not be approached until fourelimination half-lives have elapsed. Sampling prior to this time may not be beneficialunless a problem is anticipated e.g. non-compliance or toxicity. Results must be judgedin light of clinical observations and other relevant investigations.Clinical advice and assistance can be obtained from the laboratories per<strong>for</strong>ming the tests. Adviceon drug dose selection and interpretation of measured plasma drug concentrations can be obtainedfrom Clinical Pharmacists or the Pharmacy Department. <strong>Drug</strong> dosing in overweight patientsExercise caution with overweight individuals where drug dosing with water-soluble agents suchas gentamicin should be based on ideal body weight.Ideal body weight (IBW)IBW Females (kg)IBW Males (kg)= [45.5 + (2.3 x every inch over 5ft)]= [50+ (2.3 x every inch over 5ft)]For dosing of water-soluble agents such as gentamicin in obese patients (actual body weight >20%above IBW) use adjusted body weight <strong>for</strong> dose calculationAdjusted body weight (kg) =Ideal body weight + 0.4 (actual body weight – ideal body weight) Estimation of renal function.Please note that renal function can be expressed as either creatinine clearance (CrCl) using a24-hour urine collection or calculated using the Cockroft and Gault <strong>for</strong>mula, or estimatedGlomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) which is calculated using the MDRD <strong>for</strong>mula.eGFR estimates are reported in mL/minute/1.73m 2 . They are not the same as creatinineclearance estimates, which are reported in mL/min. eGFR estimates have not yet been validated<strong>for</strong> drug dosing and all dosing advice in this section is based on creatinine clearance. If youhave any questions please refer to Appendix 3 of the BNF or contact pharmacy <strong>for</strong> advice.Cockroft and Gault <strong>for</strong>mula <strong>for</strong> creatinine clearance:Creatinine clearance (mL/min) = _Y x (140-age) x weight*__Serum creatinine (micromol/L)Where Y = 1.23 <strong>for</strong> males and 1.04 <strong>for</strong> femalesAge is in yearsWeight is in kg*For overweight patients use Ideal Body Weight (IBW) to calculate Cockroft and Gault- 77 -<strong>Wirral</strong> <strong>University</strong> <strong>Teaching</strong> Hospital NHS Foundation Trust April 2011
IBW Females (kg) = [45.5 + (2.3 x every inch over 5ft)]IBW Males (kg) = [50 + (2.3 x every inch over 5ft)]Calculating creatinine clearance from a 24-hour urine collection:CrCl (mL/min) = U Cr VS Cr tU Cr = urine creatinine concentration (micromol/L)V = volume of urine (mL)S Cr = serum creatinine concentration (micromol/L)t = time over which sample was collected (min)- 78 -<strong>Wirral</strong> <strong>University</strong> <strong>Teaching</strong> Hospital NHS Foundation Trust April 2011
Teicoplanin<strong>Therapeutic</strong>sDosage <strong>for</strong>m: Intravenous bolus, intravenousinfusion or intramuscular injection.Loading dose:For patients 85kg give 6mg/kg every 12hours <strong>for</strong> 3 doses.Maintenance dose:For patients 85kg give 6mg/kg once daily.In some clinical situations, such as infected,severely burned patients or Staphylococcusaureus endocarditis, unit maintenance dosesof up to 12mg/kg have been administered IV.<strong>Therapeutic</strong> range: pre-dose ‘trough’>20mg/L, up to 50mg/L in resistant infections.The relationship between toxicity and serumdrug concentration is unclear but therapeuticfailures are more common with trough levels97% excretedunchanged in urine.Vd: 0.94–1.4L/kg.SamplingVolume of blood: Fill to lineTube to use: Ochre top.Lab per<strong>for</strong>ming assay: Royal Liverpool<strong>University</strong> Hospital (RLUH) MicrobiologyDepartment.Emergency service: No.Sampling times: The Pharmacy Departmentwill advise on levels to be taken. Troughlevels should be taken immediately be<strong>for</strong>e adose.RLUH will only per<strong>for</strong>m assays on Mondays,Wednesdays and Fridays. Samples shouldbe sent to <strong>Wirral</strong> Clinical Biochemistry asearly as possible on these days so they cango on the transport run to RLUH.Resample time: Dependent on clinical statusof patient. In patients who require monitoring;as a guide; a trough level is usually taken onday 5 or 6 of therapy and repeated weekly iflevels are not in range.Reporting procedure: Available via PCIS.Additional In<strong>for</strong>mationTeicoplanin is administered by the IV routein the treatment of endocarditis and otherserious infections caused by Gram-positivecocci including multi-resistant staphylococci.It is also used <strong>for</strong> surgical prophylaxis inpatients with a history of MRSA.Peak levels are not required.<strong>Therapeutic</strong> response usually seen in 48-72hours.<strong>Therapeutic</strong> drug monitoring may be used tooptimise therapy in burns or obese patients,patients with proven or suspected MRSAbacteraemia, patients requiring high dosetherapy <strong>for</strong> more resistant organisms,patients not responding to therapy andpatients with infective endocarditis.- 80 -<strong>Wirral</strong> <strong>University</strong> <strong>Teaching</strong> Hospital NHS Foundation Trust April 2011
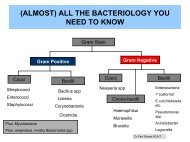
Vancomycin<strong>Therapeutic</strong>sDosage <strong>for</strong>m: Intravenous infusion.Loading dose: See product monograph inmain Trust antibiotic <strong>for</strong>mulary.Maintenance dose: See product monographin main Trust antibiotic <strong>for</strong>mulary.<strong>Therapeutic</strong> range:Pre-dose ‘trough’ 10 to 15mg/L; troughconcentrations up to 20mg/L may be requiredin deep-seated or resistant infections.In MRSA bacteraemia aim <strong>for</strong> trough~15mg/L.Toxic effects: Hypotension and anaphylacticreactions occur if given too quickly. Ototoxicityand nephrotoxicity are rare, although risk isincreased if co-administered withaminoglycosides. Groups at special riskinclude patients with impaired renal functionand the elderly.PharmacokineticsElimination half-life: 6 to 10 hours (normalrenal function); up to 216 hours in end stagerenal failure.Major route of elimination: 80 to 90%excreted unchanged in urine.Vd: 0.7L/kg (0.9L/kg in ESRF)Factors affecting plasma concentration:Increased in renal impairment.Decreased in severe burns.SamplingVolume of blood: Fill to lineTube to use: Ochre or green top.Lab per<strong>for</strong>ming assay: <strong>Wirral</strong> ClinicalBiochemistry.Emergency service: Yes, but should not benecessary.Sampling times: The Pharmacy Departmentwill advise on levels to be taken. Troughlevels should be taken immediately be<strong>for</strong>e adose.Resample time: Dependent on clinical statusof patient. In patients who require monitoring;as a guide, a trough level is usually taken onday 2 or 3 of therapy and repeated weekly.Reporting procedure: Available via PCIS.Additional In<strong>for</strong>mationVancomycin is administered by theintravenous route in the treatment ofendocarditis and other serious infectionscaused by Gram-positive cocci includingmulti-resistant staphylococci.Peak levels are not usually required.Oral vancomycin is not absorbed but can beused <strong>for</strong> the treatment ofpseudomembranous colitis due toClostridium difficile. <strong>Monitoring</strong> is notrequired.Intraperitoneal administration of vancomycinmay be used in the treatment of peritonealdialysis associated peritonitis. See RenalUnit guidelines <strong>for</strong> initial dose and contactthe renal pharmacists <strong>for</strong> advice onmonitoring.- 81 -<strong>Wirral</strong> <strong>University</strong> <strong>Teaching</strong> Hospital NHS Foundation Trust April 2011